- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
General sputum analysis: types, how to pass, indicators, norm and decoding
The content of the article:
- How to donate phlegm
- What is a general sputum test
- Other types of sputum examination
Sputum analysis plays an important role in the diagnosis of destructive and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. Sputum is a secretion of the mucous membrane of the bronchi and pulmonary alveoli, which is released when coughing. In healthy people, it is normally not separated, with the exception of smokers, lecturers, singers.
The composition of the sputum is heterogeneous, it includes different elements (mucus, fibrin threads, blood, pus), and the presence of all of them at the same time is not necessary. The properties of sputum are largely determined by the nature of the pathological process occurring in the lungs or bronchi, therefore, the study is necessary to identify the causative agent of inflammation.
How to donate phlegm
To obtain a reliable test result, it is necessary to correctly collect sputum and store it before delivery to the laboratory. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- biological material is collected in a sterile disposable container, which should be obtained in advance from the laboratory or purchased from the pharmacy;
- collection is carried out in the morning before breakfast;
- before collecting sputum, the oral cavity must be rinsed well with warm boiled water; teeth cannot be cleaned;
- when spitting sputum into a container, you should not touch your lips to its edges (it is especially important to observe this rule during bacteriological research);
- the collected material should be delivered to the laboratory within 1-2 hours.
In an adult, the process of collecting sputum is not difficult. It is much more difficult to collect material from children in their first years of life. To do this, they irritate the nerve endings located in the region of the tongue root with a sterile cotton swab. When coughing jerks appear, an open Petri dish is quickly brought to the child's mouth, where pieces of sputum flying out of the baby's mouth fall.
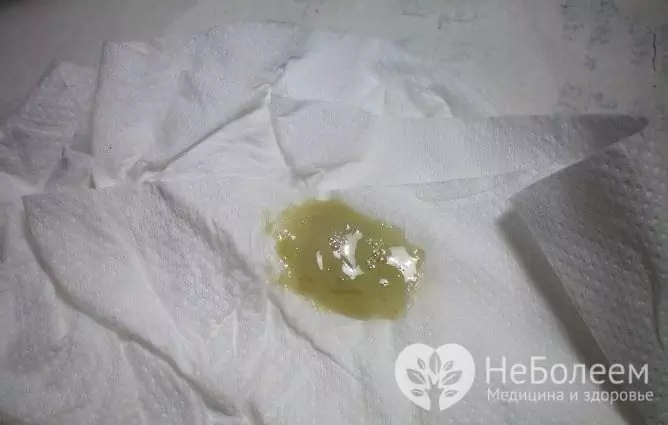
Sputum analysis is used to diagnose diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
If a patient has a cough with sputum that is difficult to separate, it is recommended to drink several glasses of warm alkaline mineral water, for example, Borjomi, to liquefy it the evening before the study. Soda-salt inhalations also have a good mucolytic effect. If there is no nebulizer at home, then boil water in a saucepan and add 150 g of salt and 10 g of soda (per 1 liter) to it, and then breathe steam over it for 5-7 minutes. You can provoke an increase in coughing, and, thereby, sputum discharge, by taking several deep, slow breaths.
What is a general sputum test
Most often in clinical practice, clinical (general) analysis of sputum is carried out, which includes the study of its physical properties, microscopy and bacterioscopy.
Physical properties of sputum:
- Number. The volume of sputum separated can range from 2-3 ml to 1-1.5 liters per day, depending on the nature of the inflammatory process. With pneumonia, acute bronchitis, the amount of sputum is insignificant. Pulmonary edema, gangrene and lung abscess are accompanied by abundant secretion. Also, a large volume of sputum can be secreted with lung cancer or tuberculosis in the decay stage.
- Colour. The sputum is white or colorless, has a slimy character and is observed in patients with ARVI, bronchitis. Green sputum is secreted in patients with purulent processes in the lungs (gangrene, abscess), and yellow in eosinophilic pneumonia. Brown or rusty phlegm is characteristic of croupous pneumonia.
- Smell. Normally, freshly excreted sputum has no smell. With lung cancer, putrid bronchitis, bronchiectasis, abscess or gangrene of the lung, it acquires a cadaverous (putrid) smell.
- Layering. Purulent sputum when standing is divided into two layers, and putrid - into three.
- Impurities. Depending on the characteristics of the pathological process, sputum may contain various impurities. For example, sputum with blood (hemoptysis) is characteristic of lung cancer in the decay stage. The cause of finding pieces of food in the sputum can be esophageal cancer.
In the microscopic picture of sputum, there may be:
- squamous epithelium - more than 25 cells in the field of view indicates that the material is contaminated with saliva;
- cylindrical ciliated epithelium - found in sputum in bronchial asthma;
- alveolar macrophages - characteristic for the stage of resolution of acute bronchopulmonary diseases or for chronic processes;
- leukocytes - in significant quantities are found in sputum during purulent and putrefactive processes in the lungs;
- eosinophils - observed in pulmonary infarction, eosinophilic pneumonia, bronchial asthma;
- elastic fibers - a sign of the decay of lung tissue (echinococcosis, tuberculosis);
- coral fibers - typical for chronic diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, for example, for cavernous tuberculosis;
- Kurshman spirals - are observed in patients with bronchial asthma, lung tumors;
- Charcot-Leiden crystals - are a decay product of eosinophils and are detected in sputum with eosinophilic pneumonia, bronchial asthma.
For laboratory staff, special atlases on clinical research methods have been created, in which photos of different types of elements present in sputum are presented.
The detection of bacterial flora in a significant amount during bacterioscopy suggests the bacterial nature of the inflammatory process, and the fungal mycelium is fungal. Bacterioscopic examination of sputum for tuberculosis is based on the detection of Koch's bacilli in it. If tuberculosis is suspected, the direction indicates "sputum for CD" or "sputum for BK".
Deciphering the analysis of sputum is rather difficult, since the same indicator can serve as a sign of different diseases of the respiratory system. Therefore, only a specialist should decipher the results, taking into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease (without fever or with fever, the presence of shortness of breath, signs of intoxication, coughing, auscultatory data, X-ray picture).
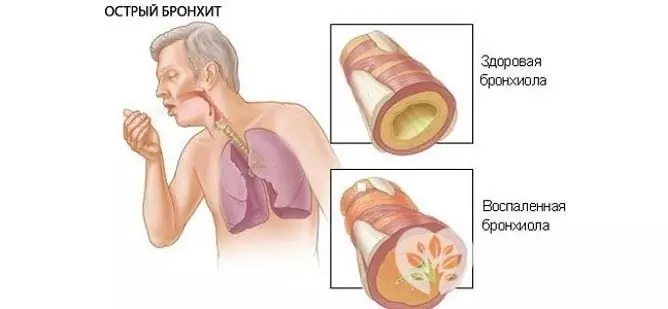
In acute bronchitis, a small amount of sputum is secreted
Other types of sputum examination
Most often in clinical practice, a general sputum test is prescribed. But if there is evidence, other studies are carried out:
- Chemical analysis. It has no special diagnostic value and is usually carried out only for the purpose of detecting hemosiderin in sputum.
- Cytological analysis. It is prescribed for suspected lung malignant neoplasms. The detection of atypical cells in the sputum confirms the diagnosis, but their absence does not allow the exclusion of a cancerous tumor.
- Bacteriological research. Aimed at identifying the causative agent of the infectious and inflammatory process. In addition, sputum culture allows you to determine the sensitivity of the identified pathogen to antibiotics, and this, in turn, gives the doctor the opportunity to choose the right treatment.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.






