- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Stomatitis in children, treatment

Among infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, stomatitis is most common, causing severe discomfort to babies. This term comes from the Latin word "stoma", which means inflammation of the oral mucosa.
The nature of the treatment of stomatitis in children depends on the type of pathogen that caused the inflammation. Most often, the disease develops against the background of a general decrease in the child's immunity. Sometimes the cause of stomatitis in children, especially small children, is the usual trauma of the oral cavity, because babies constantly pull various objects into their mouths.
Children's stomatitis: classification and causes
It is characteristic that for each age group its own type of stomatitis is typical, but, of course, there are exceptions:
- Candidal or fungal stomatitis. The causative agents of this disease are fungi of the genus Candida, which can be found in the oral cavity as opportunistic microflora and do not cause inflammation. Most often, candidal stomatitis occurs in children 0-3 years old;
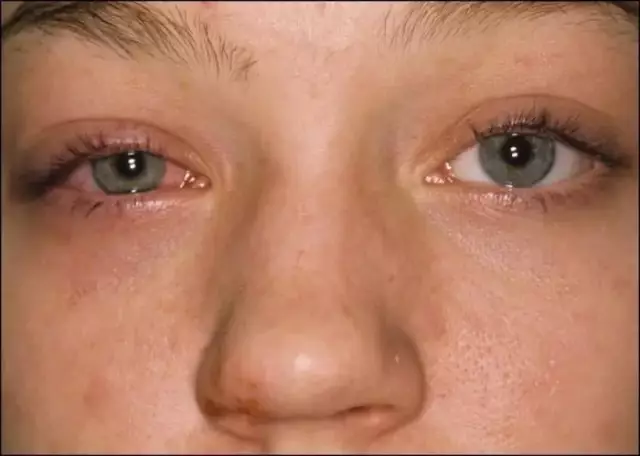
- Herpetic stomatitis. It is caused by the herpes virus and very often becomes chronic with recurrent relapses. Most common in children 1-3 years old;
- Aphthous or allergic stomatitis. This is a fairly rare type of disease, the causes of which are not fully understood. According to some data, it is an allergic-type reaction, according to others, it is associated with malfunctions of the digestive tract. Most often found in schoolchildren;
- Bacterial stomatitis. This type of disease is typical for children of different ages and occurs due to mechanical or thermal injury to the oral cavity, as well as in violation of personal hygiene rules, during teething in babies, etc.
The cause of stomatitis in children is that the mucous membrane of their oral cavity is very thin and delicate, easily injured, but the immune system cannot yet cope with the numerous infectious agents that enter the baby's mouth. Human saliva perfectly protects the oral cavity from bacteria, germs and viruses, but children still do not have enough antiseptic enzymes in it. As a result, inflammation occurs, manifested either by single sores or by extensive foci.
Candidal stomatitis in children: treatment
In order to cure stomatitis in a child, as a rule, you just need to create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity that slows down the growth of microorganisms and causes their gradual death. To do this, you can use a soda solution (1 tbsp. L. Per glass of water) or a 2% boric acid solution.
Aniline dyes such as methylene blue can be used to treat stomatitis in children. The oral cavity is processed 5-6 times a day, special attention is paid to the cheeks and gums of the child, since the pathogenic flora is most often found in the plaque accumulating at the necks of the teeth.
Another drug for the treatment of stomatitis is Candide solution. Its active ingredient destroys the cell walls of the fungus. The course treatment is carried out within 10 days. When the first signs of improvement appear, in no case should the treatment be abandoned, otherwise, as in the case of taking antibiotics, the resistance of the pathogen to the drug is formed.
In rare cases, you can use "Diflucan", it is prescribed to children in adolescence, the dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
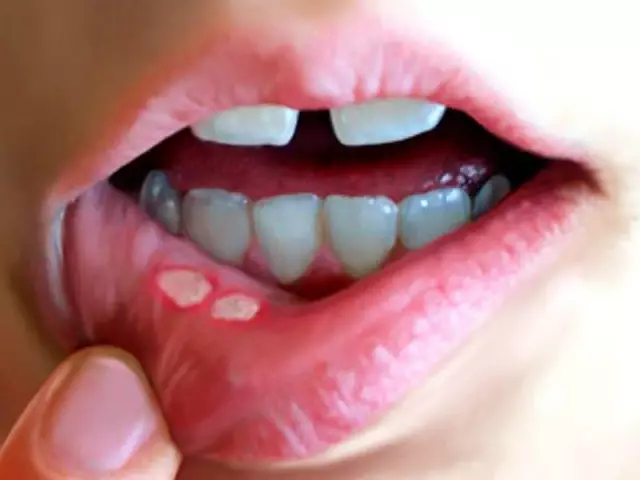
Aphthous stomatitis in children: treatment
The goal of the treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children is the complete elimination of the disease or its stable remission. This is achieved using both local and general therapy, the choice of which depends on the clinical picture of the disease.
Basically, the treatment consists in antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and directly aft. You can rinse the mouth with special solutions (furacilin, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine) or decoctions from medicinal plants.
If necessary, in order to improve the general condition of the patient, antiallergic, antipyretic and other drugs (containing heparin, novocaine, lidocaine, hydrocortisone, etc.) can be used.
It is possible to accelerate the healing of aft using citral solutions, preparations with propolis and vitamins C and P.
When a viral infection is the cause of stomatitis in children, antiviral therapy is performed.
If aphthous stomatitis is left unattended and left untreated, after about 1-2 weeks the aphthae will disappear on its own, and the disease may turn into a chronic stage, which is very difficult to cure completely.
Herpetic stomatitis in children: treatment
The main principle in the treatment of herpetic stomatitis in children is complexity, that is, a combination of general therapy and local procedures.
If the baby has symptoms of intoxication, it is necessary to drink plenty of fluids and take medications that lower the temperature. A severe form of the disease is treated permanently.
Local therapy consists of treating the oral cavity with propolis. This substance has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. To relieve the symptoms of inflammation, chamomile or sage baths are used. For a baby who still does not know how to rinse his mouth, parents carry out the treatment of the oral cavity on their own.
During the healing period, drugs are prescribed to help restore the damaged mucous membrane. These are keratoplasty, which include sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil and vitamin A.
Treatment of stomatitis in children according to Komarovsky
There are many different tactics for treating stomatitis in a child. When choosing a technique, you should adhere to the recommendations of a specialist, for example, Dr. Komarovsky.
Treatment of stomatitis in children according to Komarovsky has long proven its effectiveness and speed.
You can choose competent tactics based on the stage and severity of the course of the disease. Therapy should include both local and general treatment.
First of all, it is necessary to organize rational and correct feeding of the child. Before eating, it is advisable to anesthetize the oral mucosa with a solution of lidochlorgel or anesthesin. It is mandatory to clean the mouth after feeding. To do this, you can use a solution of potassium permanganate, furacilin or strong tea.
Food should be semi-liquid or liquid and not irritate the mucous membranes.

The tasks of local therapy for acute stomatitis are as follows:
- Maximum relief or relief of oral pain;
- Prevention of repeated rashes;
- Accelerated healing of rash elements.
Stomatitis does not appear immediately, the first manifestations are expressed in mild edema and redness on the oral mucosa. The child is capricious, refuses to eat, complains of pain in the mouth.
If parents notice the signs of the disease in time and start treatment, then the acute stage of the disease will not develop. Despite this, the treatment of stomatitis in children, even in a mild form, should be dealt with by a qualified specialist who will prescribe effective therapy and talk about preventive measures in the future.
YouTube video related to the article:
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.