- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Osteochondropathy
Brief description of the disease

Osteochondropathy is a disease of children and adolescents, in which a degenerative-dystrophic process develops in the bones.
With osteochondropathy, the calcaneus, femur, apophyses of the vertebral bodies, and tibial tuberosity are most often affected.
Reasons for the appearance
To date, the causes of the onset of the disease have not been fully understood, but several decisive factors are distinguished:
- congenital or familial predisposition;
- hormonal factors - the disease develops in patients with pathology of endocrine gland function;
- metabolic disorders of essential substances. Osteochondropathy is often caused by impaired absorption of calcium and vitamins;
- traumatic factors. Osteochondropathy occurs after excessive physical exertion, incl. increased muscle contractions, frequent injuries. Initially, these types of loads lead to progressive compression, and then to narrowing of the small vessels of the spongy bones, especially in the areas of greatest pressure.
Osteochondropathy symptoms
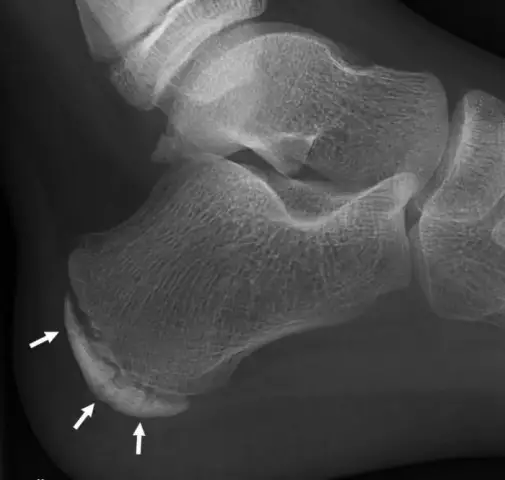
Osteochondropathy of the calcaneus (Haglund-Schinz disease) develops most often in girls 12-16 years old, is characterized by gradually increasing or sharp pain in the calcaneus tuberosity that occurs after exercise. At the point of attachment of the Achilles tendon, a swelling is noted above the calcaneal tubercle. Patients begin to walk, leaning on a sock, and playing sports, jumping becomes physically impossible.
Osteochondropathy of the spine (Scheuermann-Mau disease) develops most often in young men 11-18 years old. The first stage is characterized by increased thoracic kyphosis (curvature of the spine in its upper part), the second - by back pain (especially with prolonged walking, sitting), rapid fatigue and weakness of the back muscles, an increase in thoracic kyphosis. At the third stage of spinal osteochondropathy, there is a complete fusion of the apophyses with the vertebrae. Over time, osteochondrosis develops with increasing pain syndrome.
Osteochondropathy of the femur (Legg-Calve-Perthes disease) develops in most cases in boys 4-12 years old. At the beginning of the disease, there are no complaints, after which pains appear in the hip joint, radiating to the knee. Pain arises after exercise and disappears after rest, so children do not always complain about them. The movements of the hip joint are gradually limited, muscle atrophy develops, and the thigh on the sore side is losing weight.
Osteochondropathy of the tibial tuberosity (Schlatter's disease) develops in boys 12-16 years old, especially in those who are engaged in ballet, sports dances, and sports. The patient complains of pain under the patella, swelling. With the tension of the quadriceps femoris muscle, when squatting, climbing stairs, the pain increases.
Diagnosis of the disease
To determine the osteochondropathy of the calcaneus, they are based on clinical data and the results of an X-ray examination (fragmentation, compaction of the apophysis, "roughness" on the tuberosity of the calcaneus are noted). Differential diagnosis of osteochondropathy with a heel spur (in older patients), achillobursitis is also carried out.
Diagnosis of osteochondropathy of the spine occurs on the basis of examination data (thoracic kyphosis is enhanced) and X-ray examination (the pictures show that the shape of the vertebrae is changed - they acquire a wedge-shaped shape).

Osteochondropathy of the femur is also determined by radiographic images. Five stages of changes in the femoral head were identified.
Osteochondropathy of the tibial tuberosity is established according to the clinical picture and is specified after an X-ray examination.
Treatment of osteochondropathy
Therapy for osteochondropathy of the calcaneus consists in the appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (if severe pain is haunted), physiotherapy procedures, and in reducing physical exertion. To relieve the load on the heel bone, special instep insoles are used.
Spinal osteochondropathy is treated with massage, swimming, underwater stretching, physiotherapy exercises. In some cases, with a strong violation of posture, an operation is prescribed.
Treatment of osteochondropathy of the femur can be operative and conservative. Various osteoplastic operations are prescribed depending on the stage of the disease. Conservative treatment of osteochondropathy consists in adherence to bed rest (the patient should not sit), massage of the legs, physiotherapy procedures. Skeletal traction is practiced on both hips.
For the treatment of osteochondropathy of the tibial tuberosity, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed, heat. If the pain is severe, a plaster cast is applied. Sometimes they resort to surgery - a fragment of the tuberosity is removed. Loads on the quadriceps femoral muscle are excluded.
Prevention of the disease
For the prevention of heel bone osteochondropathy, it is recommended to wear loose shoes.
Prevention of osteochondropathy of the spine consists in physical therapy to create a muscle corset. Intense physical activity must be limited. Wearing a corset for this disease is ineffective.
Massage, swimming is a good prevention of osteochondropathy of the femur.
To prevent osteochondropathy of the tibial tuberosity, athletes are advised to sew 2-4 cm thick foam pillows into the uniform during training.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!