- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Obturation

The human body consists of various organs, many of which are hollow anatomical formations, that is, they have internal cavities. These are, for example, bronchi, esophagus, intestines, vessels. Such a structure contributes to the occurrence of such a condition as obstruction, that is, partial or complete blockage of the lumen of the organ cavity. This can be due to a disease, or, on the contrary, be induced artificially for the purpose of treatment.
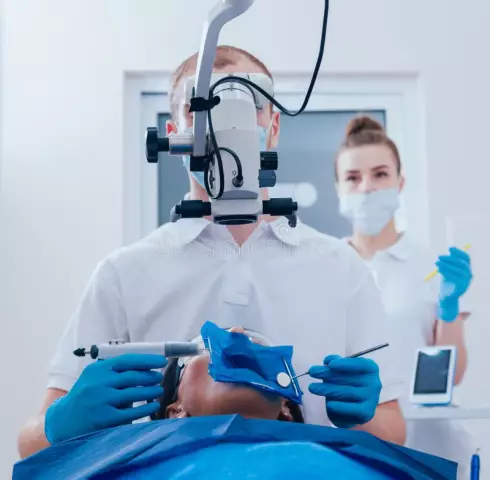
Root canal obturation
Artificial closure of the lumen of the cavity organ is typical for such a field of medicine as dentistry. It is carried out when filling teeth in the case of periodontitis or pulpitis treatment. Root canal obturation can be of two types: permanent and temporary. It is carried out with the help of special filling materials. In this case, the most rational is the use of gutta-percha, that is, latex processed in a certain way. As a rule, this material does not cause allergies, and its ability to expand when heated allows it to accurately fill the required cavity. Gutta-percha is used in combination with a paste-like substance - a sealer.
Temporary obturation of the canals is carried out in cases where the setting of a permanent filling is impossible due to the presence of a local inflammatory process. Percussion pain or swelling in the area of the tooth may indicate this. The obturation of the canals in this situation requires the use of plastic non-hardening materials; moreover, they must have certain medicinal properties. The time for which such materials are installed varies from several days to several months. After the symptoms of inflammation disappear, a permanent filling is established.
Obstruction of the urinary tract
Narrowing of the lumen of the urinary tract can occur at any age. In children, this is most often a congenital pathology. For adults, acquired defects of the excretory system are more characteristic. At the same time, obstruction of the urinary tract is not in itself a disease, it only indicates the manifestation of any disease in the body. Mechanical closure of the urinary tract is possible, for example, due to blockage by stones or a tumor. Functional disorders are also quite common. They result from inflammatory damage to the ureters or bladder and lead to narrowing of the ducts.
Regardless of the cause, obstruction of the excretory tract disrupts their function and leads to the development of renal failure, acute or chronic.

The main symptoms of narrowing of the channels are difficulty in the outflow of urine and pain of varying intensity, the strength of which depends on the speed of onset of obstruction. The most excruciating pain is caused by stones stuck in the ureter. In this case, renal colic occurs, requiring immediate medical attention.
If the obstruction of the urinary tract grows gradually, the pain may be less pronounced or completely absent. However, chronic impairment of the outflow of urine, as a rule, leads to irreversible changes in the kidneys. That is why it is necessary to eliminate as soon as possible not only the obstruction itself directly to normalize the elimination of toxins from the body, but also the cause of its occurrence.
The presence of cavity organs in the human body is, on the one hand, a kind of risk factor, as evidenced by the possibility of their obturation and, as a result, dysfunction. On the other hand, free internal space allows, if necessary, to compensate for the emerging pathological changes in the body.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!