- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Joint cyst

A cyst is a soft, hollow, pathological formation filled with fluid that forms in various tissues and organs.
Joint cyst
A joint cyst is a secondary disease, a cavity connected to the joint tissue, filled with fluid, which is formed as a result of inflammatory processes, trauma, degenerative diseases of the joint.
A joint cyst in most cases affects the most mobile articular complexes of the body: knee, hip, ankle joints.
The cyst of the joint is a rounded, sedentary neoplasm, reaching from a few millimeters to 5 cm in diameter, easily palpable. The cyst of the joint is characterized by a firm-elastic consistency and clear boundaries. The cystic formation is localized in the projection of the synovial bag or the tendon of the joint. In most cases, the cyst of the joint forms on the back of the joint. The cyst of the joint is not soldered to the subcutaneous fatty tissue and skin. Externally, the cyst of the joint has no special signs, the surface of the skin over the cystic formation remains unchanged (there is no redness, changes in its structure). In medical practice, no cases of degeneration of joint cysts into malignant formations have been recorded.
The joint cyst forms and develops asymptomatically, without causing inconvenience to the patient. There is no tenderness to palpation. Some painful sensations can occur during the work of the joint.
The cysts of the joints are very labile (change their size, can disappear completely). Cystic formations can be single (with the formation of one cavity) and multiple (with the formation of many small cysts).
The main symptoms of a joint cyst:
- A tumor in the joint area, which has clear boundaries, well amenable to palpation;
- Painful sensations when the joint works;
- Dysfunction of the joint until complete loss of mobility;
- Numbness of nearby tissues, swelling.
A cyst of the joint is more often observed in patients suffering from arthritis, arthrosis, osteoarthritis. The cyst of the joint is not an independent disease, but is a consequence of trauma, chronic, degenerative diseases of the joint, and inflammatory processes.
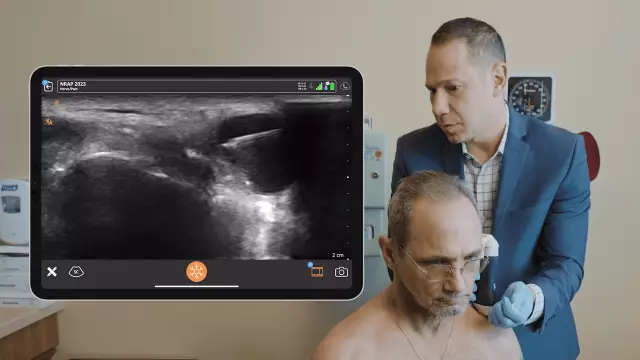
The main methods for diagnosing joint cysts are:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- Fluoroscopy;
- Puncture.
These research methods make it possible to establish the disease that caused the formation of the cyst, to identify the degree of joint damage, to determine the size and localization of the joint cyst in the tissues, to conduct a biochemical study of the contents of the cystic formation.
Knee cyst
The knee joint is the articular complex that connects the tibia and femur, as well as the patella (patella). The cyst of the knee joint forms on the back of the knee. The formed cyst is localized in the popliteal fossa. A knee cyst is also called a Becker cyst.
Cystic formation does not cause discomfort to the patient, however, reaching a significant size, it can squeeze blood vessels and nerves, which in turn leads to thrombosis, phlebitis, inflammation, neuritis, varicose veins, edema, loss of sensitivity and numbness of the lower leg.
The main risk in diagnosing a cyst of the knee joint is its rupture with the outpouring of the contents into nearby tissues, which can provoke an inflammatory process in the tissues. In most cases, the cyst of the knee joint is caused by frequent injuries.
Cyst of the hip joint
The hip joint is a polyaxial, spherical articular complex formed by the articular surface of the femoral head and the semilunar surface of the acetabulum. A cyst of the hip joint may not have external manifestations, like a cyst of the knee joint.
The pathogenesis of the cyst of the hip joint is also characterized by the formation of a cavity filled with synovial fluid. With this type of cystic formation, the patient feels pain during movement much earlier than with cysts affecting other joints (knee, ankle). Many patients report stiffness of movement, discomfort, numbness, loss of sensitivity of the affected area.

A cyst of the hip joint is diagnosed with MRI and x-rays. This type of cystic formation is more likely to occur due to inflammatory, degenerative diseases than trauma.
Ankle cyst
The ankle joint is the joint between the foot and the lower leg bones (talus, fibula, and tibia). The cyst of the ankle joint is smaller in size, its formation is also asymptomatic, localized on the back of the joint. Ankle cyst is also a consequence of joint degenerative processes and injuries.
Joint cyst treatment
Treatment of a joint cyst can be conservative and radical. A cyst of the joint, which does not cause discomfort to the patient, also requires timely treatment in order to avoid rupture of its capsule and inflammation of nearby tissues.
Conservative methods of treating joint cysts involve:
- Crushing - the essence of the method is to actually squeeze the contents of the cystic formation back into the mother's cavity. This method was widely used until the 80s of the 20th century. With this method of treatment of the cyst of the joint, the capsule is completely preserved, in which the synovial fluid is produced and accumulated. This treatment technique is a temporary measure. Relapse with this method is inevitable;
- Puncture of the cyst of the joint - this method of treatment of the cyst of the joint is at the periphery of the diagnosis and treatment of education. The piercing of the cyst and the extraction of its contents is carried out in order to conduct a biochemical analysis and identify inflammatory processes. The contents of the cyst are pumped out through a puncture needle. Anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the cleaned cystic cavity, a tight pressure bandage is applied to the cyst site, and the joint is immobilized in order to reduce the production of synovial fluid. This technique is mainly used in cases where surgical excision of the cyst is not possible. After the puncture, the risk of relapse remains high;
- Drug treatment - the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids.
A radical method of treating a cyst of the joint is surgical excision of the neoplasm. Currently, endoscopic techniques for removing joint cysts are used, which have a number of advantages: low mechanical damage to tissues, minimally invasive manipulation, painlessness, and rapid patient recovery after manipulation.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. During the manipulation, the surgeon performs complete removal of the cyst capsule, which prevents its reappearance, and also sutures the weak spot of the joint capsule with a special suture that helps to strengthen it.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!