- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Why dizziness occurs with cervical osteochondrosis and how to treat it
The content of the article:
- What is Vertigo?
- Why dizziness occurs with cervical osteochondrosis
- Causes of cervical osteochondrosis
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- How to relieve a dizziness attack at home
- In what cases it is necessary to urgently seek medical help
- Prevention
- Video
Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis (cervicogenic vertigo) is observed quite often. According to statistics, systematic dizziness is observed in about 35% of the adult population. Moreover, in almost half of the cases, its occurrence is associated with one or another pathology of the cervical spine.
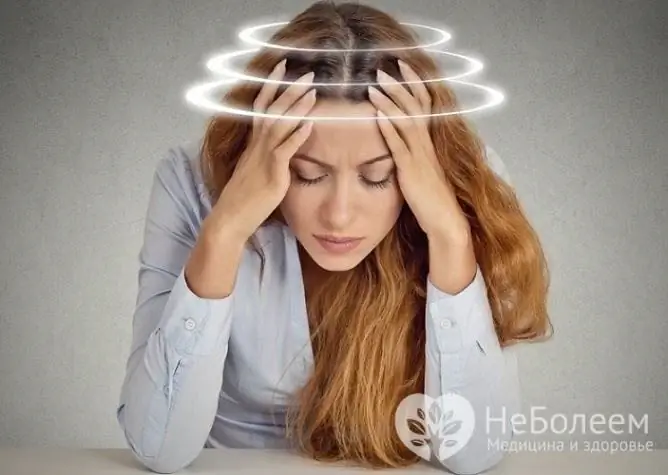

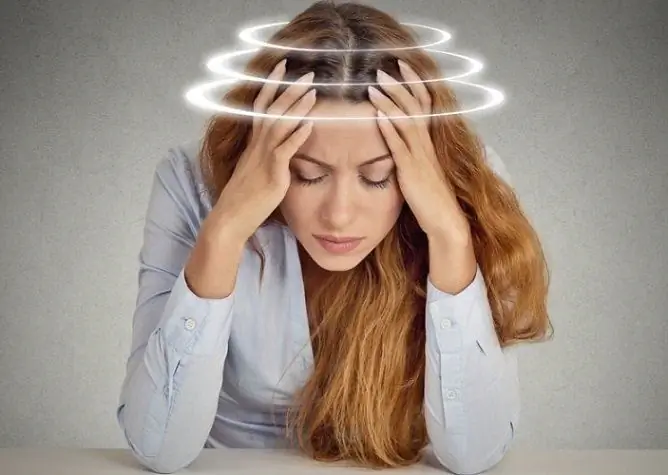
Dizziness is one of the common symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
What is Vertigo?
Dizziness, or vertigo, is a pathological condition in which a person has a feeling of incorrect perception of the position of the body in the surrounding space. It begins to seem to him that objects begin to revolve around him or, conversely, his body revolves around objects.
During an attack of vertigo, the patient loses confidence in his actions and his movements become awkward. In addition, he may develop autonomic and neurological symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- unstable blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- hyperhidrosis of the face and upper limbs.
Why dizziness occurs with cervical osteochondrosis
The pathological mechanism of osteochondrosis development is based on degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs. Over time, the cartilage that forms them decreases in volume and collapses. As a result, its cushioning properties deteriorate sharply, and the load on the vertebral bodies increases. In turn, this leads to the formation of bone spines and growths on their surface, which injure the soft tissues surrounding the spine and cause an inflammatory reaction.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is accompanied by compression (compression) of the vertebral (vertebral) arteries and spinal nerve roots. Violation of the blood supply to the spinal cord and medulla oblongata leads to the development of chronic ischemia and hypoxia of these anatomical structures, which, in combination with irritation of autonomic nerve fibers, causes the occurrence of cervicogenic vertigo.
Causes of cervical osteochondrosis
The occurrence of osteochondrosis is caused not by one, but by a combination of several factors. Therefore, this disease is multifactorial. Most often, the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the intervertebral discs is provoked by:
- hereditary predisposition;
- metabolic disorders;
- chronic hypodynamia;
- significant physical activity;
- chronic infectious and / or somatic diseases.
Any of these factors can cause osteochondrosis. When several factors are combined, the risk of the disease increases several times.
Symptoms
At the very beginning of the development of cervical osteochondrosis, dizziness is very weak. As a rule, the patient begins to feel dizzy with sudden neck movements, and at rest, the discomfort quickly disappears.
As the underlying pathology progresses, the severity of vertigo also increases. Dizziness begins to appear at rest, and later becomes permanent. Moreover, it is accompanied by a feeling of stuffiness or tinnitus, headache, heart palpitations, sweating.
Diagnostics
Dizziness is not an independent disease, but a symptom that accompanies the development of many pathological processes. Therefore, in order to identify the underlying disease, the patient must consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe the examination necessary in each specific case, which may include the following methods:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- computed and / or magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck;
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- vestibular tests.
If necessary, the patient is consulted by doctors of narrow specialization:
- neurologist;
- neuropsychiatrist;
- vertebrologist;
- otolaryngologist.
Dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be differentiated from other types of vertigo, which can be observed in other diseases:
- acute and chronic disorders of cerebral circulation;
- Meniere's disease;
- labyrinthitis;
- neuritis (inflammation) of the auditory nerve;
- migraine;
- climacteric syndrome;
- panic attacks;
- tumors of the cervical spine or brain.
Treatment
Treatment of dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should be complex and long-term. It usually includes the following components:
| Therapy component | Explanation |
| Drug treatment |
A patient with vertigo is often prescribed: · Drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood, dilating blood vessels; · Nootropic drugs (improve metabolic processes in brain cells, stimulate the activity of thought processes); Muscle relaxants (these tablets relieve muscle spasm, which is the basis of the compression of blood vessels). |
| Daily regime |
Quite often, especially in the initial stages of osteochondrosis, careful adherence to the daily regimen allows you to get rid of the manifestations of dizziness, which means: · Correct alternation of periods of rest and loads; · A night's sleep lasting at least 8 hours; Full active rest |
| Diet | From the diet, you should remove foods that contribute to spasm of blood vessels and, as a result, an increase in blood pressure (spicy and salty foods, alcohol, strong tea, coffee, chocolate, energy drinks) |
In some cases, the intake of decoctions of medicinal plants (hawthorn fruits, fennel or parsley seeds, ginger root) has a good therapeutic effect. However, herbal medicine can be used only as directed by a doctor, since there may be individual contraindications to it.
To train the vestibular apparatus, patients are advised to regularly do exercises:
- rotation of the eyes in one direction or the other;
- standing on one leg with eyes closed and open;
- riding on a boat swing;
- rotation by the body of the body;
- head rotation.
Regular swimming activities can also improve the condition of patients with vertigo. Preference should be given to the crawl style on the back. In no case should you swim with the "beach" breaststroke when the swimmer's head remains constantly above the surface of the water. In this case, there is a significant overstrain of the neck muscles and, as a result, the compression of the vertebral arteries increases.

Crawl swimming helps to train the vestibular apparatus and thereby relieves dizziness
In complex therapy, an important role is played by other non-drug methods of treatment:
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- kinesiotherapy;
- stretching the spine using special devices;
- physiotherapy.
How to relieve a dizziness attack at home
To reduce the severity of dizziness at home, you can use the following techniques:
- Take a deep breath, then, bending your head forward, exhale slowly;
- Sit on a chair with your back on its back, with your feet on the floor. Fix your gaze on any stationary object and continue looking at it until the unpleasant symptoms stop.
- Wash yourself with cold water.
- Apply a few drops of ammonia to a small piece of cotton wool and gently inhale its vapors (with a cotton swab should be quickly carried out at a distance of 5-6 cm from the nose).
- If an attack of vertigo began on the street, then you need to sit down and bend over to your knees. Stay in this position until the condition improves.
In what cases it is necessary to urgently seek medical help
Urgent medical attention is usually needed in the following cases:
- an attack of dizziness occurred for the first time and is combined with severe headache, vomiting, severe tachycardia, chest pain or feeling short of breath;
- there are disturbances of consciousness (disorientation in time and space, agitation, deafness);
- an attack of vertigo lasts more than one hour;
- dizziness is combined with a sudden onset of weakness in one half of the body, disorders of skin sensitivity.
The appearance of such symptoms may indicate the development of a serious illness in the patient (stroke, heart attack), requiring emergency medical care. Attempts to treat a patient on their own, relying on the advice of relatives and friends, can cause very serious consequences.
Prevention
Disease prevention includes the following areas:
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- posture control;
- normalization of body weight;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages);
- proper balanced nutrition.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.