- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Diuretics for facial swelling
The content of the article:
-
Diuretics for facial swelling
- Loop diuretics
- Thiazide diuretics
- Potassium-sparing diuretics
- Features of the use of diuretic drugs
- Folk remedies
- Puffiness of the face with various pathologies
- Causes and risk factors
- Video
Diuretics for facial edema are essential medicines. Pharmacies offer a wide selection of diuretics, however, before starting therapy, you should find out the reason for the development of this condition, since swelling can be caused by both physiological and pathological reasons, and the latter are quite serious. For example, swelling of the face in the morning after sleep may indicate that a person had a late dinner, drank a large amount of liquid at night, drank alcohol the day before - in this case, there is no particular danger. But also this symptom may indicate decompensation of cardiac pathology or impaired renal function, in such situations, just eliminating edema cannot be done.
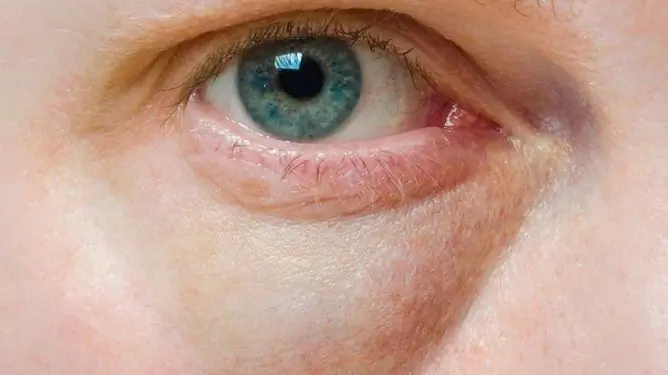
Puffy bags under the eyes can be caused by kidney disease
Diuretic tablets for facial edema are not indicated in all cases. So, with allergies, antihistamines are prescribed, with edema of traumatic origin, a cold compress will be useful, with inflammation, remediation of the focus and anti-inflammatory therapy are required, etc. Therefore, first you need to determine why a person's face swells, and only then select a treatment.
Diuretics for facial swelling
Diuretic drugs are divided into several groups, some of which can be used for swelling of facial tissues.
Loop diuretics
Drugs in this group promote the elimination of water and sodium from the body, cause a decrease in the concentration of magnesium and potassium in the blood. Loop diuretics usually last about 6 hours and are usually given in short courses.
Such drugs are most often used for edema that develops against the background of pathologies of the cardiovascular system (especially with heart failure) and kidney pathologies.
The active substance of loop diuretics can be:
- furosemide;
- bumetanide;
- torasemide.
Furosemide is a loop diuretic
Thiazide diuretics
The action of thiazide diuretic drugs is aimed at reducing sodium absorption by the kidneys and at excreting it in the urine. Thiazide diuretics are less effective than loop diuretics, but they can be used for a longer time. These drugs are often prescribed for long courses (3 months or more).
This group includes products, the active ingredients of which are:
- chlorthalidone;
- hydrochlorothiazide;
- cyclopentiazide.
A feature of thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics is the speed of the onset of the effect and its duration. The use of drugs from this group leads to a decrease in the level of blood pressure, so they are prescribed mainly for hypertension, heart failure.

Hydrochlorothiazide - a thiazide diuretic
Potassium-sparing diuretics
Medicines of this group have a moderate diuretic effect, increase the release of sodium ions, but reduce the release of potassium. To achieve the desired therapeutic effect, the use of these drugs may not be enough, therefore they are often prescribed in conjunction with other drugs.
Potassium-sparing diuretics include aldosterone antagonists, which block aldosterone receptors, slow down the excretion of urea and potassium, and increase the excretion of water, sodium, and chlorine.
The active ingredients in potassium-sparing diuretics are:
- spironolactone;
- eplerenone;
- amiloride.
Spironolactone - a potassium-sparing diuretic
Features of the use of diuretic drugs
Diuretic drugs can help by temporarily relieving the swelling, but they do not affect the cause of its development. So, if swelling of the face has arisen against the background of any disease, some time after the use of a diuretic, they are more likely to appear again. Therefore, to eliminate the problem, it is necessary to carry out treatment aimed at the cause, while the therapy should be comprehensive, including drugs from other groups.
After prolonged use of diuretics, it is usually recommended to follow a heavy diet. It is recommended to include dairy products, baked potatoes, bananas, oranges in the diet.
Folk remedies
Sometimes medications made from natural ingredients that have a mild to moderate diuretic effect are helpful for facial swelling. However, you should use any methods of traditional medicine only after consulting your doctor.
For edema, herbal remedies are usually used in the form of decoctions and infusions. Medicinal plants with a diuretic effect include:
- lingonberry leaves;
- chamomile medicinal;
- bearberry;
- parsley and dill seeds;
- birch leaves and buds;
- juniper fruits;
- thyme;
- calendula;
- horsetail;
- bearberry;
- mother and stepmother;
- valerian;
- motherwort;
- oregano;
- Melissa;
- Linden;
- St. John's wort;
- mint;
- nettle;
- linen;
- barberry;
- shepherd's bag;
- chicory.
Ready-made diuretic preparations (kidney tea, etc.) to eliminate edema can be purchased at the pharmacy. You can also prepare herbal remedies at home. To eliminate facial puffiness, you can use the following recipes:
- Field horsetail infusion. 4 teaspoons of dry herbs are poured into 500 ml of boiling water, infused for 20 minutes and filtered. The finished infusion is taken 3 tablespoons 4 times a day.
- Infusion of shepherd's purse. 1 tablespoon of dry raw materials is poured with 1 glass of boiling water, infused for 10 minutes, filtered and consumed 3 times a day before meals.
- Infusion of parsley seeds. Parsley seeds (0.5 teaspoon) are poured with a glass of drinking water, infused for 7-9 hours and taken 2-3 tablespoons every 2 hours during the day.
- Celery green juice. Take 1 teaspoon of celery juice 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Puffiness of the face with various pathologies
The table shows the localization of puffiness on the face in some pathological conditions.
| Localization of edema | Pathological condition |
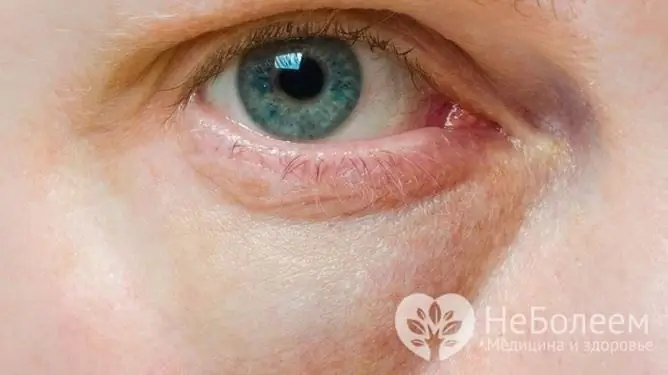
| Eye area, lower eyelid | Diseases of the urinary system |
| Mainly upper eyelid | Pathology of the cardiovascular system |
| Under the eyes, on the sides of the nose | Inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses |
| Cheek, gum | Dental diseases (normally it can occur for a short time after tooth extraction) |
In case of kidney disease, in addition to swelling, the skin of the patient's face can acquire an earthy tint. Usually, the face swells first, which is most noticeable in the morning, and then the legs and arms. By the evening, the swelling subsides.
In diseases of the cardiovascular system, in addition to edema of the face, shortness of breath and a high pulse may be observed. Swelling in this case usually first occurs on the legs, and then can spread to the rest of the body. Such edema, as a rule, worsens in the evening.
Causes and risk factors
The reasons for the development of edema are often diseases of the urinary and cardiovascular system. Also, the accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the face can be caused by injuries, sunburn, insect bites, allergic reactions, tooth extraction, inflammation in the paranasal sinuses.
Risk factors for developing puffiness include:
- endocrine diseases;
- period of pregnancy;
- insufficient night sleep and chronic fatigue;
- drinking a lot of liquid, salt, spicy and smoked foods (especially in the evening).
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.