- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hypoglycemic coma
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Disease stages
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Hypoglycemic coma is an acute life-threatening condition caused by a sharp drop in the concentration of glucose in the blood; extreme hypoglycemia.

Hypoglycemic coma occurs when glycemia is below 3.0 mmol / liter
Causes and risk factors
The main causes of hypoglycemia are:
- overdose of hypoglycemic drugs or insulin;
- insufficient carbohydrate intake after the usual dose of insulin;
- hypersensitivity to insulin;
- decreased insulin-activating liver function;
- hyperinsulinism;
- alcohol intoxication.
Much less often, the state of hypoglycemia is due to:
- overdose of beta-blockers and aspirin;
- chronic renal failure;
- hepatocellular carcinoma;
- pituitary insufficiency.
Exposure to any of these factors causes a decrease in blood glucose levels.
Insufficient glucose intake causes energy starvation of brain cells, disruption of redox processes in them, which is equivalent to the changes observed during acute brain hypoxia. This leads first to functional, and then to organic degenerative changes in neurons, with significant hypoglycemia - to their death.
The most sensitive to hypoglycemia are the neurons of the cerebral cortex, and the least sensitive to the structures of the medulla oblongata. That is why in patients with hypoglycemic coma, cardiac activity, vascular tone and respiration persist for a long time, even if irreversible decortication occurs.
Disease stages
There are several stages in the development of hypoglycemic coma:
- Cork. It is associated with the development of hypoxia of cells of the cerebral cortex.
- Subcortical-diencephalic. Increasing hypoglycemia leads to damage to the subcortical-diencephalic zone of the brain.
- Precoma. It is caused by a violation of metabolic processes in the structure of the midbrain.
- Coma itself. The functions of the upper parts of the medulla oblongata are impaired.
- Deep coma. The lower parts of the medulla oblongata are involved in the pathological process, the functions of the vasomotor and respiratory centers are disrupted.
Symptoms
Hypoglycemic coma develops in stages. At first, there are precursor symptoms, indicating a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood. These include:
- anxiety, fear;
- feeling of severe hunger;
- profuse perspiration (hyperhidrosis);
- dizziness and headache;
- nausea;
- sharp pallor of the skin;
- hand tremor;
- tachycardia;
- increased blood pressure.
If help is not provided at this stage, then against the background of a further decrease in blood glucose levels, psychomotor agitation will appear, auditory and visual hallucinations will occur. Patients with severe hypoglycemia often complain of impaired skin sensitivity (paresthesia) and diplopia (double vision).
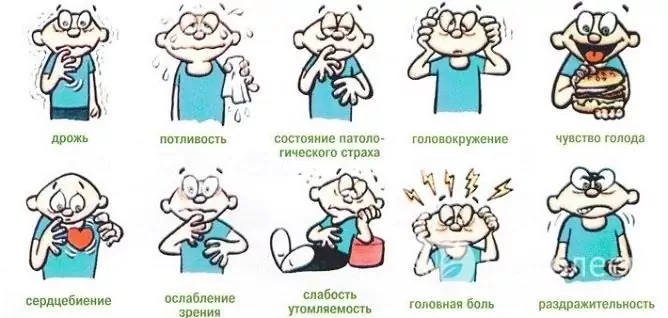
It is important to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia in time to prevent the development of hypoglycemic coma.
In some cases, the period of precursors is so short that neither the patient himself nor the people around him have time to orient themselves and take action - the symptoms grow rapidly, literally within 1-2 minutes.
With the growth of hypoglycemia and the depletion of neuroendocrine defense reactions, the condition of patients deteriorates significantly. Excitement is replaced by lethargy, and then complete loss of consciousness. Tonic seizures, focal neurological symptoms occur. Breathing becomes shallow, blood pressure gradually decreases. The pupils stop responding to light, the corneal reflex fades away.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hypoglycemic coma is carried out on the basis of anamnesis and clinical picture of the disease. The diagnosis is confirmed by a biochemical blood test. A hypoglycemic state is indicated by a decrease in glucose concentration to a level of less than 3.5 mmol / l. Symptoms of a coma appear when glucose levels are less than 2.77 mmol / L. At a blood glucose concentration of 1.38-1.65 mmol / l, the patient loses consciousness.
The diagnosis of "hyperglycemic coma" is confirmed by a biochemical blood test
Treatment
Therapy for hypoglycemic coma begins with intravenous administration of hypertonic glucose solutions. With a deep coma, glucagon or hydrocortisone is additionally injected intramuscularly. To improve glucose metabolism, the use of ascorbic acid and cocarboxylase is shown.
If a patient has signs of cerebral edema against the background of a hypoglycemic coma, then osmotic diuretics are prescribed.
Correction of violations of acid-base state, violations of water-electrolyte balance is also carried out. According to indications, oxygen therapy is carried out, cardiovascular agents are prescribed.
Possible complications and consequences
Hypoglycemic coma is often accompanied by the development of complications, both current and distant. Current complications arise in parallel with the hypoglycemic state and accompany it. These can be myocardial infarction, stroke, aphasia.
Long-term complications of hypoglycemic coma appear several days or even weeks after the acute condition. The most common complications are encephalopathy, parkinsonism, epilepsy.

One of the complications of hypoglycemic coma is myocardial infarction
Forecast
With timely assistance, a hypoglycemic coma quickly stops and does not entail serious consequences for the body. In this case, the prognosis is favorable. However, often occurring hypoglycemic conditions lead over time to the development of serious cerebral disorders.
In patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypoglycemic coma is more severe and more often than in others, it causes complications (for example, retinal hemorrhage or myocardial infarction).
Prevention
To prevent hypoglycemia, the prescribed dosage of insulin or sugar-reducing drugs should be carefully followed. Patients should be informed about the need for a mandatory meal after the injection of insulin. Compliance with the daily regimen and diet helps reduce the risk of a drop in blood glucose concentration.
Patients with diabetes mellitus and their loved ones should be aware of the signs of a hypoglycemic state. When these appear, the patient urgently needs to drink warm sweet tea, eat a sugar cube, candy or a piece of white bread.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






