- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Upper eyelid edema: causes and remedies
The content of the article:
-
Why do the upper eyelids swell
- Angioedema
- Kidney disease
- Barley
- Blepharitis
- Periorbital cellulite
- Purulent conjunctivitis
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Diet errors
- Sleep disturbance
- Reactions to cosmetics
-
What to do with edema
- Etiotropic treatment
- Folk recipes
- Video
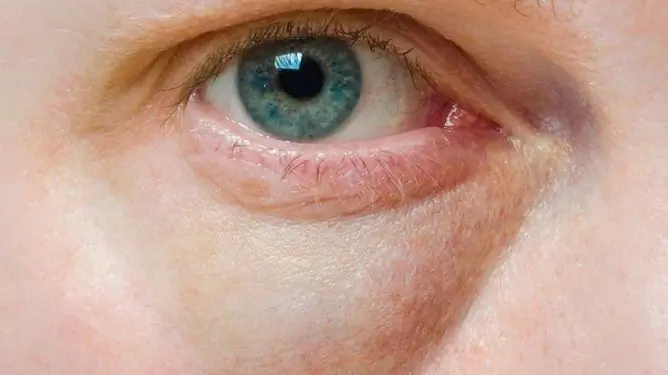
Swelling of the upper eyelid can occur for a variety of reasons. The most harmless of them are excess salt intake, improper head position during sleep, lack of sleep, and alcohol consumption. But persistently swollen eyelids can be a symptom of serious eye, kidney, or heart disease. Loose tissue of the eyelids contributes to the rapid onset and spread of edema, therefore, the treatment of pathology cannot be postponed.

Puffiness of the upper eyelids can be caused by various reasons, some require medical attention.
Why do the upper eyelids swell
Puffy upper eyelids are not only a cosmetic defect, but often a medical problem. Edema is the accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, which can occur for various reasons, both local and general.
| Causes of eyelid edema | Explanation | Diseases |
| Inflammatory | Puffiness is one of the signs of inflammation. Often, inflammatory eye diseases lead to swelling of the upper eyelid. The cause is most often an infection (bacterial or viral). | Barley, blepharitis, abscess, acute conjunctivitis, preseptal cellulite |
| Allergic | One type of allergic reaction is angioedema. Saliva or insect venom (with a bite), cosmetics, pollen, medications can act as allergens. | Angioedema, allergic conjunctivitis |
| Diseases of the internal organs | Diseases of different organs and systems are manifested by different types of edema, including edema of the eyelids. | Kidney disease (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrotic syndrome), thyroid pathology, hormonal disorders, heart disease. |
| Others |
Puffiness is caused not only by various diseases, but also by less dangerous causes - disturbed sleep patterns, improper diet, excessive consumption of water and salt, and the use of low-quality cosmetics. |
|
Angioedema
Puffiness of the upper eyelid often occurs due to allergies, for example, with Quincke's edema. This is a dangerous condition characterized by widespread swelling in various areas, including the eyelids.
Contact with any allergen can be the reason.
- insect bite (especially bees and wasps);
- taking medications;
- Food;
- pollen of plants.
The danger of pathology lies in the fact that edema can spread to the airways and lead to their obstruction.
Kidney disease
Swelling of the eyelids may indicate a disease of the internal organs, such as kidney disease. Renal edema has some features:
- arise in the morning;
- decrease in the evening;
- symmetrical;
- localized mainly on the face.
Various kidney diseases can lead to fluid retention, but most often - glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. Fluid retention in renal disease is associated with increased protein secretion. Hypoproteinemia (deficiency of proteins in plasma) leads to a decrease in oncotic blood pressure, which provokes edema.
Barley
Barley is a fairly common occurrence. Barley develops due to infection of the hair follicle of the eyelash or sebaceous gland.
Different microorganisms can cause infection:
- gram-positive bacteria - streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus (in 90% of cases);
- demodex mite;
- fungi.
Failure to observe the rules of personal hygiene - the habit of rubbing the eyes with your hands, wiping your face with a dirty towel, washing your hands without soap - contributes to the ingress of infection into the hair sac.
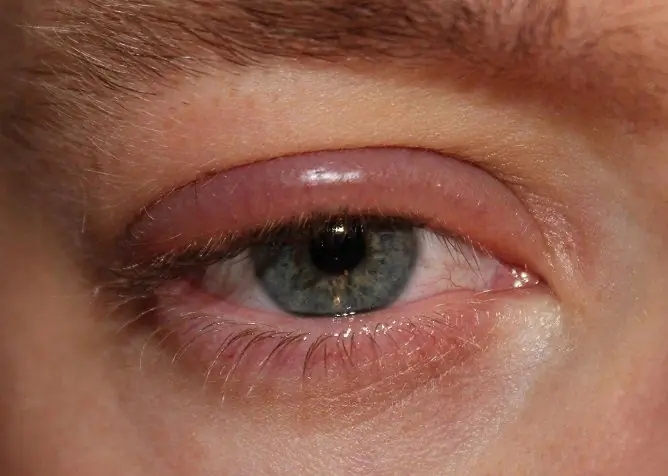
Barley is often one-sided, both the upper and lower eyelids can be affected. The following symptoms are characteristic of barley: swelling, redness and soreness of the eyelid skin. After a few days, a yellowish head appears at the top of the swelling (as seen in the photo).

Barley is a common cause of upper eyelid swelling
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelid. The main cause of blepharitis is a bacterial infection (staphylococcus, streptococcus). Less commonly, inflammation develops due to viruses, allergies, and constant eye irritation with dust and smoke.
Puffiness is just one of the symptoms of blepharitis. Other signs are also characteristic:
- local soreness;
- pronounced redness;
- scales at the base of the eyelashes.
With blepharitis, the entire eyelid or some of its parts can be affected (inflammation of the ciliary edge, in the thickness of the eyelid, in the corner).
Periorbital cellulite
Periorbital cellulitis is an inflammation of the tissues in front of the connective tissue membrane. The disease occurs for various reasons:
- damage to the skin around the eyes and infection;
- insect bite in the eyelid area;
- spread of infection from the sinuses;
- spread of infection from the oral cavity.
The disease is characterized by diffuse edema, soreness, redness of the skin, and a local increase in temperature.
With periorbital cellulitis, there are no signs of damage to the eyeball - exophthalmos, limitation of mobility, visual impairment. This is the main difference from orbital cellulite, in which the orbit is directly involved in the inflammation.
Purulent conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the lining of the eyes. Suppurative inflammation can lead to swelling of the upper eyelid. At the same time, there are other signs:
- hyperemia of the conjunctiva;
- purulent discharge from the eyes;
- burning in the eye, foreign body sensation.
Swelling of the eyelid is not the main symptom of purulent conjunctivitis. Puffiness occurs a second time, due to irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyelid.
The cause of purulent conjunctivitis is bacteria, often - Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci, mycoplasmas. The habit of not washing your hands, rubbing your eyes contributes to the spread of infection.
Premenstrual syndrome
If a woman's eyelid swelling occurs cyclically, it may be one of the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Hormonal disorders provoke the development of symptoms - an excess of estrogen and a lack of progesterone.
The edematous form of PMS is characterized by fluid retention, which is manifested by edema of different localization, including edema of the eyelids. The main feature of PMS puffiness is that the symptom disappears with the onset of menstruation.
Diet errors
Excessive salt intake can provoke swelling of the eyelids. Salt retains fluid in the body, which is what causes edema.
Eating the following foods can lead to swelling:
- salt;
- alcoholic drinks;
- pickles and marinades;
- smoked meats;
- milk products;
- nuts.
Sleep disturbance
A common cause of swelling of the eyelids is the incorrect position of the head during sleep. In addition, lack of sleep or, conversely, excessive sleep may be the cause.
Reactions to cosmetics
Swelling of the eyelids can occur if you use low-quality or unsuitable cosmetics - mascara, eyeliner or eyeliner, eye shadow. These agents can directly contact the mucous membrane, cause irritation, and then swelling. If the cream gets into the eyes, it can also irritate the mucous membranes.
In addition, an allergy to a new cosmetic product may be the cause. This is manifested by swelling, redness, lacrimation, and increased sensitivity to light.
What to do with edema
Edema can also be treated at home. Medications are used in the form of eye drops, ointments and tablets. Additionally, you can use folk recipes - various compresses, lotions, rinsing. The choice of a specific treatment method depends primarily on the cause of the edema. If the symptoms do not go away within 2-3 days, the condition worsens or a visual impairment appears, you need to consult a doctor and follow his recommendations.

In the treatment of eyelid puffiness, an ointment may be required
Etiotropic treatment
The main treatment depends on the cause of the edema. In each case, the approach to treatment is different.
| Disease | Do you need to see a doctor | How to treat |
| Barley | Yes |
In most cases, the treatment is local: Treatment of the focus with antiseptic solutions - ethyl alcohol, iodine solution. Instillation into the conjunctival cavity of drops, for example, Sulfacyl sodium. Laying eye ointments that have antibacterial effects. For example, Levomycetinovaya, Tetracycline ointment. |
| Purulent conjunctivitis | Yes |
Local treatment is indicated: Rinsing the eyes with saline. Instillation of drops that contain antibiotics (Sulfacyl sodium). Laying ointments (Levomycetinova, Tetracycline). |
| Blepharitis | Yes |
To treat the disease, antibacterial agents are used: Erythromycin, Gentamicin, Chloramphenicol. Additionally, local remedies can be used - compresses, drops, ointments. |
| Periorbital cellulite | Yes | Antibiotics from the macrolide or penicillin group are used. For example, Erythromycin, Amoxiclav. Local treatment is not indicated. |
| Angioedema | Yes, immediately |
First of all, you need to stop contact with the allergen (pull out the sting, stop taking medications). A cold compress can be applied to the swollen area. Medications are prescribed: • Antihistamines. Reduces the effects of histamine, which causes edema. These include Loratadin, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine. It is enough to take 1 tablet. • Glucocorticoids. Prescribed as injections - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone. • Adrenaline. It is used in severe cases for vasoconstriction. It is injected subcutaneously. |
| Kidney disease | Yes |
Treatment depends on the specific disease: • For pyelonephritis, antibacterial agents such as Ciprofloxacin are prescribed. • For infectious glomerulonephritis, antibiotics are also prescribed, but from a different group - penicillins and macrolides. • For autoimmune glomerulonephritis, steroids are indicated (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone). Diuretics may be used for symptomatic treatment. |
Folk recipes
Additionally, you can use folk remedies. They will not eliminate the cause, but will help reduce symptoms.
- Contrasting face wash.
- Rubbing the skin with ice.
- Lotions from black and green tea.
- Compresses from decoctions of parsley, sage, chamomile, calendula.
- Raw cucumber or potato mask.
Folk remedies are not a substitute for complete treatment. They can only be used in combination with other methods.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.