- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Eczema
Brief description of the disease

Eczema is an allergic disease characterized by a recurrent course and a significant area of skin lesions. The disease is the body's response to stimuli and is based on the phenomenon of spongiosis (inflammation of the epidermis with subsequent accumulation of fluid in the intercellular space of the skin).
In the event that a person is diagnosed with eczema, the choice of treatment method will depend on the type of disease and the intensity of the allergic process. Doctors distinguish true, seborrheic, dyshidrotic, dry, weeping and professional forms of the disease. They manifest themselves in different ways. Some people develop eczema on their hands, while others develop eczema on their legs or in the chest and abdomen. Be that as it may, but eczema can manifest itself at any age and on any part of the skin, which gives the patient both physical and psychological discomfort.
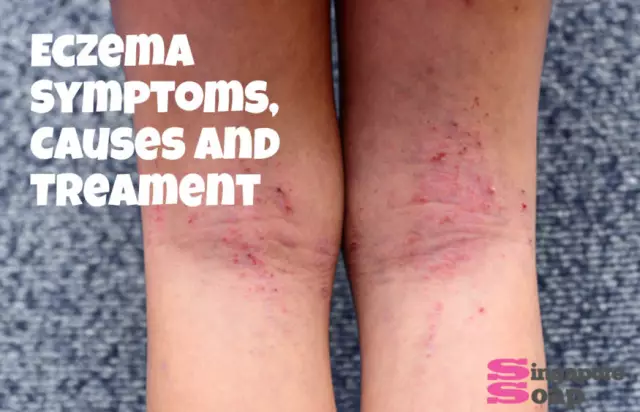
Eczema - symptoms of the disease
The clinical signs of the disease depend on the form of the allergic reaction. However, there are some common symptoms as well. First of all, they must include redness of the skin and its swelling. Initially, a person develops small nodules that progress rapidly, grow into bubbles filled with fluid or pus, and then burst with the formation of erosion and keratinized crust on the surface of the skin. Regardless of where eczema is noted - on the legs, arms or head - it gives a person many inconveniences, since the process of bubble formation is quite unpleasant and is accompanied by severe itching and burning.
Types of eczema
True eczema - has an acute, chronic and intermediate form, belongs to the category of dermatoses. True eczema, the symptoms of which are characterized by the formation of many small blisters and itchy erosion, can last from 1.5 to 2 months, and in some cases up to six months. The acute form is well expressed, it is characterized by severe swelling and weeping, the appearance of itching and burning in the area of damaged areas. The chronic process is almost asymptomatic. The only reliable sign for a correct diagnosis is severe itching.
Dyshidrotic eczema is a kind of true form. Most often localized on the soles and palms. It is characterized by abundant bubbles that merge into one continuous focus of destruction, which are covered with dense scab. Very often this form of the disease is chronic in nature with regular periods of exacerbation and is difficult to treat. Dyshidrotic eczema can occur in people at any age and often causes secondary infections.
Dry eczema - most often seen in the elderly and worsens during the winter season. Symptoms are similar to dermatitis, therefore, a comprehensive examination of the patient is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. Localized dry eczema on the legs, accompanied by cracks and peeling.
Weeping eczema - affects the upper chest, arms, scalp, interscapular region, and folds of the limbs. Initially, multiple scales appear on the patient's skin, which quickly develop into bright red nodules, and then into bubbles filled with purulent contents or a transparent liquid. Weeping eczema on the hands, treatment of which is prescribed after determining the cause of the disease, causes severe itching and burning. When combing, the bubbles burst with the release of a large amount of liquid and the formation of erosive areas. Bursting of bubbles can also occur spontaneously - under the pressure of the substances contained inside. Often, weeping eczema covers a significant area of the skin and greatly impairs the quality of human life.
Eczema - treatment of the disease

The best results are shown by complex treatment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient's body. The choice of a specific technique depends on the cause, type and intensity of the allergic reaction. In most cases, eczema, the symptoms of which are similar to dermatitis, disappear after elimination of the allergen, so the main efforts of doctors should be directed to finding the source of the infection. At the same time, it is necessary to relieve itching, normalize the state of the central nervous system, improve blood circulation and metabolic processes, and reduce the level of excitability of the cerebral cortex.
If a patient is diagnosed with eczema, treatment involves an integrated approach and the use of a variety of techniques, including:
- elimination of endocrine and nervous disorders;
- sanitation of foci of infection;
- antiallergic diet (we will talk about it a little later);
- taking sedatives;
- the use of tranquilizers, neuroleptics and antidepressants;
- injections of antihistamines;
- a course of treatment with anti-bradykinin drugs - ropyrin or pirabutol;
- in severe forms of the disease, it is advisable to use corticosteroid hormones;
- immunocorrective drugs - thymalin, taktivin, decaris, pentoxil, diucifon and some others - also show high efficiency.
We mentioned above that when diagnosed with eczema, treatment requires a strict diet. It is necessary to plan the nutrition schedule and the composition of the products so that the body continues to receive all the substances it needs, but at the same time it is free from the presence of components that irritate the damaged areas of the skin. To do this, you should avoid constant neutralization of acid in the stomach, exclude spicy foods, chocolate, smoked meats, citrus fruits, eggs and alcohol from the diet.
In the event that a person has eczema on the hands, feet or body, milk, boiled vegetables, fruits, butter and other natural products are recommended.
Eczema in children
The first symptoms of eczema can already appear in infants. The lesions are, as a rule, indistinct, do not have pronounced boundaries. Children are characterized by eczema on the hands, cheeks, ears, scalp and buttocks. The child begins to scratch the itchy areas and thereby causes himself more pain. It comes to the point that the baby cannot sleep because of the constantly itchy skin.
Treatment of eczema in children is complicated by the constitution and age of the child, as well as by the characteristics of his nervous system. You should adhere to a diet, limit the amount of liquids, carbohydrates and table salt, exclude meat broths, cocoa, milk, chocolate, semolina from the products. Eczema in children is treated with non-specific desensitizing agents, calcium and iron preparations. Also, hyposensitizing nonspecific agents are prescribed - riboflavin, pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, cobalamin.
Sedatives and tranquilizers must be used - mezapam, nozepam, trioxazine, valerian. Of the antihistamines, diazolin, fenkarol, suprastin and diprazin are recommended. The pediatrician will tell you the exact dosage of all of the above means.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!