- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Wasted ovarian syndrome
Wasted ovarian syndrome is a lack of functional activity that develops in women under 40 and leads to infertility. If you do not take action in time, then gradually the unfavorable consequences of estrogen deficiency (osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases, etc.) will appear throughout the body. This syndrome almost never goes away on its own. Only in every 5th patient menstruation can recover for a while, and only every 20th woman with premature ovarian failure can become pregnant on her own. That is why gynecologists have been talking about this syndrome more and more often and warn that you need to be very careful about your health and take care of your ovaries.
Depleted ovarian syndrome is characterized by a decrease in the synthesis of estrogen in the follicles and infertility

The reasons
Both congenital and acquired factors lead to early termination of ovarian function. They either disrupt the growth and maturation of follicles, or cause their premature death. The result is first a decrease in the number of follicles in the ovaries, and then their complete disappearance.
Among the congenital causes of depleted ovaries, scientists call Turner syndrome, when one X chromosome is missing in the chromosome set, and "super-woman" syndrome, when there is one extra X chromosome.
Acquired factors that can lead to premature "shutdown" of the ovaries can be autoimmune (type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis) or infectious (mainly viruses) nature.
Despite the modern diagnostic capabilities of gynecology, in most cases it is very difficult to identify the true cause of the depleted ovarian syndrome, and sometimes it is not possible at all. According to statistics, for every second woman with premature ovarian failure, the cause remains unknown.
Who Should Worry
If your age is under 40 and there is no menstruation for at least 4 months, then you should definitely check your hormone levels. This may be the first sign of wasted ovarian syndrome. And the earlier it is identified and treatment is started, the higher the chances of restoration of menstrual and reproductive function.
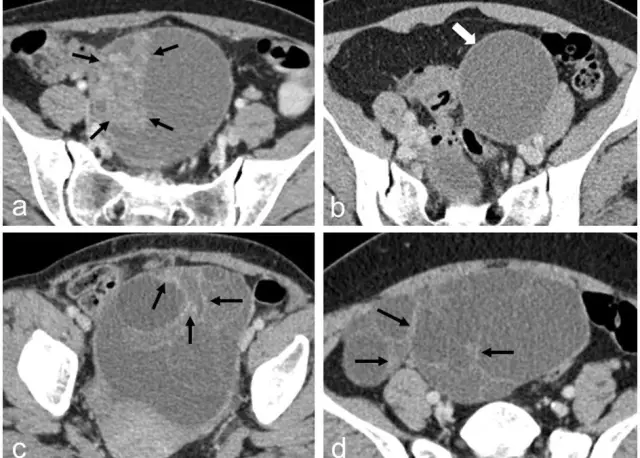
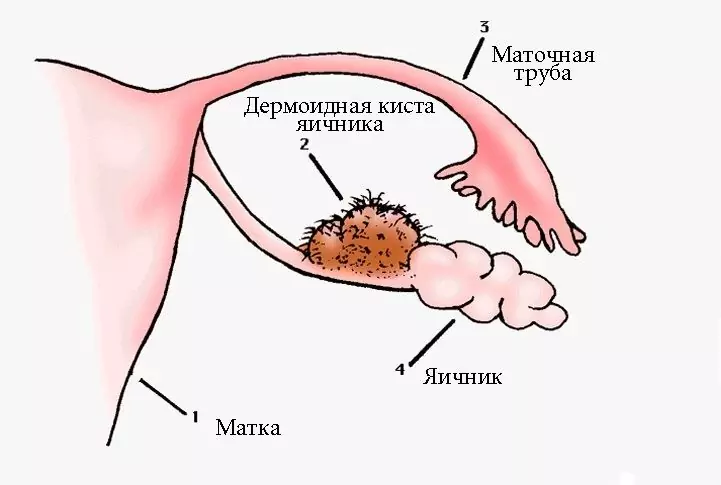
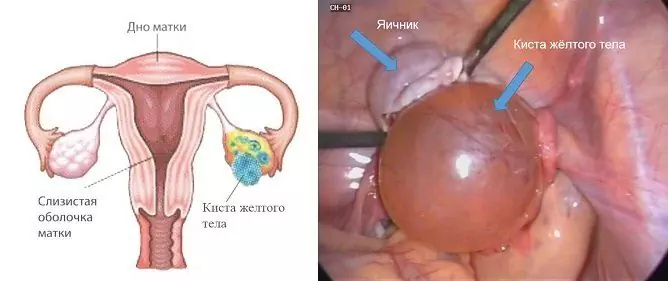
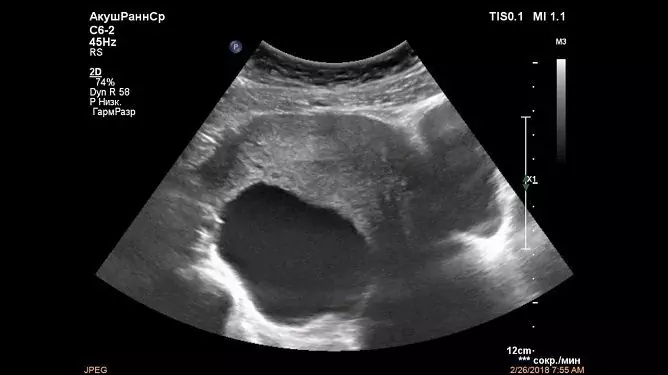
In the diagnosis of depleted ovarian syndrome, gynecologists are guided by the number of follicles according to ultrasound data and the level of follicle-stimulating hormone. If it is several times more than the norm, then this indicates a decrease in the hormonal activity of the ovaries, which is confirmed by low levels of estradiol in the blood.
The absence of menstruation for 4 months or more, an increase in follicle-stimulating hormone and a decrease in estradiol in a young woman under 40 years old are important criteria for the diagnosis of ovarian failure
Premature "shutdown" of the ovarian function is latent - it does not hurt and does not bother. However, over time, it leads to serious consequences. In modern gynecology, this is problem number 1. When the ovarian follicular reserve is completely depleted, it is almost impossible to restore it. Therefore, it is necessary to work on warning. The risk group includes women who have at least one predisposing factor:
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- long (35-38 days or more) cycle from the first menstruation;
- infertility without an established cause;
- unsuccessful attempts at in vitro fertilization;
- smoking;
- operations on the pelvic organs, especially those involving the ovaries;
- taking chemotherapy drugs for the treatment of malignant tumors;
- hearing loss due to Perrault's syndrome (impaired ovarian development and damage to nerve cells in the inner ear);
- autoimmune diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, adrenal insufficiency, myasthenia gravis);
- childhood infections - chickenpox, rubella, mumps.
Especially women under the age of 40 who have already encountered symptoms of estrogen deficiency - delayed menstruation, hot flashes, sweating, sleep disturbances, pain during intercourse - should be on the alert. You can't hesitate - you have to act.
What to do?
Every woman has a risk of ovarian failure. Stressful situations at work, alcohol and smoking, lack of adequate rest, unbalanced and sometimes even unhealthy diet, a sedentary lifestyle and poor ecology all contribute to follicular damage. Under such conditions, functionally active ovarian cells begin to die faster and recover more slowly.
To reduce the negative effects of modern life, scientists advise:
-
Do sport.
Adequate physical activity will help remove free radicals from the body that damage cells. In addition, this is a great way to deal with physical inactivity.
-
Sleep at least 7 hours a night.
During night sleep, the body recovers from the stress of the day. This occurs under the influence of melatonin, which is synthesized in the pineal gland of the brain at night.
-
Eat properly.
Eat 300-400 g of vegetables and herbs per day to reduce the intake of harmful substances from the intestines into the body. At the same time, do not forget to drink 2-2.5 liters of clean water.
-
Relax.
Try not to take work home on weekends. Use this time to good use - visit the theater or go to nature outside the city. It is advisable to go on vacation at sea at least once a year
-
Take care of the ovaries.
As a result of many years of research by domestic scientists from the Military Medical Academy and the Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, on the basis of the theory of peptide bioregulation, a new class of drugs was developed - Cytamins. Cytamines are based on peptides that regulate the state of the body's cells and ensure the normal functioning of all internal organs and tissues. At the same time, they have a targeted effect, i.e. selectively regulate the cells of the organ for which they are intended. So, to normalize the function of the ovaries, a remedy was developed - Ovariamin.

Ovariamin is a complex of polypeptides and nucleic acids that in a woman's body create optimal conditions for the correct functioning of the follicular apparatus. Ovariamin acts purposefully - on the ovaries, without affecting other organs.
Regulatory polypeptides in the composition of this agent are perceived by the cells of the female body as their own, therefore Ovariamin is well tolerated, does not cause adverse reactions and has no contraindications.
Maintain women's health on top! Ovariamin can help protect the ovaries from premature ovarian failure. Talk to your gynecologist about the use of cytamines.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.