- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ovarian fibroma

Ovarian fibroma is a benign tumor of the ovary. In gynecology, ovarian fibroma occurs in about 10% of all benign ovarian tumors. It happens that fibroma occurs even during puberty, but women are mainly susceptible to it during premenopause and menopause, i.e. between the ages of 40 and 60.
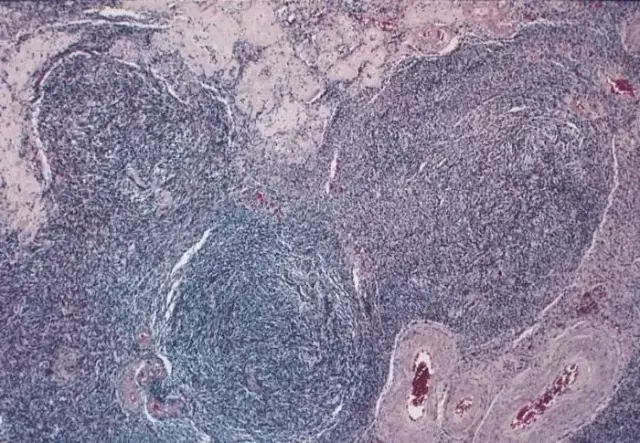
Externally, ovarian fibroma is a round formation with a knotty or even surface, reaching 10-12 cm in size. If there are pseudocavities, then the consistency of the fibroid is tightly elastic, when calcium salts are deposited, the fibroma is hard, and with pronounced edema, it is soft. Mostly ovarian fibroma is mobile and unilateral, has a leg. If we consider the formation on a cut, then it has a white or grayish-white color, with a small number of vessels. If a woman's tumor has been observed for a long time, then she may have hemorrhages, foci of necrosis and ischemia. Histologically, a fibroma consists of bundles of spindle-shaped cells of connective tissue that are intertwined in different directions.
Forms of ovarian fibroids
There are two forms of ovarian fibroids:
- Delimited, when the neoplasm has a pronounced capsule, which separates it from the ovarian tissue;
- Diffuse when the ovary is completely affected.
Often, ovarian fibroids are edematous and contain cysts. As a rule, the tumor grows slowly, but with dystrophic changes, its growth can significantly accelerate. The borderline state of fibroma is considered to be an increase in its mitotic activity with a low malignant potential.
If the fibroma is small, then, as a rule, it does not have any effect on the function of the ovary and does not interfere with the onset of pregnancy and the successful bearing of the child. Cellular fibroma of the ovary can recur, especially if its capsule was damaged during surgery. Complications of the tumor include necrosis, torsion of the leg, the possibility of malignancy and suppuration of the tumor.
The main reasons for the development of ovarian fibroma
It is difficult to establish the exact reasons for the development of ovarian fibroma, but it is reliably known that the risk factor is an unfavorable hormonal background of a woman, including due to endocrine disorders (violation of reproductive and menstrual functions), various inflammation of the ovaries and appendages (oophoritis, adnexitis), a decline in the body's immune forces …
Often, ovarian fibroma is combined with an ovarian cyst, uterine myoma, so we can talk about common etiological factors in the development of these diseases.
Ovarian fibroid symptoms
If the size of the fibroid is up to 3 cm, and the ovary continues to function fully, then for a long time there may be no symptoms of ovarian fibroma at all. As the education grows, signs of Meigs syndrome (pleurisy, anemia, ascites) begin to be observed, manifested by pain, periodic abdominal distention, rapid fatigue and general weakness, shortness of breath, tachycardia.
Ascites is a common symptom of an ovarian cyst that occurs when a transudate is released from the formation into the abdominal cavity. Hydrothorax occurs due to the entry of ascitic fluid from the abdominal cavity into the pleural cavity through the aperture of the diaphragm. It happens that ovarian fibroma is accompanied by cachexia and polyserositis (mainly with malignant degeneration of education). In many ways, the symptoms of ovarian fibroma and the severity of the disease depend on the degree of compression of adjacent organs by fluid.
With hemorrhages and necrosis, pronounced symptoms of peritoneal irritation appear in the tumor.
As a rule, with fibroma, the menstrual cycle is not disturbed. If ovarian fibroma is combined with other diseases of the female genital organs, then the symptoms of ovarian fibroma may be joined by those symptoms that are characteristic of another disease.
Diagnosis of ovarian fibroma
Since fibroma can be asymptomatic for a long period of time, it is often discovered by accident during examination or surgery for another disease.
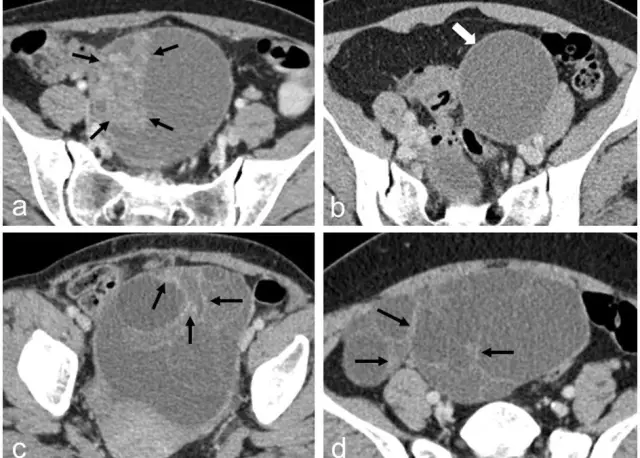
The diagnosis of ovarian fibroma is made on the basis of examination by a gynecologist, clinical data, laboratory diagnostics (tumor markers CA-125, HE 4, general blood count), as well as instrumental studies (CT of the pelvic organs, MRI, ultrasound). If necessary, a histological examination of the tissue of the removed tumor is also done.
Ovarian fibroma treatment

As a rule, medical (conservative) treatment of ovarian fibroma is not performed. The tumor must be removed by surgery. The nature of the operation depends on the size of the fibroma, the age of the patient, the condition of the uterus and the second ovary, and various pathologies of the internal organs.
If the tumor is observed in a young woman and has a small size, then the advantage in the treatment of ovarian fibroma is given to laparoscopic removal of the tumor while maintaining generative and menstrual functions. For premenopausal women, doctors recommend complete removal of the appendages. If the ovaries are affected on both sides, doctors try to keep part of one of them.
Ovarian fibroma prognosis and disease prevention
Mostly the prognosis of ovarian fibroma is favorable, and the probability of malignancy of the tumor is no more than 1%. After the end of the rehabilitation course of treatment, a woman can plan a pregnancy.
There are no specific ways to prevent this disease. As a precaution, it is recommended to conduct an ultrasound of the pelvic organs once a year and visit a gynecologist.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!