- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Syphilis in men
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms and stages of the disease
-
Symptoms of syphilis in men
- Primary syphilis in men
- Secondary siflis
- Tertiary syphilis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
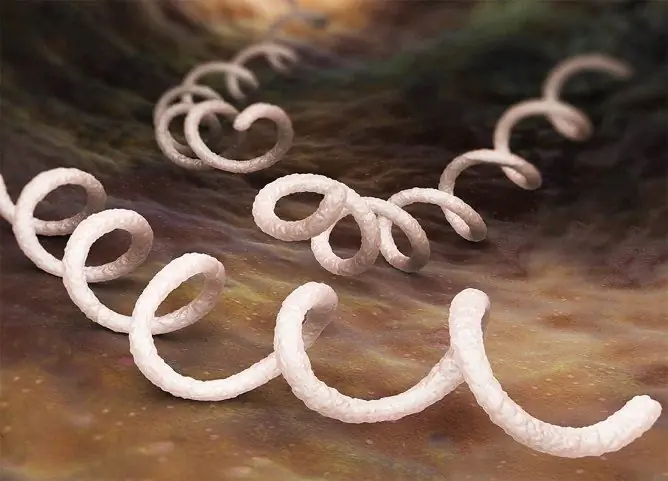
Syphilis in men is a venereal, that is, a sexually transmitted infectious disease, with a long course of which all organs and systems of the body are affected. The causative agent is pale treponema, or pale spirochete (Treponema pallidum) - a spiral microorganism 7-20 µm long and 0.2-0.5 µm thick, capable of translational, flexion, undulating, rotational movements, which are provided by the cell's own contractions and fibrils. When conducting laboratory studies, pale treponema does not perceive staining well, only the Romanovsky-Giemsa method can give it a pale pink color, which is what caused the name. Since this species belongs to facultative anaerobes, the most favorable breeding environment is the lymphatic system, which is poor in oxygen. In the bloodstream, in high concentration, pale treponema appears during the period of secondary syphilis. The microorganism is able to persist for a long time in a humid and warm environment, the optimum temperature is 37 ° C, resistant to low temperatures, but it quickly collapses upon drying, heating, and the action of antiseptics.
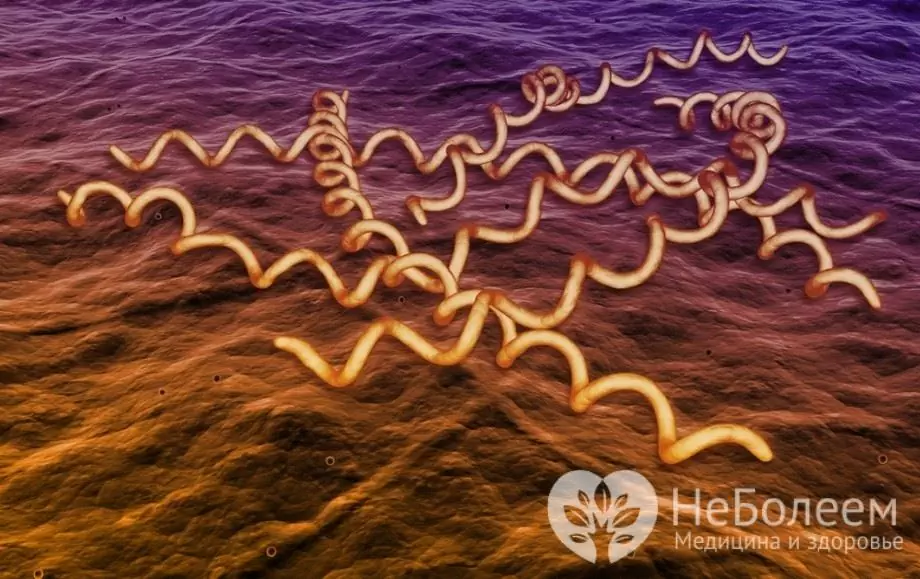
Pale spirochete - the causative agent of syphilis
Syphilis in men is one of the most common and contagious sexually transmitted infections. A patient with syphilis is contagious at almost all stages of the disease, but the degree of contagion varies. The most dangerous contacts during the period of primary and secondary syphilis in the presence of skin manifestations (chancre and skin rashes, respectively).
Causes and risk factors
In the vast majority of cases, treponema pallidum is infected through sexual contact. It is also possible to use a contact-everyday transmission route, i.e., through common objects, personal belongings, close contacts of a non-sexual nature. There is a chance of contracting syphilis through an infected blood transfusion. A child can get an infection from a sick mother during intrauterine development, during childbirth, and also during breastfeeding.
At risk of contracting treponema pallidum are medical workers who deal with invasive procedures, as well as socially disadvantaged people (drug addicts, etc.).

Surgeons are at risk of contracting syphilis
Forms and stages of the disease
Syphilis is congenital (early and late) and acquired. In addition, syphilis is atypical, which in most cases is caused by self-medication with antibiotics (erased form), infection during blood transfusion (in this case, there are no signs of primary syphilis) or low immunity (malignant form).
The disease proceeds with certain well-defined periods.
- Primary syphilis is characterized by the appearance of a hard chancre.
- Secondary syphilis - manifested by skin rashes, the so-called secondary syphilis. Has the following forms: fresh, latent, recurrent.
- Tertiary syphilis is a late, advanced stage of the disease, in which the body is destroyed. It can proceed in the form of neurosyphilis (predominant damage to the nervous system) or visceral syphilis (predominant damage to internal organs).
Symptoms of syphilis in men
The incubation period of syphilis in men is on average 2-6 weeks from the moment of infection, but it can be lengthened, for example, when antibiotic therapy is carried out during the treatment of another pathology.
Primary syphilis in men
The stage of primary syphilis begins with the formation of a primary syphiloma, or a hard chancre, which forms at the site of an infectious agent entering the body. Chancre can appear both on the skin and on the mucous membranes (external genital organs, perianal region, mouth, lips, corners of the mouth, lower abdomen, fingers, etc.), can be single or take on a multiple form in the case of numerous microdamages of the skin and / or mucous membrane at the time of infection with treponema pale. Typically, with syphilis in men, a hard chancre forms on the head of the penis, foreskin, shaft of the penis, or on the mucous membrane of the urethra.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Chancre is a painless, rounded ulceration with smooth edges and a shiny cyanotic red bottom. At the base of the hard chancre there is a dense infiltrate, which explains its name. The size ranges from a few millimeters to 5 cm, but is usually about 1 cm in diameter. Primary syphiloma does not increase in size, may have scanty serous discharge, is usually painless, and this painlessness may cause it to go unnoticed. However, in some cases, the chancre is painful. As a rule, this occurs when it forms on the nail phalanx of the fingers, as well as in the fold of the anus (in this case, the chancre does not take the form of a round ulcer, but a narrow slit-like defect,which can be misdiagnosed as anal fissure). Chancre does not respond to local antiseptic therapy, but gradually heals on its own within one and a half to two months.
After 5-7 days after the formation of the primary syphiloma, the patient has an uneven increase, as well as compaction of the lymph nodes closest to the hard chancre. Enlarged lymph nodes are painless, they can enlarge on one or both sides, and there are no other signs of inflammation other than enlargement. In cases where a hard chancre does not form (a blood transfusion form of syphilis) or develops without being noticed by the patient (for example, when located inside the urethra), the enlargement of the lymph nodes becomes a manifestation, that is, the first manifestation of the disease. Symptoms of general intoxication are usually not pronounced, but sometimes patients complain of a deterioration in general well-being, headache, a slight increase in body temperature, aches in joints and / or muscles,insomnia and other neurotic disorders.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Secondary siflis
The disease passes into the stage of secondary syphilis after 2-4 months from the moment of infection, immediately after the resolution of the hard chancre, or some time later. In the absence of treatment, secondary syphilis lasts from 2 to 5 years and is characterized by generalization of the infection. It is clinically manifested by the appearance of rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, which most often look like roseola, but can take on a different character (papules, pustules, miliary rash). Syphilis are found throughout the body, including the face, scalp, feet, and palms. The rashes occur in waves - after a while, new ones are added to the existing elements, which is why the rash has a different degree of maturity and differs in color (as a rule, repeated rashes are less bright). What distinguishes them from infectious rashes of other origin is thatthat they are not accompanied by a noticeable deterioration in general well-being.
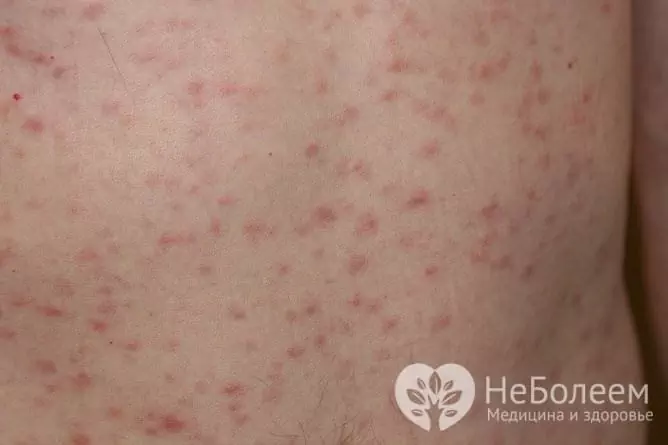
With secondary syphilis, rashes occur on the skin
Other signs of syphilis in men at this stage include:
- pronounced hyperemia of the tonsils, which is similar to the usual angina, but differs from it in the absence of fever and pronounced signs of general intoxication;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth, ulceration on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity;
- leukoderma (literally "white skin") - areas of pigmentation disorders of the skin in the form of white spots;
- alopecia, or baldness - more often takes on a focal character: areas of baldness appear on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes. In rare cases, alopecia can take a diffuse, that is, widespread appearance;
- painless enlargement of lymph nodes throughout the body.
Gradually, the signs of secondary syphilis subside, and the disease takes on a latent form, in which it can proceed for years or even decades, periodically exacerbating. With relapses, the symptoms characteristic of the secondary period reappear, in one combination or another.
Tertiary syphilis
In the absence of adequate treatment, pale spirochetes in the body evolve, assuming other forms (cysts, L-forms), which cause irreversible damage to the body. This stage of syphilis in men is characterized by the formation of dense infiltrates (gum), which then disintegrate. Gummas contain a small amount of pale treponemes. When gummy syphilides spread to joints, bones, internal organs and blood vessels, as a result of their disintegration, perforations, bleeding, and cicatricial deformities occur.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Diagnostics
The basis for the diagnosis of syphilis in men is a laboratory examination. Physical examination data are important, but play a secondary role, since the manifestations of primary and secondary syphilis are similar to many other pathologies, and in addition, they may be absent at certain periods or in atypical forms of the disease.
In order to detect the pathogen, serological studies (specific and nonspecific) of blood and cerebrospinal fluid are used: the Wasserman reaction (a somewhat outdated and inaccurate method), immunofluorescence and passive hemagglutination reactions, as well as the polymerase chain reaction method.
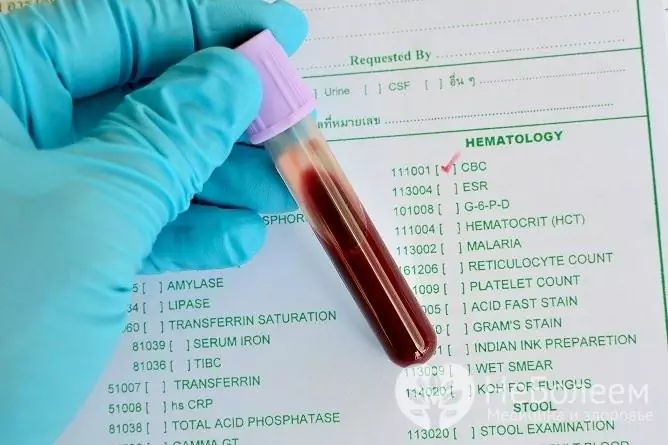
To identify the causative agent of syphilis in men, blood and cerebrospinal fluid are tested
In addition, the infectious agent can be detected by microscopy of the serous discharge of the hard chancre and secondary syphilides.
Treatment
Drug treatment of syphilis in men at all stages consists, first of all, in the use of antibacterial drugs. Antibiotic therapy in the late stages of the disease can be supplemented by the use of iodine- and bismuth-containing drugs, stimulants of biological origin. Physiotherapy and immunotherapy are used as additional methods. To assess the effectiveness of the therapy, non-specific serological reactions are used. After completion of treatment, dispensary observation of the patient is established.

Syphilis therapy in men at all stages consists in the administration of antibiotics
If syphilis is detected in a man, preventive therapy is required for all his sexual partners.
Possible complications and consequences
Against the background of long-term syphilis, men can develop severe disorders on the part of almost all body systems, which cause disability or death of the patient.
Forecast
In the case of adequate treatment of primary and secondary syphilis, the prognosis is favorable. With the transition of the disease to the tertiary stage, the prognosis is negative.
Prevention
The main measures for the prevention of syphilis in men are:
- regular preventive examinations of persons belonging to the risk group;
- an immediate visit to a doctor if any suspicious signs appear, refusal of self-medication;
- refusal of casual sex, in doubtful cases, the use of a condom;
- observance of the rules of personal hygiene, refusal to share linen, towels, razors, toothbrushes, etc.;
- healthy lifestyle.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!