- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Arthralgia
The content of the article:
- Causes
- Types of arthralgia
- Arthralgia symptoms
- Features of the course of arthralgia in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention
- Consequences and complications
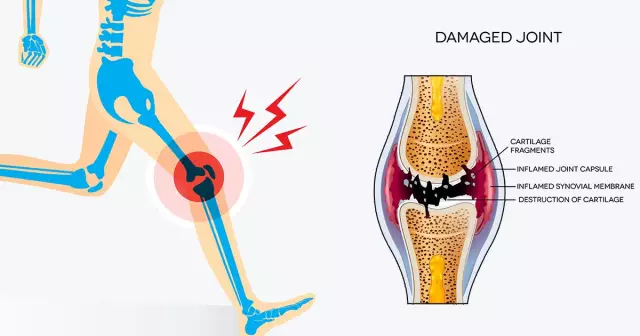
Arthralgia is persistent pain in the joints, which can be harbingers of organic lesions of the joint tissues or a sign of a serious extra-articular pathological process.
In most cases, arthralgia occurs in large joints (shoulder, elbow, hip, knee), much less often the pathological process affects small joints (interphalangeal, wrist, ankle, etc.). Arthralgia in children requires special attention, since ignoring it can lead to the fact that a serious pathological process will be missed, sometimes with irreversible consequences.

Arthralgia is the general name for any joint pain
Causes
Determination of the reasons for the occurrence of arthralgia is of great differential diagnostic value.
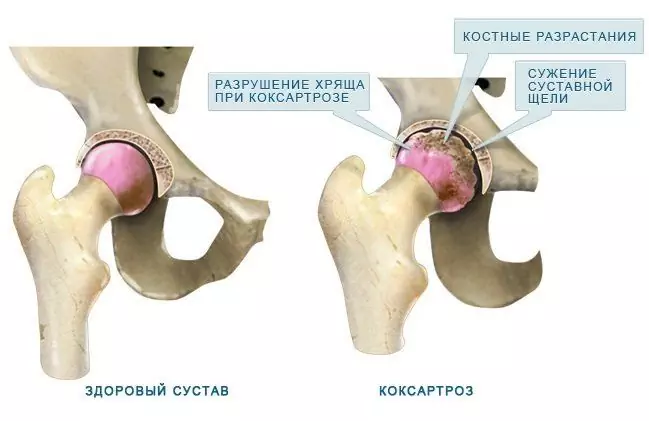
A common cause of arthralgia is osteoarthritis and viral polyarthrosis, in which the infectious agents are usually influenza, rubella, chickenpox, parotitis, hepatitis A and B viruses, as well as cytomegalovirus and parvovirus. Arthralgia also occurs against the background of bacterial infection, autoimmune inflammation, HIV infection, malignant neoplasms, endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, ovarian dysfunction, etc.). Possible reasons for the development of arthralgia include overweight, disorders of the musculoskeletal system, excessive loads and microtraumas of the joints, prolonged drug therapy with certain drugs, intoxication with heavy metals, post-allergic reactions, neuroses, etc. Arthralgia of the knee joint develops with those types of physical activity,where there is a constant load on the knee joint, and arthralgia of the hip joint is a frequent occurrence in weightlifters.

Arthralgia of the knee joint develops with frequent stress on the knee
Since chronic hypothermia is a risk factor for the development of arthralgia, pathology is often observed in mining workers, sailors, fishermen, etc.
Types of arthralgia
Depending on the intensity of pain, arthralgia can be:
- weak;
- moderate;
- intense.

Types of arthralgia, depending on the location
Depending on the frequency of manifestation, arthralgia is classified into permanent and transient.
Based on the number of affected joints, the pathological process is subdivided as follows:
- monoarthralgia - pain is localized only in one joint;
- oligoarthralgia - pain in less than five joints;
- polyarthralgia - pain occurs in more than five joints.
Depending on the localization, there are:
- arthralgia of the knee joint;
- hip joint;
- elbow joint;
- shoulder joint;
- arthralgia of other localization (joints of the fingers, wrist, ankle joint).
Depending on the etiology and nature of the inflammation:
- arthralgia against the background of acute infectious processes;
- arthralgia in acute or recurrent arthritis;
- post-inflammatory and post-traumatic arthralgia;
- long-term current monoarthralgia of large joints;
- oligo- or polyarthralgic syndrome, in which the synovial membranes are involved in the pathological process or degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cartilage are observed;
- pseudoarthralgia - pain feels like articular pain, although it is caused by extra-articular causes (such as fibromyalgia).
Arthralgia symptoms
The main manifestation of arthralgia is joint pain.
Due to the fact that arthralgia is inherent in the clinical picture of many diseases, the signs of the underlying disease usually come to the fore, especially when it is acute.
In the early stages of the pathological process, joint pain may be the only symptom of the disease. In this case, the painful sensations are of a different nature (acute or dull, constant or intermittent, aching or pulsating, night or starting). Some pathologies are characterized by migratory joint pain.

The main symptom of arthralgia is joint pain
The pain usually gets worse with exertion. In the presence of an inflammatory process, skin hyperemia, swelling in the joint area, increased skin temperature, restriction of movement in the affected joint, and its deformation are added to the symptoms of arthralgia. Arthralgia is often combined with myalgia (muscle pain).
Features of the course of arthralgia in children
Arthralgia in children is most often a sign of an acute infectious disease. In these cases, joint and muscle pain can occur even in the prodromal period, then they are joined by fever and signs of intoxication of the body (headache, a general decrease in well-being, weakness, loss of appetite). Arthralgia of infectious etiology is accompanied by complaints of aches in the joints of the upper and lower extremities. In this case, the mobility of the joints does not undergo changes. In most cases, with a decrease in the toxic syndrome caused by the underlying disease, arthralgia also disappears. The persistence of arthralgia after the infectious process subsides may indicate the development of reactive arthritis.
Oligoarthralgia and polyarthralgia in children against the background of rheumatic diseases manifests itself in the form of intense joint pain. Usually, the large joints of the lower extremities are involved in the pathological process, while their mobility is limited.
The gradual development of arthralgia over a long period may indicate that the child has deforming osteoarthritis or other degenerative-dystrophic processes in the joints. As a rule, in such cases, the child has arthralgia of the knee joint or involvement in the pathological process of the hip joint. Children can complain of a dull aching pain that occurs during physical exertion and subsides at rest, movements in the joints are usually accompanied by a crunch. In some cases, patients have meteorological dependence.

In children, arthralgia is most often a sign of an infectious disease.
The development of oligo- or polyarthralgia in children, accompanied by deformation of the distal phalanges of the fingers and nails (“Hippocratic fingers”, drumstick syndrome), may indicate serious diseases of the heart, liver, lungs and other internal organs.
With the development of arthralgia against the background of endocrine diseases, muscle pain is usually observed in children, as well as pain in the pelvic bones and in the spine.
With inflammation of the joints in children, residual arthralgia often develops. At the same time, pain in the affected joints and limitation of movement in them, as a rule, are temporary and disappear after a few weeks. However, in some cases, relapses are observed due to hypothermia of the body, excessive stress, as well as weather changes (wet, cold, windy weather is especially unfavorable).
Diagnostics
Since arthralgia can act as a manifestation of various diseases, the diagnosis of the main pathological process comes to the fore. First of all, they collect complaints and anamnesis, as well as a physical examination.
From the methods of hardware diagnostics, they resort to X-ray of the joints, ultrasound, if necessary - to computed and magnetic resonance imaging, arthroscopy. Diagnostic puncture of the affected joint is performed, followed by laboratory examination of the punctate.

CT and MRI may be required to find out the cause of arthralgia
The examination is supplemented by laboratory diagnostics: general and biochemical blood tests, serological, bacteriological, immunological (rheumatic tests) studies.
Treatment
In addition to treating the underlying disease that caused arthralgia, symptomatic treatment is used to eliminate it.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the joint, as well as relieving pain. For these purposes, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and / or analgesics are used, which can be used both orally and topically in the form of a cream, ointment or application to the area of the affected joint, and sometimes a combination of oral and local forms of drugs is prescribed. In order to minimize possible side effects, these oral medications are prescribed in a short course. In diseases of infectious etiology, anti-infectious drugs are used, the appointment of which usually occurs after the identification of the pathogen and determination of the sensitivity of the infectious agent to drugs. For pathologies of connective tissue, steroid anti-inflammatory drugs are used,immunosuppressive drugs.
Physiotherapeutic methods are effective in the complex therapy of many diseases, the manifestation of which is arthralgia, complementing the main treatment. Most often they resort to magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis of drugs, ultra-high-frequency therapy, hydrotherapy, as well as paraffin and mud therapy. Physiotherapy is contraindicated in acute inflammatory processes (as well as in exacerbation of chronic) and in autoimmune diseases.

Magnetic therapy is effective as a physiotherapeutic treatment for arthralgia.
If it is necessary to carry out long-term therapy in order to reduce the drug load on the body, in some cases, phytotherapy is used, while infusions of medicinal plants (chamomile flowers, birch buds, juniper), coniferous or turpentine baths are used. Apitherapy is highly effective in treating some forms of arthralgia.
Prevention
In order to prevent arthralgia, it is recommended:
- timely access to a doctor if you suspect the development of a pathological process in the joints;
- adequate treatment of infectious diseases;
- avoiding excessive physical exertion, but at the same time sufficient physical activity;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- balanced diet;
- maintaining a normal body weight;
- rejection of bad habits.
Consequences and complications
Lack of timely diagnosis and treatment in the presence of arthralgia can lead to irreversible disorders in the articular tissues and destruction of the joints. Arthrosis, contractures, muscle rigidity and ankylosis may develop, leading to disability.
If arthralgia is a sign of a serious pathological process in the body, the lack of adequate treatment will worsen the prognosis of the underlying disease.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!