- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ankle injury: symptoms, treatment, rehabilitation
The content of the article:
- The reasons
- Anatomical and physiological features
- Symptoms
- First aid
- Treatment
-
Complications
- Hemarthrosis
- Synovitis
- Post-traumatic arthrosis
- Rehabilitation
- Video
Ankle injury is included in the international classification of diseases of the tenth revision (ICD-10) and has the code S90.0. It is possible to get injured in a domestic environment, during sports or work, but it is quite rare in peacetime.

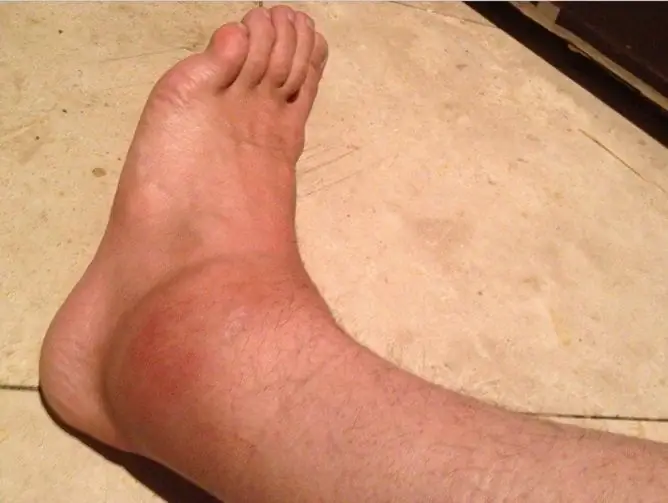
Ankle injury can occur from a fall or during sports
The ankle joint is a movable joint of three bones of the lower limb: tibia, fibula and talus. The joint performs a number of important functions, including:
- shock absorption when moving, jumping;
- regulation of coordination of movements;
- distribution of the load on the entire plane of the foot.
A bruised ankle wound is characterized by damage to the soft tissue in this area, the immediate cause of which is a blow or fall.
Most often, with timely diagnosis and treatment, this type of injury has a favorable prognosis, in which a complete recovery occurs. However, in rare cases, the process becomes recurrent, provoking the development of synovitis, post-traumatic arthrosis and other complications.
The reasons
The mechanism for the formation of an ankle injury is the direct action of a traumatic factor in the form of a blow with a hard object on the ankle joint. The second mechanism is a fall on a given area. In both cases, this is a closed injury that does not significantly disrupt the structure of the injured tissues.
The soft tissues surrounding the joint (skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, blood vessels, nerve endings) and the periosteum can be injured.
Anatomical and physiological features
Covering the talus block from both sides, the tibia and fibula form a joint. The visible distal processes of the shin bones that rise under the skin on the inside and outside are called the ankles. It is also formed by numerous ligaments and muscles.

The ankle joint has a complex structure and performs an important function in the musculoskeletal system
The ligamentous apparatus is responsible for the tight fixation of the bones together, keeping them in the required position. The muscles, together with the ligaments, provide movement in this joint. In the ankle, movement is physiological only in one plane - the frontal one.
The muscles involved in the movement of the joint are divided into 2 large groups:
| Group | Description |
| Flexor muscles | Provides frontal flexion of the foot |
| Extensor muscles | Provides foot extension in the frontal plane |
There is also a small muscle group responsible for movement in the outer and inner (right and left) sides.
The blood supply is carried out by the large peroneal and tibial arteries, the outflow of venous blood occurs into the deep veins of the leg. The articular capsule is innervated by the branches of the tibial and deep nerve of the lower leg.
Ankle functions:
- Regulation of coordination of movements and maintaining balance in a standing position, while walking, running, when moving on uneven surfaces.
- Even distribution of weight on the feet.
- The implementation of shock absorption, smoothness of movements and soft transfer of the load on the feet (while running, walking).
Symptoms
Immediately after receiving an injury, a person feels a sharp pain that can be observed for several more days. Damage to the skin, subcutaneous tissue or muscles is mainly accompanied by bruising (hematoma).
The victim is trying in every possible way to spare the injured limb, since the movement provokes an increase in pain. Therefore, one leg may be lame. However, lameness is not accompanied by loss of support (the patient may step on the injured leg).
Due to the rapidly developing massive edema, there may be a feeling of numbness in the foot or toes. Hyperemia (redness) and local hyperthermia (temperature increase) are possible.
Signs that should alert (typical for fractures):
- Audible crepitus (crunch) in the injured area.
- The presence of pathological mobility (in any other axis, except for the frontal).
- Gross deformity of the joint or foot.
- Loss of support (a person cannot step on an injured leg, this causes severe pain).
- Visible shortening of the injured limb in comparison with the healthy one (assessed by the level of the feet in the supine position).
First aid
After injury, it is necessary to give the limb an elevated position by placing a pillow or roller under the lower leg. You need to apply cold in the form of a heating pad or ice pack, bottle of ice water. If there is damage to the skin, it is advisable to rinse the damaged area under cold running water and treat with Chlorhexidine.

In first aid, a fixation bandage is usually applied
For intense pain, pain relievers are prescribed in tablets, for example, ibuprofen, nimesulide, diclofenac, ketorolac and others. A bandage may be required.
After providing first aid, it is recommended to consult a traumatologist-orthopedist to exclude other ankle injuries: fracture, dislocation, rupture, sprains, etc. These rules apply both to bruises in adults, including the elderly, and in children.
Treatment
After collecting complaints, anamnesis, examination, palpation, assessment of the objective condition, additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed by the doctor. For this purpose it is used:
- X-ray of the ankle: to exclude a fracture;
- computed tomography (CT): with the help of CT it is possible to visualize the state of soft tissues in the area of injury.

To exclude a fracture, an ankle x-ray is prescribed
Treatment consists in giving the limb an elevated position, applying cold in the first few days. During movements, in particular walking, it is sometimes recommended to use a cane, apply an elastic bandage.
To reduce swelling and pain, the doctor may prescribe pain relievers (NSAIDs) in tablet form, in the form of capsules, rectal suppositories. If the integrity of the skin is not compromised, you can use topical products containing NSAIDs (ointments, gels).
A few days after the injury, local dry heat (UHF therapy) or other physiotherapy methods are prescribed to accelerate tissue regeneration and recovery.
Before you start treating a bruise at home, you need to get a doctor's recommendation. It is permissible to use compresses a few days after the injury. Traditional methods suggest using warm compresses from table salt placed in a linen or linen bag.
Complications
As a result of the impact of intense mechanical force with the development of massive damage, in case of untimely referral to a specialized specialist, non-compliance with the treatment regimen, care, full rehabilitation, and for a number of other reasons, complications may develop.
Hemarthrosis
Pathology is characterized by hemorrhage into the joint cavity, in which the patient may experience pain, swelling, and an increase in joint size. Hemarthrosis is dangerous by the development of synovitis, with additional infection - purulent arthritis and the deposition of fibrin filaments on the articular surfaces with the formation of adhesions.

In severe cases, bruising leads to the development of complications.
Usually, a bruised ankle wound does not require a puncture of the joint, but if intra-articular bleeding continues, this manipulation is necessary. After puncture and aspiration of the contents, a pressure bandage can be applied to provide temporary rest to the injured area.
Synovitis
Often aseptic, less often infectious inflammation of the synovium, which is accompanied by the accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity. The main symptoms are:
- pain;
- an increase in joint volume;
- fluctuation and decreased motor activity.
Infectious synovitis is treated with antibacterial drugs. Surgical interventions are rarely performed, mainly when conservative therapy is ineffective. The essence of the operation is to partially or completely remove the synovium.
Post-traumatic arthrosis
A subspecies of secondary arthrosis (arising against the background of previous changes), characterized by degenerative and dystrophic changes in the joint.
It is characterized by the appearance of a crunch and low-intensity pain that occurs during movement. Further, there is stiffness of the joint, pain occurs during rest, "in the weather" or at night, which gradually leads to severe deformation of the joint and the appearance of contractures.
Treatment in the early stages is conservative, anti-inflammatory, in advanced cases, surgical reconstructive therapy is required.
Rehabilitation
The timing of the beginning, duration and methods of rehabilitation should be discussed with a traumatologist-orthopedist and a physiotherapist. With light bruises, rehabilitation measures can be carried out within a week after the injury.

Rehabilitation, including massage, is needed to speed up recovery.
For this purpose, appointed:
- ankle massage. Light, painless massage movements should be gradually and regularly applied to the damaged area;
- warm-up. In the prone or sitting position, you should bend and unbend the toes of the injured leg, then knead the foot in a circular motion;
- physiotherapy procedures. It is prescribed 4-5 days after a minor injury in order to improve blood circulation, regenerate damaged tissues. The use of UHF therapy, magnetotherapy, mud therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin applications is recommended.
Accurate adherence to the recommendations and prescriptions of the doctor, timely initiated rehabilitation measures minimize the risk of possible complications, accelerate recovery and restore the previous physical activity.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.