- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
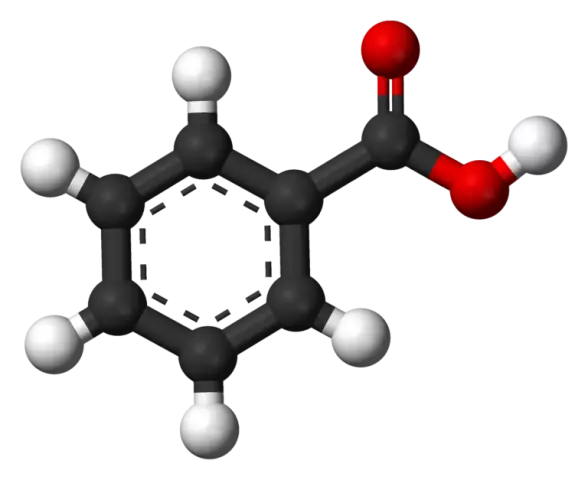
Propionic acid

Propionic acid is a colorless, caustic liquid with a characteristic, rather pungent odor.
Physical and chemical properties of propionic acid
Propionic acid has the following chemical formula: CH 3 CH 2 COOH. At a temperature of 440 degrees Celsius, it can spontaneously ignite. Mixes well in various proportions with organic solvents and water.
By its chemical properties, propionic acid is one of the typical representatives of the class of saturated carboxylic acids. It enters into various types of chemical reactions with the formation of acid halides, amides, ethers and other compounds.
Getting propionic acid
This chemical compound was first synthesized by Johan Gottlieb in 1844 as one of the by-products of the decomposition of sugars. In the future, it was obtained by other chemists in various ways, without realizing that in fact it was one and the same substance. And only three years later Jean Baptiste Dumas established this fact and gave the name to the new substance - propionic acid.
Currently, the production of propionic acid on an industrial scale is carried out by carbolation of ethylene in the presence of a nickel catalyst and water, with further oxidation of the propionic aldehyde obtained as a result of the first reaction.
Some types of bacteria form propionic acid during their life. For example, as a result of enzymatic fermentation, Emmental cheese contains about 1% of this substance.
Propionic acid in foods

Propionic acid has pronounced bactericidal and fungicidal properties, i.e. prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Therefore, many manufacturers add propionic acid to food as a preservative called E-280.
Directly propionic acid or ammonium propionate (ammonium salt of propionic acid) are used only for the manufacture of products intended for animal nutrition. Propionic acid may only be added to products intended for humans in the form of its calcium or sodium salts (calcium propionate or sodium propionate).
In Russia, it is allowed to add propionic acid to products in the following quantities:
- In rye and prepackaged sliced wheat bread - up to 3.0 g per kilogram;
- In pita bread, baked goods - up to 2.0 g per kilogram;
- In Easter cakes - up to 1.0 g per kilogram;
- In cheeses and their analogues - in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN 2.3.2.1293-03.
Propionic acid has a pronounced odor and taste. Therefore, with all the desire, food manufacturers cannot add it to their products in a concentration of more than 0.3%. Most often, this food additive is used for canning baked goods. It can also be used to preserve whey during transportation.
Propionic acid harm
This supplement is considered practically safe for human health. These data are confirmed by the results of numerous scientific studies, which indicate that in small quantities, propionic acid does not have mutagenic, teratogenic and other properties dangerous to the human reproductive system. In addition, in the human body, propionic acid is very quickly oxidized and its metabolites (decomposition products) are naturally excreted.
But there is also the opinion of independent experts who believe that the food additive E-280 should be included in the list of carcinogenic substances. Therefore, if you have a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of malignant neoplasms, then it is best for you to stop eating foods that contain propionic acid or its salts.
For those working with propionic acid, safety precautions are important. If concentrated propionic acid comes into contact with the skin and mucous membranes, severe burns occur. And if ingested, it leads to the formation of ulcers and wounds in the mouth, pharynx, esophagus and stomach.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.