- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Symptoms of a lack of female hormones estrogen
The content of the article:
-
Symptoms of a lack of female hormones
- Reproductive dysfunction
- Change in appearance
- Other signs
- Lack of female hormones: the main reasons
- During menopause
- In reproductive age
- How to identify a lack of hormones
-
Treatment
- Assortment of drugs
- Contraindications
- Video
Estrogens are an important group of female sex hormones that are responsible for reproductive function, feminization, and regulate the menstrual cycle. Symptoms of a lack of female hormone estrogen are extremely varied. This is due to the fact that receptors for them are contained in many organs, therefore, with their deficiency, the entire body suffers.
Estrogen deficiency leads to serious disorders in the body
Symptoms of a lack of female hormones
Deficiency of female hormones has many clinical manifestations. The main effect of estrogens is on the internal genital organs, therefore, with their deficiency, the menstrual cycle is disturbed, a woman cannot become pregnant. The work of other internal organs also suffers - the heart, blood vessels, bones, organs of the urogenital tract. Appearance changes - figure, skin, hair.
Reproductive dysfunction
The main group of symptoms is associated with impaired reproductive function.
Estradiol is responsible for the proliferation and rejection of the upper layer of the endometrium, therefore, with a hormone deficiency, the menstrual cycle is disrupted. Menstruation becomes irregular, painful, the cycle lengthens. With a significant deficit, menstruation disappears altogether.
Change in appearance
Estrogen is a beauty hormone. Its deficiency significantly affects the appearance of a woman. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The figure changes - the feminine outlines are lost. The volume of the chest and buttocks decreases, the waist increases. Fatty tissue is deposited mainly in the abdomen. There is also a tendency to gain weight.
- The skin becomes less elastic and wrinkles appear. Oily skin may increase, against the background of this, skin rashes appear.
- Hair loses shine, becomes dull, splits, falls out.
Other signs
Deficiency of female hormones affects all organs that have estrogen receptors. Their greatest number is determined in the uterus, mammary glands, vagina, blood vessels, brain, bone tissue.
| Symptom group | Description |
| Urogenital disorders |
The urogenital tract is very sensitive to female hormones. With estrogen deficiency, vaginal dryness, itching, discomfort, soreness during intercourse, contact bleeding are observed. The ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic organs suffers. Urinary incontinence may develop, in severe cases, organ prolapse. |
| Vasomotor phenomena | Vasomotor events are early symptoms of estrogen deficiency. Characterized by hot flashes, increased sweating, facial flushing, fluctuations in blood pressure. |
| Psycho-emotional phenomena | Lack of estradiol also affects the brain. Clinically, this manifests itself in the form of psychoemotional phenomena: emotional lability - unreasonable mood swings, decreased memory, attention, tearfulness, depressive episodes. |
| Violation of cardiovascular activity |
Estradiol has a cardioprotective effect. With its deficiency, the strength of the heart contractions decreases, tachycardia develops, and a frequent headache appears. In the late period, symptoms of atherosclerosis may develop, since estrogens prevent the deposition of lipids in the vascular wall. |
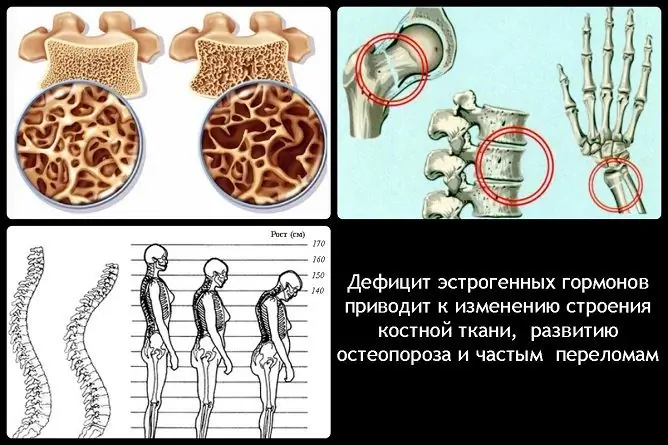
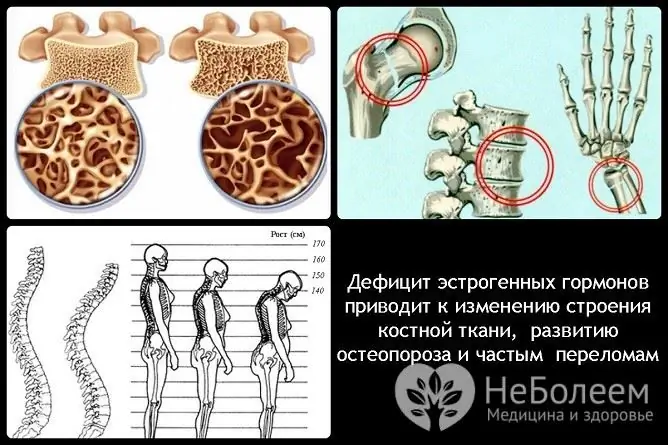
| Osteoporosis and Frequent Fractures |
Estradiol prevents bone resorption, therefore, with its deficiency, the absorption of calcium worsens, and the fragility of bones increases. Clinically, a decrease in bone density is manifested by frequent fractures. |
Lack of female hormones: the main reasons
Deficiency of estrogen can occur at any age, but women are more susceptible to it after 50 years. At this age, there is a natural period of extinction of reproductive function - menopause. Less commonly, hormonal disorders occur in young women. The reason can be a variety of conditions, ranging from the surgical removal of the uterus with appendages, ending with improper diet and drastic weight loss.
During menopause
Deficiency of estrogen during menopause is a consequence of the physiological extinction of ovarian function. The supply of functioning follicles is depleted, the sensitivity to the follicle-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland decreases, therefore, the production of estrogens decreases.
The name "estrogens" combines three hormones: estrone, estradiol and estriol. If during the period of reproductive activity, the main of them is estradiol, then during menopause - estrone. The source of synthesis is adipose tissue, which continues to produce a small amount of estrone even after the extinction of ovarian function.
In reproductive age
At reproductive age, the most common cause of estrogen deficiency is extirpation of the uterus with the appendages. The operation can be performed for fibroids, other tumors, significant bleeding during childbirth.
There are a wide variety of other causes that can also lead to hormone deficiency:
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
- Lack of animal fats in the diet.
- Sudden weight loss.
- Genetic abnormalities.
- The defeat of the pituitary gland - a lack of follicle-stimulating hormone, an excess of prolactin.
- Ovarian disease - cysts, autoimmune disease, ovarian failure syndrome, resistant ovary syndrome.
How to identify a lack of hormones
A blood test can confirm a lack or excess of estrogen. The level of estradiol is investigated. Its amount in the blood varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Normal levels of estradiol are as follows:
| In the follicular phase | 68-1269 pmol / l |
| In the ovulatory phase | 131-1655 pmol / l |
| In the luteal phase | 91-861 pmol / l |
| Postmenopausal | up to 73 pmol / l |
If treatment with hormonal drugs is planned, an additional examination is required. The following studies are assigned:
- coagulogram;
- biochemical blood test - ALT, AST, bilirubin, prothrombin index, protein fractions;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Breast ultrasound, mammography.
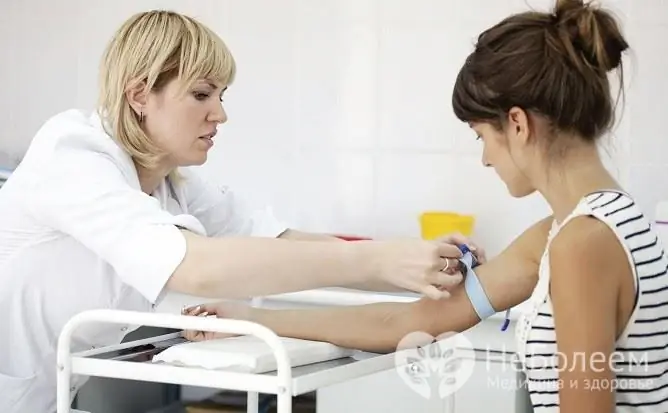

Estrogen levels are determined with a blood test
Treatment
Lack of estrogen negatively affects a woman's health. For treatment, hormone replacement therapy is used. Hormone therapy is systemic and local. For systemic therapy, pills are taken orally, for local - ointments, gels, vaginal suppositories, transdermal patches.
Assortment of drugs
There are many drugs for hormone therapy for hypoestrogenism. A wide assortment makes it difficult to choose, but there are clear indications for the use of one or another group of drugs. The choice depends on several factors - the reasons for the hormone deficiency, the woman's age, the presence of concomitant diseases.
| Group of drugs | Indications | Representatives | |
| Preparations containing only estrogens | Indicated exclusively for the treatment of women who underwent removal of the uterus with appendages. In other cases, estrogen monotherapy is not used. | Estrofem, Premarin, Proginova, Klimara, Ovestin | |
| Combined drugs (estrogens and gestagens) | For cyclic therapy |
At a young age, before menopause, women are prescribed drugs that mimic the normal menstrual cycle. They come in three varieties: two-, three-phase, with the additional addition of an antiandrogenic component |
Femoston, Klimonorm, Divina, Divitren, Cyclo-Proginova, Trisequencing, Klymene |
| For continuous therapy | In the postmenopausal period, when after the last menstruation more than a year has passed, drugs for continuous therapy are prescribed. There are no menstrual bleeding when taken | Cliogest, Premella | |
Contraindications
Hormone replacement therapy is not indicated in all cases of hormone deficiency. There are also certain contraindications:
- tumors of the uterus and mammary glands;
- mastopathy;
- endometriosis;
- increased blood clotting;
- severe cardiovascular disease;
- liver disease.
In these cases, local drugs can be used that are not absorbed into the general bloodstream. They allow you to get rid of urogenital disorders, but do not protect other organs. Phytoestrogens and nutritional adjustments can also be applied.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.