- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
The use of Duphaston with an ovarian cyst
The content of the article:
- Treatment Approach
-
Description of the dosage form
- Composition
- pharmachologic effect
- Indications for use
- Contraindications
- Reception scheme
- Side effect
- Overdose
- Interaction with other medicinal products
- Application features
- Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- Recommendations for ovarian cysts
- Reviews about Duphaston with ovarian cyst
- Ovarian cysts: an overview
- Video
With ovarian cysts, Duphaston is used as an auxiliary component of treatment. The drug is a synthetic prototype of the natural hormone progesterone and has a pronounced hormonal effect. Therapy will have a clear dependence on the phase of the menstrual cycle.

Duphaston is used in the treatment of many gynecological diseases, including some types of cysts
Treatment Approach
Duphaston with a follicular cyst and other types of cysts can only be taken after consulting a doctor (gynecologist), who, in accordance with the size, type, localization and clinical picture, determines the dose of the drug. Ultrasound control (cyst size, density) is carried out 1 time in 2-3 weeks.
If you experience bleeding, severe pain or other side effects, you must stop taking the tablets.
Description of the dosage form
The drug is a white rounded biconvex tablet. The edges are beveled, covered with a shell, in the middle there is a dividing risk (on each half there is the number 155). The back of the tablet is engraved with the letter S.
Composition
It belongs to the group of histogenic drugs. The tablet includes:
- the main substance is dydrogesterone (10 mg);
- excipients (lactose, starch, magnesium stearate);
- shell components.
It is produced in the form of blisters of 20 pcs.
pharmachologic effect
Oral administration. The drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, the highest concentration in the blood is achieved after 2 hours. Metabolized in the liver. 50-70% of the drug is excreted in the urine. The effect fades away by the end of the first day, since by this time up to 80% of the drug has already been removed (after 72 hours, the female body is completely cleared of it). Clear data on a possible impairment of excretion of the substance in patients with kidney disease has not been established.
Indications for use
The drug is effective in a number of gynecological diseases, because:
- does not possess estrogenic, androgenic, anabolic, glucocorticoid and thermogenic activity (in contrast to classical oral contraceptives);
- does not have a pronounced effect on the blood coagulation system;
- does not affect ovulation processes and does not cause menstrual irregularities.
It is used for the following pathologies:
- lack of progesterone (infertility, problems with conception);
- endometriosis (endometrioid cyst);
- a history of threatening miscarriage or frequent miscarriages (habitual abortion) due to progesterone deficiency;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- irregular periods (dysmenorrhea) or missing menstruation (amenorrhea);
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
- replacement therapy for insufficient ovarian function;
- as a neutralization of the action of estrogens during menopause or after surgery (as part of hormone replacement therapy).
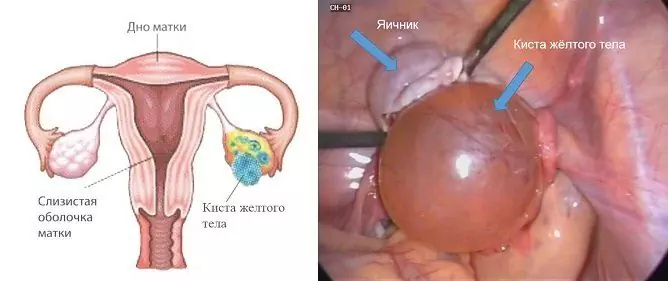
With the development of any cystic formation (corpus luteum cyst, follicular cyst), the tissues of the affected ovary are compressed and lose some of their function. For this reason, Duphaston in these conditions often acts as a substitution therapy.
Contraindications
The drug has only a few contraindications, which include the following conditions:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug (lactose intolerance);
- signs of an allergic reaction during a previous pregnancy (itching, rash).
There are no clear contraindications for persons with chronic liver and kidney damage. You should not take the drug during lactation, as some of it is excreted in breast milk. For pregnant women, there are no clear restrictions (admission is permissible after consulting a gynecologist).
Reception scheme
Each form of cystic formation and the symptoms / complications they cause requires an individual course of therapy. If necessary, the course can be repeated after some time (usually a month break).
The main points are presented in the table.
| Disease | Dose | Features: |
| Endometriosis (including endometrioid cysts). | Drink 10 mg 2-3 times a day. | Application from 5 to 25 days of the cycle. Sometimes continuous reception is allowed. |
| Infertility due to a lack of progesterone (for example, corpus luteum cyst). | Drink 10 mg per day. | Application from 14 to 25 days of the cycle. Carry out for 6 menstrual cycles (pregnancy is not an indication for drug withdrawal). |
| Threatened abortion. | 40 mg once, then 10 mg every 8 hours until symptoms disappear. | There are no special features. |
| Habitual abortion. | 10 mg 2 times a day | Reception up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Then the dose is gradually reduced. |
| Premenstrual syndrome. | 10 mg 2 times a day. | Reception from 11 to 25 days of the cycle. |
| Dysmenorrhea. | 10 mg 2 times a day. | Reception from 5 to 25 days of the cycle. |
| Irregular menstruation. | 10 mg 2 times a day. | Reception from 11 to 25 days of the cycle. |
| Amenorrhea. | 10 mg 2 times a day. | Reception from 11 to 25 days of the cycle together with the drug of the estrogen group (1 tablet from 1 to 25 days of the cycle). |
| Dysfunctional uterine bleeding. | 10 mg 2 times a day. |
Reception for 5-7 days. In order to prevent bleeding, the reception should be carried out from 11 to 25 days of the cycle. |
|
Hormone replacement therapy component: · With continuous use of estrogens; With the cyclic use of estrogens. |
Reception options: 10 mg once a day; · 10 mg once a day. |
Reception options: · Take for 14 days, taking into account the 28-day cycle; · Taking the next 12-14 days of taking estrogens. |
In cases where instrumental diagnostic data (ultrasound, biopsy) indicate the persistence of progesterone deficiency, the daily dose can be increased to 20 mg per day.
Side effect
Side effects are infrequent, and most of them do not pose a serious threat. Side effects include:
- From the side of the hematopoietic system - hemolytic anemia.
- From the side of the immune system - the development of a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction.
- From the side of the central nervous system - headaches, migraines.
- On the part of the liver and bile ducts - rarely there are changes in laboratory parameters (increased liver enzymes), jaundice.
- From the reproductive system - spotting, bleeding, hypersensitivity of the mammary glands.
- On the part of the skin and subcutaneous tissue - itching, urticaria, rash, Quincke's edema.
- Common manifestations are lethargy, fatigue, and peripheral edema.
If any side effects occur, the dose of the drug should be changed.
Overdose
Data on overdose with Dufaston are not registered. When taking a large number of tablets at a time (significant excess of the therapeutic dose), you should immediately contact the emergency room of the hospital (gastric lavage is required).
There is no specific antidote. Treatment is symptomatic.
Interaction with other medicinal products
Taking Duphaston does not have a pronounced effect on taking other drugs. Cross-reactions do not occur. When taking inducers of liver microsomal enzymes (phenobarbital, rifampicin), the metabolic time may decrease (the time of complete elimination from the body decreases to 24 hours). This leads to a decrease in the Dufaston effect.
Application features
Has the following application features:
- In case of bleeding, an increase in the dose of the drug is indicated.
- When taken with estrogens, careful monitoring of laboratory and instrumental parameters is required.
- In the presence of concomitant diseases such as a progesterone-dependent tumor (meningioma), control of its growth is required (if an increase or malignancy is suspected, the drug is canceled).
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Available by prescription only.
Recommendations for ovarian cysts
There are the following general recommendations for patients with cystic formations in the ovaries taking Duphaston:
- Periodic monitoring of the state of the hormonal system (once a month a blood test for estrogens, progesterone, testosterone).
- Examination by a gynecologist at least 1 time per month with ultrasound control.
- Strict adherence to the required cycle time for taking pills (not earlier and not later).
- With a cycle of more or less than 28 days, dose selection is required on an individual basis.
- In the absence of positive dynamics after 2-3 courses of therapy, planned removal of cystic formation is indicated.
- If complications of cysts (rupture, torsion) are suspected, drug withdrawal and emergency hospitalization are indicated.
- When planning a pregnancy, taking the drug is supplemented with oral contraceptives and lifestyle correction.
- In the early stages of pregnancy, the patient's condition is monitored at least once every 2 weeks.
Reviews about Duphaston with ovarian cyst
There are no specific recommendations for taking this drug. Reviews of Duphaston with an ovarian cyst are mostly positive, but in some cases its action is not enough, it may be necessary for planned surgical intervention.

Only a qualified specialist should prescribe the drug, as well as select its dosage.
Ovarian cysts: an overview
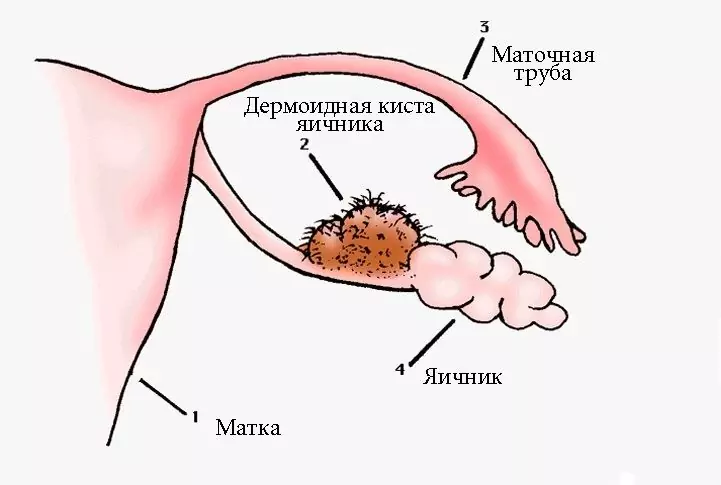
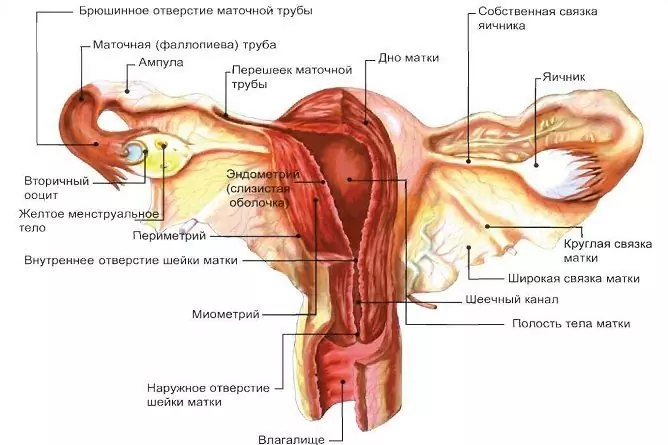
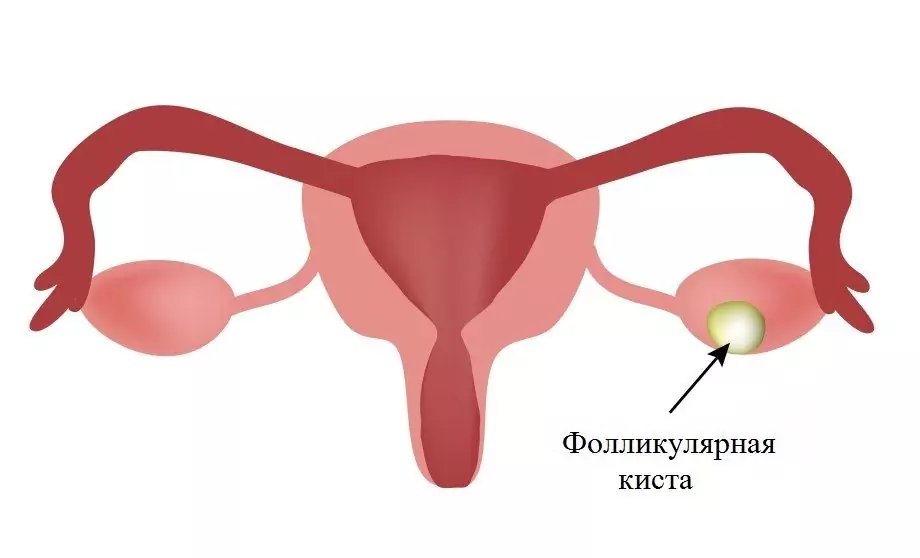
Ovarian cysts are benign neoplasms that have a cavity filled with fluid. They occur more often in young and middle-aged people. The following types of cysts are distinguished:
- corpus luteum cyst;
- follicular;
- endometrioid;
- paraovarian;
- tecaluteic;
- cystadenoma (cystoma).
Cystic lesions can be treated using one of three methods:
- Expectant tactics and taking medications, in particular, Duphaston.
- Planned surgical intervention.
- Emergency surgery.
The choice of tactics depends on the characteristics of the cyst and its clinical manifestations.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.