- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Retinal dystrophy
General characteristics of the disease

Retinal dystrophy is one of the main causes of poor vision in the elderly. The disease is an irreversible destruction of retinal tissue and a gradual suppression of the function of the organs of vision.
The reasons causing retinal dystrophy are quite different. First of all, it is age-related accumulation of metabolic decay products in tissues. An important role in the nutritional deficiency of the retinal visual cells is also played by circulatory disorders, intoxication, and infections.
Myopia is also a predisposing factor for the development of retinal dystrophy. It leads to increased pressure on the ocular membranes caused by the increased transverse size of the organs of vision of a myopic person.
Other factors triggering the mechanism of development of retinal dystrophy are presumably diabetes mellitus, smoking, excess weight, high blood pressure. Retinal dystrophy can also develop at a fairly young age against the background of pregnancy, cardiovascular diseases, thyroid pathologies, and also as a result of injuries.
Retinal dystrophy symptoms
An early symptom of retinal dystrophy is a gradual decrease in near vision clarity. The disease progresses slowly and over time leads to the perception of distorted images. Patients with symptoms of retinal dystrophy often complain of double vision of visually perceived objects, broken lines, the presence of blind spots in vision. However, complete blindness as a result of retinal degeneration develops quite rarely.
Types of retinal dystrophy
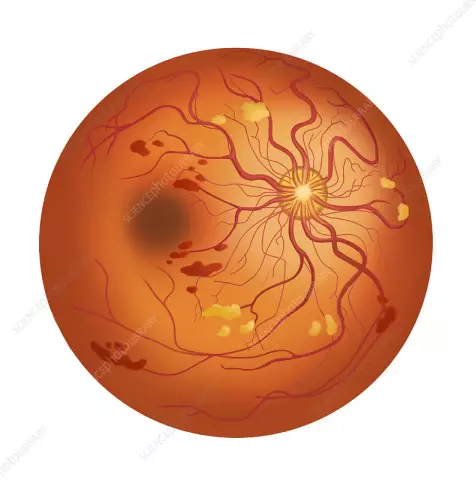
Chorioretinal dystrophy of the retina, or age-related macular degeneration of the retina, is characteristic of people over 50 years of age. The disease can lead to a complete loss of central vision. In this case, the peripheral vision of a patient with chorioretinal dystrophy of the retina remains within the normal range.
Clarity of perception of objects is impossible without central vision. People with this type of retinal dystrophy are unable to read or drive. The rate of progression of the disease depends on the type and severity of retinal chorioretinal dystrophy.
The wet form of the disease is considered the most severe, fast-flowing and difficult to treat. However, most often (in 9 out of 10 cases) there is a dry form of chorioretinal dystrophy of the retina. With it, the process of gradual destruction of cells in the central part of the retina (macula) takes several years.
With another type of retinal dystrophy, peripheral retinal dystrophy, changes affect the peripheral fundus. The danger of this disease is that the early stage of development of peripheral retinal dystrophy is almost asymptomatic. The first dystrophic changes can be diagnosed only with the help of special ophthalmic equipment.
However, it is very important to diagnose these changes at an early stage of peripheral retinal dystrophy. Only in this case it is possible to effectively prevent a serious complication of the disease - retinal detachment or rupture. Such pathologies, in contrast to their root cause, are rather difficult to treat.
Retinal pigmentosa is the rarest anomaly caused by hereditary factors. It is caused by disturbances in the work of the retinal photoreceptors, which are responsible for either twilight black-and-white or daytime color vision.
Retinal pigmentosa can be passed from mother to child in an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. Most often, men suffer from retinal pigmentary dystrophy. The clinical picture of the disease and the mechanism of development are deeply individual.
With mild retinal pigmentary dystrophy, there is only a slight decrease in visual acuity in a poorly lit space. In severe cases of retinal pigmentary dystrophy, complete fading of visual function is possible.
Diagnostics of the retinal dystrophy
The most informative methods for diagnosing retinal dystrophy are laser scanning of the retina using an optical tomograph, central computer perimetry, and fluorescence angiography of the fundus blood vessels. They allow you to identify the earliest symptoms of retinal degeneration.
Additionally, at an early stage in the diagnosis of the disease, tests can also be used to check color perception, contrast of vision, the size of the central and peripheral visual fields.
Retinal dystrophy treatment

In the treatment of retinal dystrophy of the chorioretinal form, methods of photodynamic therapy, laser photocoagulation, and injections of Anti-VEGF drugs are used. The latter are a special protein capable of stopping degenerative processes in the macula of the eye.
Photodynamic treatment of retinal dystrophy involves the intravenous administration of photosensitizing substances. They are able to bind proteins of pathological vessels and stop the development of dystrophy. The mode of photodynamic treatment of retinal dystrophy is set individually, depending on the patient's sensitivity to this type of therapy.
The basis of laser treatment of retinal dystrophy is the technique of cauterization of pathological vessels. At the site of the burn, a scar forms on the tissues of the macula of the eye, and vision in this area of the eye is not restored. But this technique allows you to prevent the further spread of the process of retinal dystrophy.
In the treatment of retinal pigmentary dystrophy, physiotherapeutic techniques are mainly used: magnetic and electrical stimulation of the eye tissues. Unfortunately, their effectiveness is not high. Vasoreconstructive operations aimed at improving the blood supply to the retina also have a limited effect.
Prevention of retinal detachment in peripheral retinal dystrophy is carried out using laser coagulation. This minimally invasive, non-invasive method of retinal dystrophy treatment avoids surgical opening of the eyeball. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and requires virtually no recovery period.
As an auxiliary treatment for retinal dystrophy of all types, dietary and vitamin therapy is used.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!