- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ovarian cyst laparoscopy
The content of the article:
- Indications and contraindications
- Types of laparoscopic intervention for ovarian cyst
-
Ovarian cyst laparoscopy: how is the operation
Preparing for surgery
-
Postoperative period: how long, recommendations
- Menstrual cycle in the postoperative period
- Planning a pregnancy after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
-
Ovarian cyst: general information
- Symptoms
- Possible complications
- Prevention
- Video
Ovarian cyst laparoscopy is a modern endoscopic technique that is widely used to remove cystic lesions. Laparoscopy can be performed for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
Laparoscopy can also be used when it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, if this cannot be done based on the results of ultrasound and other methods.
According to the reviews of patients and doctors, laparoscopic removal of the neoplasm is usually well tolerated by a woman.
The benefits of laparoscopy include:
- excellent visibility of the operating field for the surgeon (manipulation is carried out under the control of a camera with multiple magnification);
- minimal trauma;
- low risk of complications;
- good cosmetic effect - after the operation carried out by this method, only a few small scars remain on the body.

Laparoscopic intervention provides gentle, atraumatic removal of the ovarian cyst
Indications and contraindications
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian formations is the most effective and at the same time less traumatic method. This type of surgical treatment is usually used to remove cystic and other growths that are less than 10 cm in size.
Indications for laparoscopic cyst removal include:
- fixed growth (an increase is dangerous by rupture of the cyst, the development of massive bleeding, peritonitis);
- detection of a leg in a neoplasm (torsion of the leg, necrosis of the formation, rupture of the cyst with the development of life-threatening conditions may occur);
- germination of cystic formation into neighboring organs;
- the risk of malignant transformation.
Contraindications:
- acute blood loss;
- widespread tumor process;
- an acute form of the disease of infectious etiology (the intervention is postponed until the patient recovers).
When a cystic formation ruptures with the development of massive bleeding, an urgent open abdominal operation is required.
Types of laparoscopic intervention for ovarian cyst
The main types of laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts are presented in the table.
| Manipulation type | Description |
| Resection | During surgery, the ovarian membrane is cut and the cyst is removed |
| Enucleation | The cyst is exfoliated from the organ, the tissues of which are not damaged (the tissues of the capsule of the cystic formation are excised) |
| Ovariectomy | In this type of operation, the ovary is removed together with the neoplasm, usually performed in the presence of large and / or suspicious neoplasms |
The choice in favor of one method or another depends on the size, nature and location of education.
Ovarian cyst laparoscopy: how is the operation
Usually, intravenous or inhalation anesthesia is used during this operation.
Punctures of the anterior abdominal wall, through which the laparoscope accesses the operative field, do not exceed 15 mm in length. During the operation, carbon dioxide can be supplied through the punctures made, which is necessary for a better examination of organs and tissues and obtaining free space for manipulating surgical instruments. The gas supplied expands the abdomen, for this reason gastric contents can enter the respiratory tract. To prevent this, general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation are used.
When removing a cystic formation, small blood vessels are cauterized using an electrocoagulator, which avoids internal bleeding.
Preparing for surgery
You need to properly prepare for the procedure:
- Before the operation, it is required to undergo an examination, pass all the necessary tests (general and biochemical blood test, coagulogram, tests for infections, determination of the blood group and Rh factor, tumor markers, etc.). You may also need X-ray, ultrasound, electrocardiogram.
- The last meal on the evening before the operation - no later than 18:00, dinner should be light.
- The day before the operation and on the day of the laparoscopic removal of the cyst, the patient may need to cleanse the intestines with an enema or laxative.
Postoperative period: how long, recommendations
After a sparing operation, the patient does not need to stay in the clinic for a long time; it makes it possible for a woman to quickly return to her usual lifestyle. The patient is usually in the hospital ward 1 day after surgery. Rehabilitation lasts 2-3 weeks, during this time it is not recommended to have sex.
After surgery, the patient is shown diet. It is recommended to include foods rich in fiber, dairy products, lean meat in the diet; the use of fatty, fried, overly salty and spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, and foods that contribute to the development of flatulence should be limited or excluded.
Postoperative stitches should be treated daily with antiseptic solutions, and it is generally recommended to take a shower, not a bath, until the scars heal.
In the postoperative period, it is usually not allowed to visit the bathhouse, sauna, solarium, pool, beach, in order to prevent infection of scars and the development of internal bleeding, and physical activity is also contraindicated.
Menstrual cycle in the postoperative period
Postoperative bleeding may occur and should not be confused with menstrual bleeding. Cystic ovarian formation is routinely removed towards the end of the cycle. In this case, the body usually independently restores the hormonal balance, the next menstruation begins on time or with a slight delay. In some cases, after surgery, there may be a fluctuation in the menstrual cycle for 1.5-3 months, after which the cycle is restored on its own.
Possible menstrual irregularities after surgery include:
- long delays;
- cycle shift;
- soreness of menstruation;
- profuse discharge.
This may be due to the individual characteristics of the organism, the influence of anesthesia, stress.
If the restoration of the menstrual cycle does not occur for a long time, you should inform your doctor about it.
Planning a pregnancy after laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst
Laparoscopic intervention for an ovarian cyst does not interfere with ovulation, that is, the possibility of conception remains, the patient can plan a pregnancy. The timing of planning depends on the type of cyst, the state of the body after the operation and a number of other factors, so this issue should be discussed with your doctor.
Ovarian cyst: general information
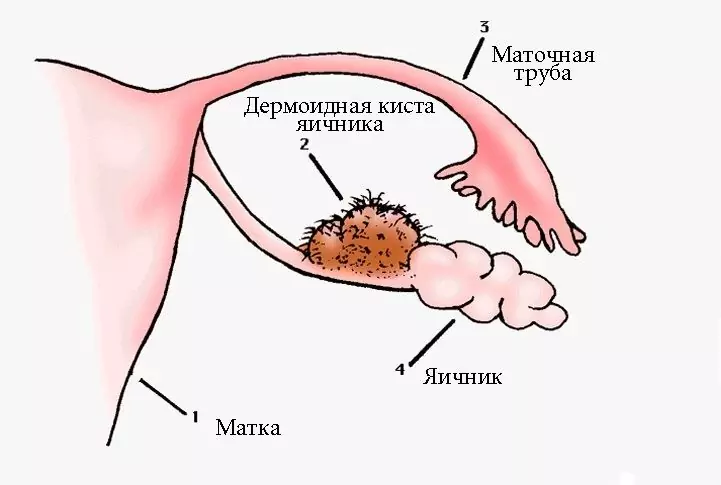
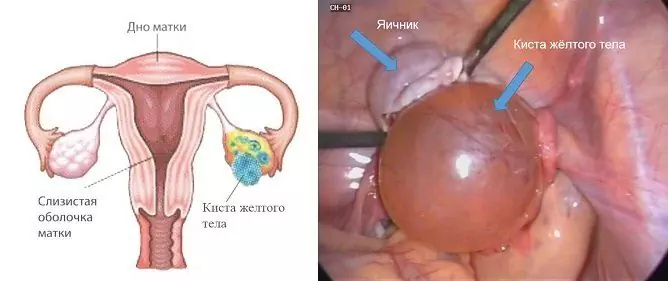
An ovarian cyst, or ovarian cyst, is a benign neoplasm filled with a liquid of a rounded shape (see photo), which belongs to a fairly common pathology in women of all age groups. A cyst can occur both on one (left or right), and on both (extremely rare) ovaries. In some cases, it can reach 10 cm in diameter.

Ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm
This pathology is most often observed in females of reproductive age. With the onset of menopause, the likelihood of developing cystic formation is significantly reduced.
Symptoms
Often the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, it can be discovered by chance during the diagnosis for another reason. In other cases, the patient experiences pain after intercourse, an irregular menstrual cycle, bleeding between periods, pain in the lower abdomen, which can worsen after physical exertion, radiate to the rectum, an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C, frequent urge to urination, nausea and vomiting.
Possible complications
In the absence of timely treatment, a number of complications may develop:
- Rupture of cystic formation, which can occur with strong pressure on the lower abdomen, as well as during intercourse. At the same time, the patient has acute pain, a decrease in blood pressure against the background of internal bleeding, impaired consciousness.
- Torsion of the cyst leg leads to its necrosis, which can be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, severe pain in the lower abdomen, pallor of the skin, and decreased pressure. A complication can develop with a sharp change in body position, physical exertion.
- Malignancy (malignant transformation).
- The development of a cyst abscess, in which the patient's body temperature may rise, there is severe abdominal pain.
- Recurrence of cystic ovarian formation. In this case, severe pain, discomfort during intercourse, asymmetric enlargement of the abdomen can be observed, arrhythmia, nausea can also occur, the patient's body weight can increase.
Prevention
To prevent the development of cystic ovarian formations, it is recommended to avoid the uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, timely treat diseases that are accompanied by hormonal disorders, avoid accidental sexual intercourse, and undergo regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.