- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Mastopathy

Mastopathy is the most common breast disease.
The first symptoms of mastopathy may appear already in adolescence, although in this case the disease does not necessarily progress, more often, after the hormonal balance is established, adolescent mastopathy passes on its own. The disease can also manifest itself at the age of early menopause, 50-55 years. The most susceptible to mastopathy are women aged 30-45 years.
With mastopathy, the structure of the gland tissue changes, fibrous tissue grows, and cysts appear, hence the name of the disease adopted by the World Health Organization - fibrocystic disease (Fibrocystic Breast Disease).
Mastopathy is so widespread that sometimes it is considered almost the norm, and for a long time they do not pay attention to the symptoms of mastopathy until they become so pronounced that they significantly worsen the quality of life. Mastopathy is by no means the norm. This is a benign tumor disease, which, under unfavorable conditions, degenerates into a malignant one.
In most cases of breast cancer, it is preceded by mastopathy.
Causes of mastopathy
The immediate cause of mastopathy is hormonal imbalance in the body. Fibrous growths in the mammary gland appear under the influence of the growth of estrogen and prolactin, a hormone that provides lactation in the postpartum period.
There can be many reasons for hormonal imbalance. Hormone production is influenced by many factors, from neurogenic (stress, overwork, chronic fatigue) to infectious (inflammatory diseases of the female genital tract).
Bad habits, especially tobacco smoking, also increase the risk of developing mastopathy.
In addition to these, risk factors include the following:
- Termination of pregnancy, including artificial (abortion);
- Endocrine diseases;
- Late first pregnancy;
- Refusal of breastfeeding or untimely interruption of breastfeeding;
- Lack of childbirth;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Long-term hormone therapy.
Types of mastopathy
Distinguish between diffuse and nodular mastopathy.
With diffuse mastopathy, proliferation of connective tissue affects the entire tissue of the gland, with nodular, connective tissue nodes are formed. The nodes can be of various sizes, and be single or multiple. The nodular form of mastopathy often leads to the development of a malignant tumor.
By the nature of the elements of the lesion, the following types of mastopathy are distinguished:
- fibrous mastopathy;
- cystic mastopathy;
- fibrocystic mastopathy.
Most often they talk about fibrocystic mastopathy, since growths of connective tissue form fibrous cords and cysts - cavities of fibrous tissue filled with fluid.
Isolated fibrous mastopathy and cystic mastopathy are somewhat less common. Mammologists believe that instead of the terms fibrous mastopathy and cystic mastopathy, it is more correct to use the terms diffuse mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component, and mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component, since fibrous growth and cysts are present in any form.
Symptoms of mastopathy
The main symptom of mastopathy with which women go to the doctor is soreness of the mammary glands. The pain initially depends on the menstrual cycle and appears a few days before menstruation and then goes away. In the later stages of the disease, the pain becomes constant and can be very intense.
The characteristic symptoms of mastopathy also include a thickening of the gland - it may be a feeling of general compaction of the gland tissue in a diffuse form, or the appearance of nodules in a nodular form of mastopathy.
Nipple discharge may appear. With mastopathy, the discharge is transparent, greenish or milk-like. Bloody discharge is an unfavorable sign, and may be evidence of malignancy, therefore, if they appear, an immediate visit to a doctor is necessary.

Symptoms of mastopathy appear, as a rule, on both mammary glands, although they can have varying degrees of severity.
Diagnostics of the mastopathy
In mastopathy, as in breast cancer, self-diagnosis is important.
Palpation examination of the mammary gland in front of a mirror with a hand behind the head allows palpation of nodular formations and compacted cords of connective tissue and cysts. When contacting a mammologist, the following studies are carried out:
- examination, carried out on the fifth to eleventh day of the menstrual cycle;
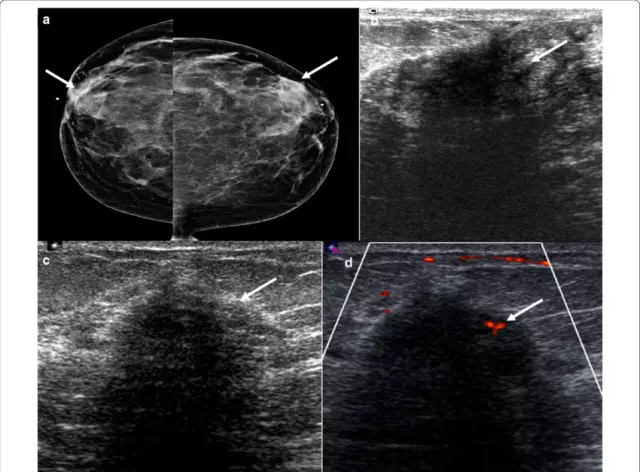
- mammography, performed from the tenth to the twelfth day of the menstrual cycle;
- ultrasound examination of the breast, carried out on the fifth to eleventh day of the menstrual cycle;
- biopsy of cysts and nodules;
- cytological examination of nipple discharge.
Treatment of mastopathy
Treatment of mastopathy can be both conservative and surgical, depending on the type of disease, its stage and some individual factors.
As a rule, surgical treatment of mastopathy is resorted to in the case of nodular and cystic mastopathy with the failure of several courses of conservative therapy, as well as if there is a suspicion of malignancy of the process. In this case, an operation called a sectoral resection of the breast is performed.
Conservative treatment of mastopathy includes medication and non-medication. Medical treatment of mastopathy is carried out mainly with hormonal drugs, and is aimed at restoring the lost hormonal balance. It is prescribed strictly individually, after a series of hormone tests.
In addition to hormones, anesthetic anti-inflammatory drugs are used, iodine preparations are used to normalize the activity of the thyroid gland, which affects sex hormones, and a course of general strengthening therapy is carried out.
Experts say that one of the main points that ensure the success or failure of the treatment of mastopathy, regardless of its forms, is the normalization of the lifestyle, as the main factor in the development of the disease.
It is necessary, if possible, to get rid of stressful situations, ensure good sleep, work and rest, switch to proper nutrition, pay attention to physical activity and walking in the fresh air, try to have a regular sex life with a regular partner. Sometimes, for the treatment of mastopathy in the initial stages, these measures are enough for a complete recovery. In the case of a more serious stage of the disease, measures to normalize the lifestyle are a necessary background to ensure the proper effect of therapeutic and surgical means. After recovery, it is necessary to continue to maintain a healthy lifestyle as a prevention of recurrence of mastopathy.
In case of mastopathy, it is forbidden to expose the breast to ultraviolet radiation (both solar radiation and artificial tanning in a solarium), thermal procedures (baths, saunas, etc.), massage, hormonal contraceptives without a doctor's prescription are prohibited.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!