- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Epidural anesthesia during childbirth - reviews, consequences

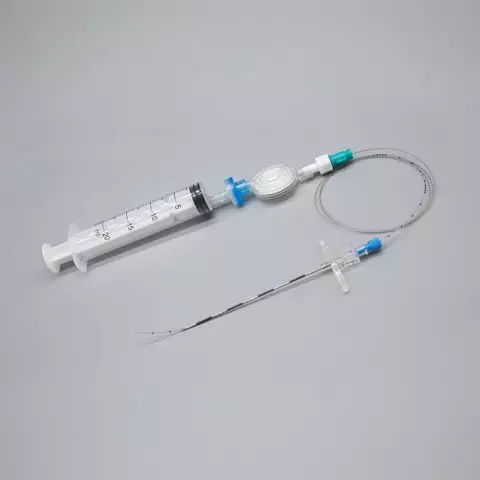
Epidural anesthesia during childbirth is one of the methods of regional anesthesia in which drugs are injected through a catheter into the epidural space of the spine. This injection results in analgesia (loss of pain sensitivity), anesthesia (general loss of sensation), relaxation or complete paralysis of the muscles.
The principle of action of epidural anesthesia is based on pain relief by blocking the transmission of nerve impulses along the ends of the spinal cord. As a result, the patient, depending on the task set by the doctors, ceases to feel any painful sensations.
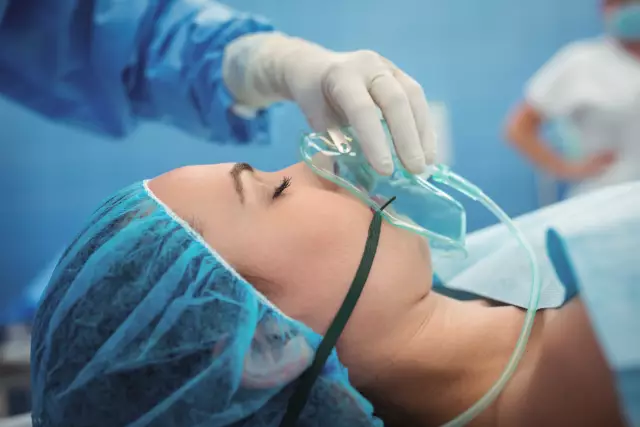
Epidural anesthesia can be used as an adjunct to general anesthesia, to relieve the patient after surgery, and to treat back diseases. The possibility of using the so-called "epidural" as a local anesthetic has led to the popularity of the use of epidural anesthesia during childbirth or caesarean section.
Use of epidural anesthesia during labor
According to reviews, every fifth woman uses epidural anesthesia during childbirth, and in European countries this figure has been increased several times: more than 50% of women in labor have already tested the effect of "epidural". Despite the fact that this method of anesthesia can successfully protect a woman from the pain experienced during childbirth, epidural anesthesia is a serious medical intervention that can have both contraindications and complications.
Pain relievers for epidural anesthesia are administered in several ways:
- Pain relief with a gradual dose increase. The anesthesiologist injects a mixture of drugs into the epidural space of the spine. As the anesthesia weakens, the specialist performs additional injections, the duration of which is 1-2 hours;
- Continuous introduction. Provides for the introduction of a catheter into the woman's spine, on the back of which a pump is connected, which continuously delivers an anesthetic drug;
-
Combined epidural anesthesia during childbirth.

Complications from epidural anesthesia during labor are rare The essence of the procedure is the preliminary introduction of a small dose of anesthetic, during which a catheter is inserted into the spine. When the effect of the first injection is over, the doctor will administer medications directly through the catheter.
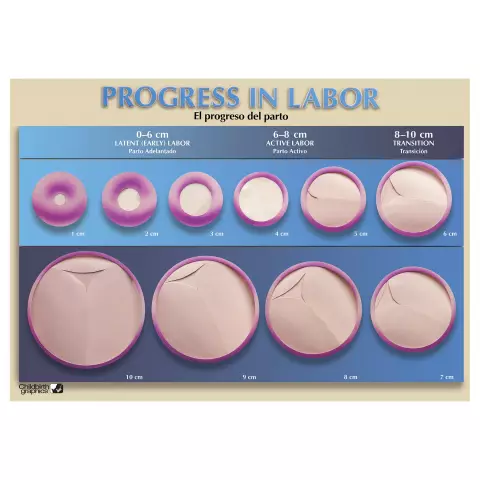
Epidural anesthesia during childbirth, according to reviews, can be performed at any time during labor, however, most often, anesthesia occurs already in the active period (when the cervix is opened by 5-6 cm).
The benefits of using an epidural during childbirth include:
- Effectiveness in pain relief;
- The speed of action. Anesthesia begins to work 20 minutes after injection;
- The fact that the woman in labor remains conscious. She realizes that she has contractions, but does not feel pain;
- Decrease in blood pressure with hypertension.
Disadvantages and consequences of epidural anesthesia during childbirth
Complications that occur after epidural anesthesia are rare, but they do occur:
- For about one person out of twenty patients, this type of anesthesia does not have much effect: there is no blockade of nerve endings. In this case, anesthesia will be either partial or not at all;
- Careless actions of the doctor can lead to accidental puncture of the dura mater, which is dangerous for the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the epidural area. This complication is characterized by headaches that can be mild or severe (lasting for years);
- The pain reliever can enter the bloodstream to the brain and cause spasms, unconsciousness;
- Accidental damage to the subarachnoid space can lead to paralysis of the lower limbs.
The consequences of epidural anesthesia during childbirth can also include:
- Increased likelihood of an increase in body temperature in the postpartum period. This complication leads to the appointment of antibiotics, which requires resolution of the issue of breastfeeding;
- Increasing the likelihood of instrumental impact on childbirth (using a vacuum extractor and the application of forceps);
- Increasing the patient's tendency to possible problems with urination (urinary retention);
- Decrease in blood pressure in a woman in labor, which can lead to impaired blood flow to the placenta, and, consequently, oxygen starvation of the fetus;
- Increased duration of the second stage of labor.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.