- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyps in the uterus: causes of formation, symptoms, treatment, consequences
The content of the article:
- Types of polyps
- Why polyps form
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Medication for uterine polyps
-
Removal of polyps
-
Hysteroscopy
How is hysteroscopy performed
- Laparoscopy
-
-
Traditional medicine methods
- Pumpkin seeds
- Tincture of the Golden Mustache
- Douching broth
- Forecast and consequences
- Prevention
- Video
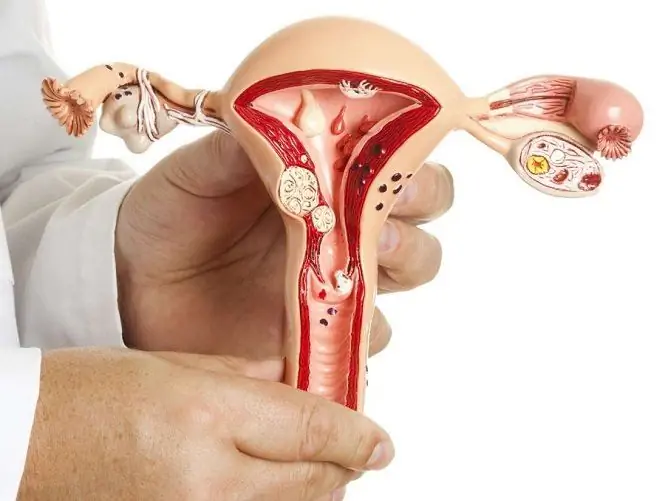
A polyp in the uterus is a benign neoplasm that forms as a result of pathological proliferation of endometrial cells. Outwardly, it is a rounded growth on a leg, resembling a mushroom, with a porous surface of a burgundy-purple or yellowish color.

Polyps in the uterus are the result of abnormal proliferation of endometrial cells
The size of the neoplasm can reach from a few millimeters to three centimeters. Polyps are single and multiple, can be localized in different places (for example, on the front and / or back wall of the uterus).
Most often, this pathology occurs in women 40-50 years before the onset of menopause, but in some cases, polyps can also form in girls in adolescence.
Types of polyps
Depending on what tissue polyps are made of, they are subdivided as follows:
| Formation type | Description |
| Fibrous | Formed from connective tissue, most often occur during menopause as a result of changes in hormonal levels |
| Glandular | They consist of glandular cells with endometrial hyperplasia. More common in young women. In some cases, they appear as fluid-filled cysts |
| Adenomatous |
Consist of altered atypical cells. More often formed at the age of over 40. Can degenerate into cancerous tumors |
| Glandular fibrous | Consist of connective tissue and glandular cells |
| Placental | Formed from placenta particles left in the uterine cavity after childbirth |
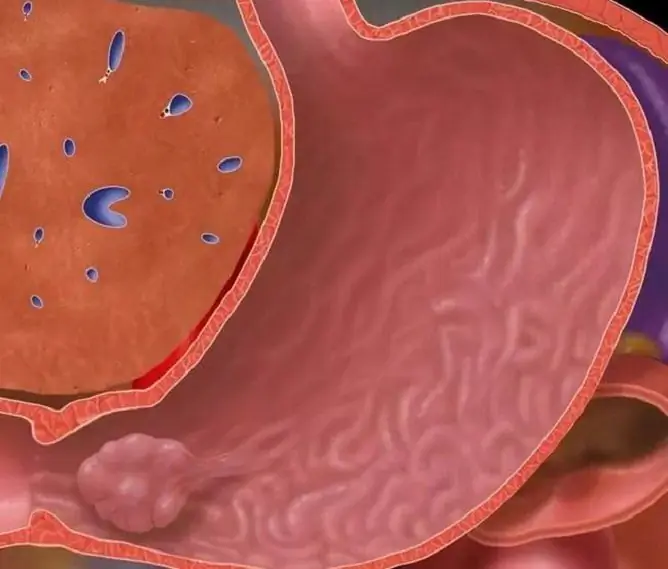
Polyps of the body of the uterus are located on the inner surface of the organ, in most cases - in the upper part.
Why polyps form
Where do these neoplasms come from? The reason for the formation of polyps in the uterus is most often hormonal disorders, namely, an excessive amount of estrogen (female sex hormone).

An excess of estrogen is often the cause.
It is necessary for the female body only in the first two weeks of the menstrual cycle. If estrogen is produced in large quantities constantly, then this leads to the proliferation of the endometrium, some parts of which do not flake off during menstruation, but remain in the uterine cavity.
If this occurs over several cycles, an outgrowth appears at this place, into which the fibers of connective tissue and blood vessels grow, which leads to the formation of polyps. Their active growth is affected by a lack of progesterone.
Other possible reasons:
- abortion. Injury to tissues during curettage leads to increased cell growth in certain areas in the uterine cavity;
- inflammatory processes in the genital area. The result can be pathological growth of the endometrium and the formation of polyps;
- endocrine diseases. Diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands or diabetes mellitus can provoke a malfunction of the body and the appearance of neoplasms;
- hereditary predisposition. In some cases, the tendency to form growths is inherited;
- overweight. It has been proven that adipose tissue is the main source of estrogen in older women, therefore, its excess leads to a change in hormonal levels and, as a result, to the formation of growths;
- stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs. Most often it occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle. This is a prerequisite for ovarian dysfunction, which in turn becomes the cause of hormonal imbalance;
- diseases that lead to impaired blood circulation. Cells that do not receive enough oxygen can rapidly divide, turning into neoplasms;
- taking certain medications (Tamoxifen, Dostinex). Medicines block receptors responsible for sensitivity to sex hormones. In some women, during the treatment period, polyps begin to grow actively in the uterine cavity.
Symptoms
It is possible to suspect that a neoplasm has appeared in the uterine cavity when the following symptoms occur:
- menstrual irregularities, profuse uterine bleeding;
- spotting between periods;
- pain in the lower abdomen or in the lumbar region;
- mucous discharge from the vagina.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a doctor at the Department of Gynecology. He will conduct an examination and appoint the necessary examination.

Transvaginal ultrasound is usually prescribed to detect neoplasms.
The most accessible and at the same time painless method for diagnosing neoplasms is transvaginal ultrasound. It is performed using a sensor that is inserted into the vagina.
In some cases, hysteroscopy is performed for examination and subsequent removal of the build-up. A tube with a micro-video camera is inserted into the uterine cavity.
Sometimes, to diagnose the pathology of the uterus and fallopian tubes, X-rays with contrast are done.
Medication for uterine polyps
Young nulliparous women are treated for neoplasms with hormonal drugs. In most cases, oral contraceptives are prescribed (Yarina, Jazz, Klayra). They need to be taken according to the scheme indicated in the instructions. The course of treatment is at least six months.

For the treatment of pathology, oral contraceptives are used, in particular Klayra
For women after 40 years of age or during menopause, treatment is carried out using drugs that protect against the action of estrogens and luteinizing hormone, which cause disruptions in the work of the pelvic organs (Zoladex, Dipherelin).
Medication is also prescribed for women who have one small growth. In other cases, surgical removal of the tumor is necessary.
Removal of polyps
Hysteroscopy
Most often, the formation is removed by hysteroscopy. This is a low-traumatic procedure that allows you to detect a growth and immediately eliminate it. This operation is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 15-20 minutes.

One of the safest methods for removing polyps is hysteroscopy
According to patient reviews, the benefits of this method include:
- absolute safety;
- lack of pain.
With the camera, you can see all the growths (including small ones) and take a photo of them. The patient can return home immediately after the operation.
Hysteroscopy is performed 2-3 days after the end of menstruation. At this time, the endometrium is very thin and even small polyps can be seen. The patient is injected into anesthesia and the cervical canal is opened with a special instrument.
How is hysteroscopy performed
A tube with a small camera at the end (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterine cavity through the vagina. All identified polyps are cut off with an electrical surgical loop and treated with liquid nitrogen.

Removal of the build-up is carried out with a surgical loop
If a single polyp of the uterine body grows large, it can be removed with forceps. The neoplasm is captured and twisted, turning around the axis. Then the bed of the build-up is scraped out with a curette and treated with an antiseptic.
With this method of removal, the vessels supplying the formation are twisted, which prevents bleeding. Scraping allows you to prevent the reappearance of pathology.
If, using a hysteroscope, the doctor finds multiple polyps on the anterior and / or posterior walls of the uterus, scraping is performed. With the help of a curette, the entire upper (functional) layer of the organ's mucous membrane is removed.
Laparoscopy
In the event that atypical cells were found in the polyp, the uterus is removed. A more gentle way than abdominal surgery is the laparoscopic method. This intervention is performed under general anesthesia.

According to indications, a laparoscopy of the uterus is prescribed
Through a small hole in the abdomen (up to 1.5 cm), the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide. This makes it possible to raise the abdominal wall in order to enable the surgeon to work freely.
A laparoscope with a camera is inserted into the incision, and the doctor is able to assess the condition of the uterus. With the help of special instruments, the organ is excised and removed. The incision is sutured and the patient is taken to the recovery room.
The woman is in the hospital for 5-7 days. She can return to work in two weeks. At the same time, there are practically no scars on the patient's body.
Traditional medicine methods
In addition to medications, alternative methods of treatment are used to combat polyps in the uterine cavity. This makes it possible to quickly get rid of the problem. The use of folk remedies must be agreed with the attending physician.
Pumpkin seeds
In order to prepare the product, a glass of peeled dried (not fried) pumpkin seeds is ground with a blender or coffee grinder. Add 3 tablespoons of honey and 300 ml of refined olive oil. The mixture is heated in a water bath and 3 boiled yolks are added to it (they must first be crushed).
The finished product is stored in a glass jar with a tightly closed lid on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. Apply it in a teaspoon once a day before meals. The course of treatment is two months, then you need to take a break. Treatment of polyps in this case is quite long, but, according to reviews, effective.
Tincture of the Golden Mustache
To prepare the remedy, you will need about twenty joints of a golden mustache. The plant is crushed and poured with 300 ml of 70% medical alcohol. The tool is insisted for a week in a dark, cool place. Shake it periodically.
Store the tincture in the refrigerator for a year. 20 drops of the medicine are diluted in a tablespoon of water and taken in the morning and evening before meals. The course of treatment is one month, then a ten-day break is taken, and the drug is resumed.
Douching broth
To prepare the broth, mix a tablespoon of chamomile flowers, sage leaves, oak bark and yarrow herb. The dry mixture is poured with two liters of water and boiled over low heat for 5 minutes.
After the product has cooled to a comfortable temperature, it is filtered through a sieve. With the help of a syringe, the vagina is irrigated with a decoction. The procedure is carried out once a day for a week, then a ten-day break is taken.
In one procedure, 1 liter of broth is used. The second part can be stored in the refrigerator in a sealed container for no more than a day. The product is heated before use. Treatment lasts no more than two months. Before using the broth, you need to consult a doctor.
Forecast and consequences
The appearance of neoplasms in the uterus is often associated with ovarian dysfunction, therefore, despite the performed surgery, they can grow again without appropriate hormonal correction.
A polyp in the uterine cavity can be detected during pregnancy. This is dangerous because there is a risk of placental abruption. Through it, the fetus, along with the blood, receives oxygen and nutrition. If the placenta is not too tightly attached to the wall of the uterus, then this can cause fetal hypoxia or delay in its development.
During pregnancy, treatment is not carried out, and all the efforts of the doctor are aimed at improving the condition of the fetus. In some cases, a change in hormonal levels leads to the fact that the neoplasms resolve on their own.
Prevention
In order to prevent the formation of growths in the uterine cavity, it is necessary:
- avoid hypothermia;
- eat right, exclude foods containing a large amount of dyes and preservatives from the diet;
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports, which helps prevent blood stagnation in the pelvic area;
- get rid of bad habits;
- visit a gynecologist every six months, coordinate with him the choice of hormonal contraceptives.
If you identify symptoms that indicate the formation of polyps in the uterine cavity, you should consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.