- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Balanitis

Balanitis is an inflammation of the glans penis. This is the most common inflammatory disease of the male reproductive system, which occurs at any age, including cases of balanitis in children.
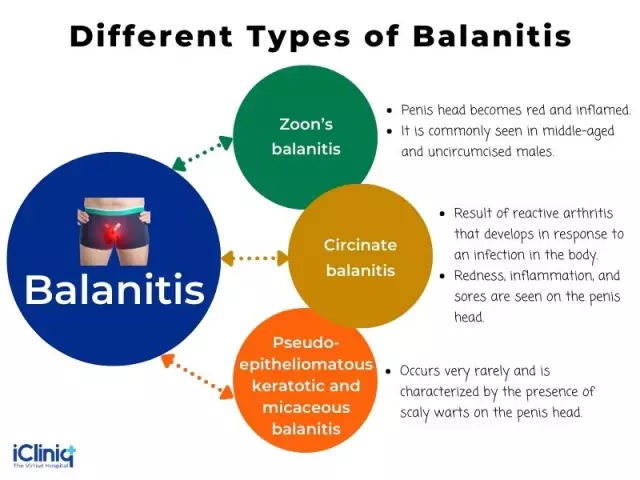
Types of balanitis
Balanitis by origin is primary and secondary, by the nature of the course, acute and chronic. By clinical manifestation, the following forms of balanitis are distinguished:
- Simple or irritative;
- Erosive;
- Ulcerative;
- Chronic hypertrophic;
- Obliterating balanitis.
Balanitis reasons
The main reason for balanitis is non-observance of the rules of personal hygiene, when favorable conditions are created for an infection that gets on the genitals. A decrease in local and sometimes general immunity is also important. Simple balanitis, if untreated, can turn into erosive, ulcerative and chronic. Obliterating balanitis, as a rule, occurs as an independent disease of the primary chronic course, and the reasons for its occurrence are still not clear.
Secondary balanitis is just one of the symptoms, which manifests itself as a general disease of the body, autoimmune, endocrinological or infectious. There are frequent cases of balanitis in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus, balanitis is also found, which is a consequence of autoimmune processes - scleroderma, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. Of the infectious diseases, balanitis is most often provoked by pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, genital herpes, and also fungi of the genus Candida. Most often it is Candida albicans, the same yeast infection that causes thrush in women, it is also the cause of candidal balanitis in men.
Balanitis in children is usually caused by a narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis), due to which smegma and urine residues accumulate in the preputial sac, which serve as an irritating factor. When an infection is attached, the head of the penis becomes inflamed (balanitis), but in this case it becomes inflamed together with the inner layer of the foreskin, and balanoposthitis develops.
Balanitis symptoms
The first symptoms of balanitis are discomfort in the area of the glans penis: burning, itching, especially when trying to open the glans. Redness and swelling of the head becomes visible. In the case of an acute illness, a general deterioration of the condition is added to the usual symptoms of balanitis: the body temperature rises, a headache appears, and the general tone decreases. The symptoms of balanitis include increased formation of smegma, sometimes its amount is so significant that it permeates underwear; as well as purulent discharge from the preputial sac.
Symptoms of balanitis in erosive and ulcerative form are, respectively, erosion and ulcers, the erosive form, if untreated, turns into ulcerative. Erosive and ulcerative balanitis is accompanied by pain in the region of the glans penis, which increases with movement.
Candidal balanitis is characterized by a strong itching sensation, the appearance of erosions on the glans penis, covered with a whitish coating, when removed, the hyperemic surface is exposed. A liquid exudate is released from the preputial sac; white curdled flakes can accumulate in the area of the coronal groove.
Obliterating balanitis manifests itself as the appearance of areas of scarring on the scalp. The areas are pale, with atrophied skin, their appearance is accompanied by a feeling of tightness. In the stage of the developed disease with balanitis obliterans, a narrowing (stricture) of the urethra may occur, resulting in urinary disorders.
The first sign of balanitis in children, especially in small children, is the child's restless behavior. The kid is naughty, he may have a fever, reacts violently when trying to bare the head of the penis. The inflamed tissue of the head is painful when urine enters it, so urination may be accompanied by crying.
Diagnostics of the balanitis
The diagnosis is usually not in doubt, and the symptoms of balanitis, revealed during examination of the external genital organs, are sufficient for its statement. Research is needed only to determine the causative agent of the disease, which is important in the treatment of balanitis. For this purpose, a bacteriological examination of a smear from the urethra is carried out. In the case of persistent balanitis that does not respond to conventional therapy, a detailed diagnosis is performed: PCR, blood sugar test, examination for the presence of STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
Balanitis treatment

Treatment of balanitis, not complicated by purulent inflammation, is usually limited to the use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Thorough hygiene of the penis is recommended, for which it is necessary to expose the head, rinse it thoroughly with warm water and soap containing a minimum amount of fragrance, then gently pat it dry with a soft towel. Such procedures must be carried out every 3-4 hours. Local treatment of balanitis is supplemented by washing the glans penis with antiseptic solutions: a weak solution of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, decoctions of medicinal herbs with antiseptic action (sage, chamomile, eucalyptus).
Treatment of balanitis in an erosive form, in addition to the above-described means, is carried out with the use of anti-inflammatory ointments, which are applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day after hygiene procedures.
If the disease is complicated by lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), or has developed into an ulcerative-necrotic, gangrenous form, local treatment of balanitis is carried out in combination with taking broad-spectrum antibiotics, a course of 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the process.
With candidal balanitis, an ointment containing an antibiotic of antifungal action is applied to the naked head, and a diet with a reduced amount of easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, sweet carbonated water, juices) is recommended.
Balanitis obliterans is treated depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, a fairly long course of application of ointments containing anti-inflammatory hormonal agents. At the stage of the appearance of urethral narrowing, balanitis is surgically treated, eliminating the narrowing and removing areas of the skin that have undergone cicatricial changes.
Treatment of balanitis in children is carried out locally, washing the head of the penis with antiseptic solutions. For this purpose, babies can be put in a bath with a decoction of medicinal herbs several times a day, having previously at least slightly exposed their head.
If it is established that one of the causes of inflammation of the glans penis was the existing phimosis, surgical treatment of balanitis and phimosis is performed, performing circumcisio - an operation of excision of the foreskin, or, as it is also called, circumcision.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!