- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Vasculitis
Brief description of the disease

Vasculitis is inflammation of the walls of blood vessels. Depending on which vessels are affected, the following types of vasculitis are distinguished:
- Phlebitis is caused by inflammation of the walls of the venous vessels.
- Arteriolitis is an inflammation of small arteries.
- Arteritis - damage to the walls of the arteries.
- Capillary - inflammation of the capillaries.
There are cases when several vessels are affected at once, this is called systemic vasculitis.
Separately, hemorrhagic vasculitis is isolated, affecting the vessels of the skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, joints.
Causes of the disease
Vasculitis can be primary, developing as an independent disease and it can occur as a complication of certain diseases.
The causes of primary vasculitis have not yet been established, and secondary vasculitis can manifest itself against the background of chronic, acute infections, vaccinations, oncological diseases, severe overheating or cooling, thermal skin lesions, incl. sunburn. Vasculitis can develop after trauma or exposure to biological poisons, chemicals.
All these negative factors can lead to the fact that the structure of vascular tissues changes, and the body begins to reject it, perceiving it as foreign, and produce antibodies.
Vasculitis symptoms
Symptoms of vasculitis at the onset of the disease are mostly similar: fever, "jumping" temperature - it rises and falls, and each rise in temperature means that a new inflammation has opened.
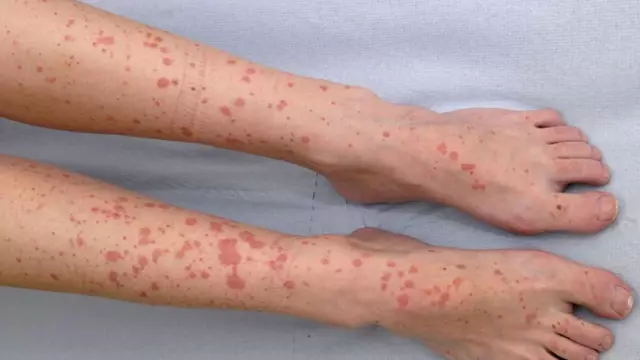
A characteristic symptom of vasculitis is cutaneous hemorrhage. After the skin, the lesion goes to the muscles, joints, nerves, which is why, with the further development of the disease, the symptoms of vasculitis differ depending on which organ's vessels are inflamed.
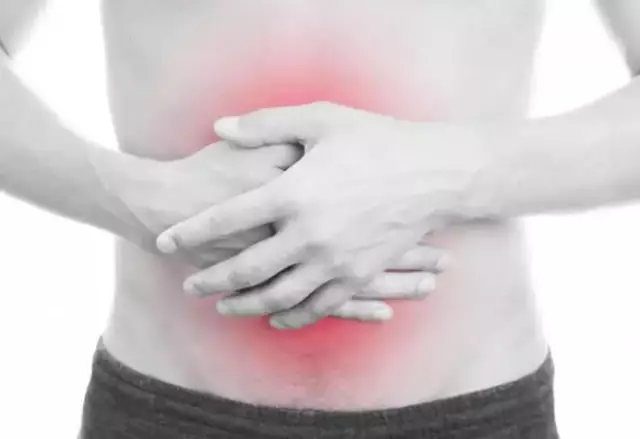
With nodular periarteritis, the patient feels pain in the muscles, sharp pains in the abdomen, he has nausea, vomiting, and fever.
With temporal giant cell arteritis, weakness, throbbing headaches are felt, there is swelling in the temporal region.
With aortoarteritis, the limbs become numb and sore, the back, stomach ache, vision is impaired, the patient faints.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis begins with skin rashes in the form of symmetrical small bruises. The rash forms on the buttocks, around the joints, on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs. Less commonly, you can see a rash on the face, feet and palms, trunk. On these grounds, the primary diagnosis of vasculitis in children is made.
The second characteristic symptom of hemorrhagic vasculitis - joint damage, accompanied by pain and / or inflammation, is observed in more than half of the patients. Usually large joints suffer, their permanent damage with impaired functionality is often not observed.
The third important symptom of hemorrhagic vasculitis is abdominal pain. It develops both to lesions of the skin and joints, and during. The pain attacks can last for several days. There are also complaints of nausea, bad stool, vomiting, fever, in rare cases, stomach and intestinal bleeding opens.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose systemic vasculitis, it is necessary to conduct a blood test, urine test, x-ray of the sternum, and examine the vessels.

To determine hemorrhagic vasculitis, urine and blood tests, sternum x-rays are also done. In addition, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound of the peritoneum, if signs of kidney damage appear, then an ultrasound of the kidneys. For the diagnosis of vasculitis in children, dynamic nephroscintigraphy may additionally be prescribed, because there may be an abnormality in the development of the urinary system, accumulative and excretory renal function.
At the stage of diagnosis, it is important to distinguish systemic vasculitis from infections accompanied by similar rashes, and to exclude thrombocytopenic purpura.
Abdominal pain can also occur with acute appendicitis, perforated ulcer, intestinal obstruction, ulcerative colitis - all these diseases should be excluded before starting treatment for vasculitis. Glomerulonephritis and lupus erythematosus are also excluded.
Vasculitis treatment
For the treatment of vasculitis, drugs are prescribed that suppress the production of antibodies, which reduce the sensitivity of tissues: cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids.
Also, for some forms of hemorrhagic or systemic vasculitis, blood purification procedures - hemosorption and plasmapheresis can be prescribed.
If the disease is mild, in remission, the treatment of vasculitis consists only in the appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Voltaren or indomethacin.
Additionally, in the treatment of vasculitis, agents that reduce vascular permeability and blood clotting may be prescribed to prevent thrombus formation.
Disease prevention
To prevent vasculitis in children and adults, it is necessary to avoid self-medication and unreasonable vaccination, to temper, to take measures to eliminate the negative effects of external factors, for example, to prevent overheating, hypothermia, prolonged exposure to the sun, to avoid direct contact with pesticides, etc.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!