- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hematometer
The content of the article:
- Causes
- Forms
- Symptoms of hematomas
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of hematomas
- Prevention
- Consequences and complications
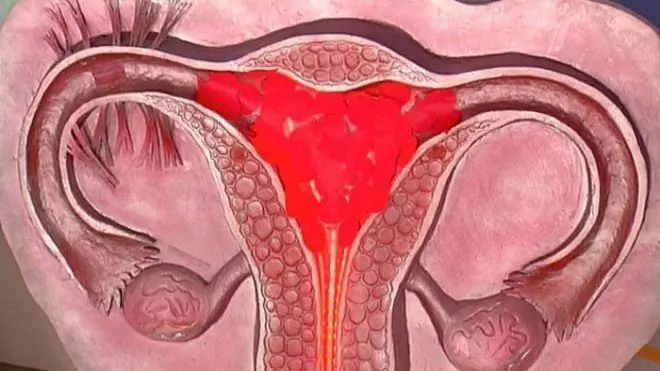
A hematometer is an accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity associated with a violation of the outflow of post-abortion, postpartum or menstrual discharge through the cervical canal.
The hematometer is not an independent pathology, it is one of the manifestations of congenital developmental pathologies or acquired diseases of the vagina and uterus.
Often, the accumulation of blood in the uterus is combined with hematocolpas and hematosalpinx, that is, with the accumulation of blood in the vagina and fallopian tubes. Untimely evacuation of the contents of the hematometer threatens the development of purulent-septic complications, which can lead to the death of the patient. In this regard, the issues of preventing the formation of hematomas, its diagnosis and treatment are very relevant for modern obstetrics and gynecology.

Hematometer - accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity
Causes
The causes leading to the appearance of hematomas are divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital causes include anomalies in the structure of the internal genital organs:
- vaginal atresia;
- intrauterine septum;
- intrauterine synechiae;
- atresia of the cervical canal.
If these anomalies are not diagnosed in childhood, then with the onset of the formation of menstrual function, a hematometer is formed.
Acquired reasons include the following conditions:
- myomatous node, located in the area of the internal uterine pharynx;
- large polyp of the cervical canal;
- cervical cancer;
- endometrial cancer;
- obstruction of the cervical canal with a large blood clot, a site of the placenta, a fragment of the ovum left after an abortion;
- cicatricial stenosis of the cervix caused by radiation therapy, surgery;
- spasm of the cervical canal after curettage of the uterine cavity or spontaneous abortion at an early stage.

Endometrial cancer can cause hematomas
Postpartum hematometer (lochiometer) is one of the complications of the postpartum period, the causes of which can be:
- overstretching of the uterus (multiple pregnancy, large fetus, polyhydramnios);
- weakness of labor;
- scars on the uterus;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- manual separation of the placenta.
Forms
Taking into account the reason underlying the pathological mechanism of the development of blood accumulation in the uterine cavity, its following forms are distinguished:
- hematometer after childbirth;
- hematometer after intrauterine manipulation;
- hematometer resulting from obstruction (obstruction) of the cervical canal and / or vagina.
Symptoms of hematomas
The clinical picture is determined by the following factors:
- the cause of the development of pathology;
- the volume of blood accumulated in the uterine cavity;
- the duration of the pathology.
It is possible to assume the formation of hematomas in a woman in the event of a sudden cessation or a significant decrease in the amount of uterine secretions after intrauterine manipulations, abortion or childbirth.
The main symptoms of hematomas in adolescent girls with congenital malformations of the genital tract are:
- prolonged absence of menstrual bleeding (false form of amenorrhea);
- a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- cramping pain in the lower abdomen.
With the rapid development of hematomas and a significant amount of blood accumulated in the uterus, signs of internal bleeding appear:
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- darkening in the eyes, flashing before the eyes of "flies";
- tachycardia;
- lowering blood pressure;
- feeling short of breath;
- pallor of the skin;
- fainting.

With the rapid development of hematomas, signs of internal bleeding appear
The blood accumulated in the uterus is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms, therefore, if the hematometer remains undiagnosed and is not removed, inflammation rapidly develops against its background (endometritis, metroendometritis, pyometra). In this case, the patient's condition rapidly deteriorates: the body temperature rises to febrile values, which is accompanied by tremendous chills and a sharp deterioration in the general condition, the pain in the lower abdomen intensifies, may radiate to the lumbar region or take on a shingles.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hematomas is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist based on clinical symptoms, patient complaints, gynecological examination data and instrumental research methods.
When carrying out a bimanual vaginal examination, an enlarged uterus, painful on palpation, is determined, which usually has a soft consistency. If a hematometer has formed in a teenage girl, then it becomes necessary to differentiate it from a normal uterine pregnancy. For this purpose, an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs is prescribed, a pregnancy test is performed. With a hematometer, ultrasound is used to detect the presence of fluid content in the uterine cavity, large blood clots. This method allows you to identify possible uterine pathological formations, for example, a myomatous node or polyp.
To confirm the diagnosis, the uterine cavity is probed through the cervical canal. With a hematometer, the introduction of the probe into the uterine cavity is accompanied by the release of blood.

If a woman suspects a hematometer, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed
In cases difficult to diagnose, hysteroscopy is indicated. This method of endoscopic diagnostics allows not only to reliably establish the presence of hematomas, but also to find out the cause of its occurrence, as well as to carry out the necessary therapeutic measures during the same procedure.

If conservative treatment does not lead to complete emptying of the uterus, vacuum aspiration of its contents is indicated
If you suspect a secondary infection and an inflammatory process, it is necessary to perform a bacteriological examination of the uterine discharge. This allows you to identify the causative agent of the infection and determine its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs (antibioticogram).
Treatment of hematomas
The main objectives of the treatment of hematomas are:
- evacuation of blood from the uterine cavity;
- elimination of the cause that caused the development of this pathological condition;
- ensuring a free outflow of contents from the uterine cavity.
In cases where the formation of hematomas is associated with blockage of the cervical canal by pieces of the placenta, blood clots or the remnants of the ovum, the emptying of the uterine cavity occurs already at the stage of diagnostic probing.
With atony of the uterus, drug stimulation of its contractility is necessary. For this purpose, uterotonics are prescribed (methylergometrine, ergot alkaloids, oxytocin). If the outflow of blood from the uterine cavity is difficult as a result of severe cervical spasm, the appointment of antispasmodics is indicated.
For the prevention of inflammatory complications, as well as for the purpose of pain relief, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketonal, Nimesulide, etc.) are used.
In those cases when the listed activities do not lead to complete emptying of the uterus, there are indications for vacuum aspiration of uterine contents.
In the presence of anatomical formations (polyps, septa, myomatous nodes) that prevent the outflow of blood from the uterine cavity, they are removed by the endoscopic method.
With the development of complicated hematometers, there may be indications for the removal of the uterus (supravaginal amputation of the uterus, extirpation of the uterus).
Prevention
Prevention of hematomas consists in the regular observation of a woman by a gynecologist. For the first time, a girl should be examined by a specialist even before the onset of puberty - this allows a timely diagnosis of possible anomalies in the development of the genital tract. If a girl does not start menstruating before the age of 16, an in-depth gynecological examination is necessary.
Other methods of preventing hematomas are:
- planning pregnancy;
- use of modern methods of contraception to avoid induced abortion;
- rational management of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period;
- early attachment of the baby to the breast and breastfeeding (this promotes the production of oxytocin, which stimulates the contraction of the uterus in the postpartum period);
- control over the timely emptying of the bladder in the postpartum period.
Consequences and complications
If the treatment of a hematometer is untimely started, it can lead to the development of serious complications:
- endometritis;
- pelvioperitonitis;
- peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- infectious toxic shock;
- secondary infertility.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!