- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Xalak
Ksalakom: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. Use in the elderly
- 12. Drug interactions
- 13. Analogs
- 14. Terms and conditions of storage
- 15. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 16. Reviews
- 17. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Xalacom
ATX code: S01ED51
Active ingredient: latanoprost (Latanoprost) + timolol (Timolol)
Manufacturer: Pfizer MFG. Belgium N. V. (Pfizer MFG. Belgium NV) (Belgium) (Belgium)
Description and photo update: 2018-27-11
Prices in pharmacies: from 689 rubles.
Buy

Ksalakom is a combined antiglaucoma remedy.
Release form and composition
The drug is produced in the form of eye drops: a clear, colorless liquid (2.5 ml each in a polyethylene dropper bottle, in a cardboard box with first opening control, 1 bottle and instructions for using Xalacom).
Composition of 1 ml of eye drops:
- active ingredients: timolol maleate - 6.83 mg (which corresponds to the content of timolol - 5 mg); latanoprost - 0.05 mg;
- additional components: sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, benzalkonium chloride (in the form of a 50% solution), sodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous, sodium chloride, water for injection.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Ksalakom, is an antiglaucoma drug that contains an analogue of prostaglandin F 2α (latanoprost) and a non-selective β 1 - and β 2 -adrenergic blocker (timolol). These active components have a different mechanism of influence on increased intraocular pressure (IOP), which leads to a more pronounced decrease in the latter in comparison with the effect observed when each of them is used as a monotherapy drug.
Latanoprost
The active substance belongs to the selective agonists of the FP prostanoid receptors, helps to reduce IOP as a result of increased outflow of aqueous humor, mainly by the uveoscleral route and through the trabecular network. Latanoprost has no significant effect on the production of aqueous humor and the degree of permeability of the blood-ophthalmic barrier.
Against the background of a short-term course of therapy with latanoprost, in patients with pseudophakia, no leakage of fluorescein into the posterior segment of the eye was noted. When using the drug in therapeutic doses, no pronounced pharmacological effect on the respiratory and cardiovascular systems was revealed.
Timolol
Being a non-cardioselective β-adrenergic blocker, which is not characterized by significant internal sympathomimetic activity, timolol does not show a direct depressive effect on the myocardium, and also does not have a local anesthetic (membrane stabilizing) effect. Blockade of β-adrenergic receptors initiates a decrease in cardiac output in healthy people and in patients with heart disease. In the presence of severe myocardial dysfunction, β-blockers can interfere with the stimulating effect of the sympathetic nervous system, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the heart.
In the bronchi and bronchioles, the blockade of β-adrenergic receptors causes an increase in airway resistance due to the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system. This effect may pose a threat to the health of patients with bronchial asthma and other bronchospastic diseases.
The use of timolol maleate in the form of eye drops provides a decrease in elevated and normal IOP both in the presence and in the absence of glaucoma. Increased IOP refers to the main risk factors for glaucomatous loss of visual fields. The likelihood of this complication, as well as damage to the optic nerve, increases with increasing fluid pressure inside the eye.
The exact mechanism of lowering IOP as a result of exposure to timolol maleate has not been identified. According to the results of tonography and fluorophotometry, it may be associated with a decrease in the production of aqueous humor. However, during individual studies, a slight increase in the outflow of aqueous humor was also found. In addition, it is possible to suppress the enhanced synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) caused by endogenous β-adrenergic stimulation. On the permeability of the blood-ophthalmic barrier, no effect of timolol was found.
The initial effect of the combined use of timolol maleate and latanoprost is observed already within 1 hour after the instillation of Xalacom, and the maximum therapeutic effect is observed within 6-8 hours. In the case of repeated use of the drug after its administration, an adequate decrease in IOP persists for 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic interactions between timolol maleate and latanoprost have not been reported. However, 1-4 hours after the introduction of Ksalacom in aqueous humor, an increase in the level of latanoprost acid was found approximately 2-fold when compared with monotherapy.
Latanoprost
The active substance, being a prodrug, actively penetrates through the cornea, in the process it is hydrolyzed to form an acid, a biologically active form. The maximum concentration (C max) in aqueous humor is observed 2 hours after topical use, the systemic bioavailability of latanoprost acid after instillation is 45%.
The volume of distribution of the substance (V d) is 0.16 ± 0.02 l / kg. In aqueous humor after topical application of Xalacom, latanoprost acid is detected during the first 4 hours, and in plasma - only during the first hour. The substance binds to plasma proteins by 87%.
Latanoprost hydrolysis occurs under the influence of esterases in the cornea of the eye with the production of acid, which, entering the systemic circulation, is metabolized mainly by beta-oxidation of fatty acids in the liver. As a result, 1,2-dinor- and 1,2,3,4-tetranor-metabolites are formed. The half-life (T 1/2) of latanoprost acid from plasma is 17 minutes, plasma clearance is 0.4 l / h / kg. Metabolites are eliminated mainly by the kidneys: approximately 88% of the dose is excreted in the urine after local use.
Timolol maleate
After the introduction of eye drops in aqueous humor, the C max of timolol maleate is reached after 1 hour. Part of the dose used is absorbed systemically and the C max of the substance in the plasma at a level of 1 ng / ml is noted 10-20 minutes after the drug is administered 1 time per day, 1 drop in each eye (0.3 mg).
The metabolic transformation of timolol maleate proceeds intensively in the liver, T 1/2 is approximately 6 hours. Metabolites and small amounts of unchanged substances are excreted in the urine.
Indications for use
Ksalakom is recommended for use in patients with open-angle glaucoma or increased ophthalmotonus to reduce increased fluid pressure inside the eye with insufficient effect of therapy with other topical drugs that reduce IOP.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- atrioventricular blockade (AV-blockade) of II - III degree without pacemaker control;
- sinus bradycardia;
- sinoatrial blockade;
- sick sinus syndrome (SSS);
- cardiogenic shock;
- clinically significant heart failure;
- severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- reactive diseases of the respiratory tract, including bronchial asthma or a history of it;
- age up to 18 years;
- hypersensitivity to any of the constituents of the drug.
Relative (Xalak should be used with extreme caution):
- open-angle glaucoma in combination with pseudophakia;
- inflammatory, neovascular, congenital or angle-closure glaucoma;
- pigmentary glaucoma (due to insufficient experience in treatment with Xalacom);
- aphakia, pseudophakia with rupture of the posterior capsule of the lens;
- the presence of risk factors for macular edema (when using latanoprost, cases of macular edema, including cystoid edema, have been recorded);
- a history of herpetic keratitis;
- AV blockade of the I degree (β-blockers have a negative effect on the time of the impulse in the myocardium);
- violations of peripheral circulation (including severe forms of Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's syndrome);
- the presence of corneal diseases (the drug can cause dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes).
It is recommended to avoid the use of Xalacom in the presence of active herpetic keratitis and recurrent herpetic keratitis, especially if it is associated with treatment with prostaglandin F 2α analogues.
For patients with COPD, timolol is prescribed only if the potential benefit from its use for the patient outweighs the likelihood of developing negative adverse reactions.
Ksalakom, instructions for use: method and dosage
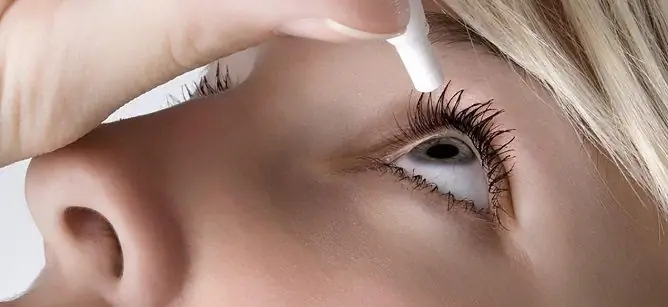
Ksalakom eye drops are recommended to be instilled in adults (including the elderly) 1 time per day, 1 drop in one or both eyes.
To reduce the risk of possible systemic effects, immediately after the introduction of each drop, you should press for 2 minutes on the lower lacrimal opening, located on the lower eyelid at the inner corner of the eye.
If a dose is missed, the next day, instillation is carried out at the usual time, introducing 1 recommended dose (without doubling it).
Side effects
Violations noted against the background of the use of Xalacom:
- organ of vision: very often - increased pigmentation of the iris; often - increased lacrimation, photophobia, eye pain, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, visual impairment, conjunctival hyperemia, refractive errors, cataracts, conjunctival lesions (including punctate hemorrhages, papillary reactions of the conjunctiva, follicles), eye irritation burning sensation / itching in the eyes), corneal lesions (including keratitis, erosion, punctate keratitis, pigmentation), loss of visual fields;
- metabolism: often - hypercholesterolemia;
- endocrine system: often - diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular system: often - increased blood pressure (BP);
- nervous system: often - headache;
- mental disorders: often - depression;
- musculoskeletal system: often - arthritis;
- skin and subcutaneous tissues: often - hypertrichosis, rash, pruritus and skin changes (including dermatochalasis, irritation);
- infections and invasions: often - infections of the upper respiratory tract, sinusitis, and other infections.
Below are the side effects recorded when using the active components of Xalacom as monotherapy drugs (with the exception of the disorders mentioned above).
Latanoprost:
- organ of vision: eye irritation (itching, burning sensation, tingling sensation, feeling of sand in the eyes or a foreign body); iritis / uveitis; edema of the eyelids, temporary point erosion of the corneal epithelium, keratitis; thickening, lengthening, increased pigmentation and an increase in the number of eyelashes and vellus hair, a change in the direction of eyelash growth, sometimes leading to eye irritation (these changes in eyelashes are reversible and disappear after completion of therapy); photophobia, blurred vision; macular edema (in the presence of aphakia, pseudophakia with rupture of the posterior lens capsule or risk factors for macular edema), including cystoid; changes in the periorbital region and eyelids, causing a deepening of the sulcus of the upper eyelid, iris cysts, periorbital edema;
- respiratory system: shortness of breath, asthma (including acute attacks or exacerbation of the disease with a history of bronchial asthma);
- nervous system: dizziness;
- musculoskeletal system: muscle / joint pain;
- cardiovascular system: palpitations, exacerbation of angina pectoris in patients with ischemic heart disease (CHD);
- infections and invasions: herpetic keratitis;
- skin and subcutaneous tissue: local skin reactions on the eyelids, rash, darkening of the eyelid skin (may be reversible);
- others: nonspecific chest pain.
Timolol (as eye drops):
- organ of vision: symptoms and signs of eye irritation (redness, increased lacrimation, burning sensation / sand in the eyes, itching); cystoid macular edema, decreased corneal sensitivity; dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes, blurred vision, keratitis, blepharitis, detachment of the choroid after filtration surgery, corneal erosion; visual impairment, including diplopia and changes in refraction, ptosis;
- nervous system: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, acute disorders of cerebral circulation, cerebral ischemia, increased symptoms of myasthenia gravis, paresthesia, fainting;
- mental disorders: behavioral changes and mental disorders such as anxiety, nervousness, insomnia, confusion, symptoms of depression, hallucinations, disorientation, depression and nightmares, memory loss;
- cardiovascular system: lowering blood pressure, cold hands and feet, Raynaud's syndrome, palpitations, intermittent claudication, progression of angina pectoris, arrhythmia, AV block, intracardiac conduction block, chronic heart failure, bradycardia, cardiac arrest;
- respiratory system: nasal congestion, cough, bronchospasm (mainly in the presence of previous bronchospastic diseases), shortness of breath, respiratory failure and pulmonary edema;
- organ of hearing and vestibular apparatus: tinnitus;
- digestive system: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, dry mouth, impaired taste, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- metabolism: hidden symptoms of hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus;
- allergic reactions: pruritus, urticaria, systemic allergic reactions, including angioedema, anaphylaxis, anaphylactic reactions, localized and generalized rash;
- musculoskeletal system: myalgia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE);
- skin and subcutaneous tissues: skin rash, alopecia, pseudo-pemphigoid, exacerbation of psoriasis or psoriasis-like rash;
- reproductive system: impotence, decreased libido, Peyronie's disease, sexual dysfunction;
- others: asthenia / fatigue, anorexia, edema, chest pain.
It is extremely rare with significant damage to the cornea that there have been cases of corneal calcification associated with the use of phosphate-containing eye drops.
Overdose
- latanoprost: against the background of an overdose, conjunctival hyperemia and eye irritation were observed. In case of unintentional oral administration of Xalacom, it should be borne in mind that 2.5 ml of solution contains 0.125 mg of latanoprost. Over 90% of this substance undergoes metabolic transformation during the first passage through the liver. Intravenous infusion of latanoprost at a dose of 0.003 mg / kg did not show any disturbances in healthy volunteers, but dizziness, abdominal pain, nausea, hot flashes, fatigue were noted with the introduction of the drug at a dose of 0.0055-0.01 mg / kg, sweating. After completion of the infusion, these effects subsided after 4 hours. In the presence of moderate bronchial asthma, administration of latanoprost in an amount 7 times higher than the therapeutic dose did not lead to bronchospasm;
- timolol maleate: in case of an accidental overdose of eye drops, violations were recorded similar to those with the systemic use of β-blockers: shortness of breath, headache, dizziness, bronchospasm, bradycardia, cardiac arrest. In vitro studies have shown that timolol is readily cleared by dialysis from whole blood or plasma, but it is less dialyzed in patients with renal failure.
In case of an overdose of Ksalakom, symptomatic treatment is performed.
special instructions
If it is necessary to use several eye drops at the same time, they should be administered at intervals of at least 5 minutes.
Ksalakom eye drops should not be used more than 1 time per day, since more frequent use weakens the effect of lowering IOP.
The preparation contains benzalkonium chloride, which can be absorbed by contact lenses. There are reports that this component can cause the appearance of punctate keratopathy and / or toxic ulcerative keratopathy. Benzalkonium chloride can also cause eye irritation and discoloration of soft contact lenses. Patients who use Xalac often or for a long time, in the presence of dry eye mucosa or in the occurrence of conditions that damage the cornea, require careful monitoring of the condition. Before instillation, contact lenses must be removed and then installed 15 minutes after the procedure.
Latanoprost
Latanoprost can cause a gradual increase in the concentration of brown pigment in the iris. Increased pigmentation was noted in 16-20% of cases among all patients who used Xalacom for 1 year (based on photographic fixation). The change in the color of the iris is associated with an increase in the amount of melanin in its stromal melanocytes, and not with an increase in the number of melanocytes themselves. As a rule, this effect is insignificant and cannot always be determined clinically. A change in the color of the iris of one or both eyes is observed in the overwhelming majority in persons with a mixed color of the iris, the basis of which is brown. Latanoprost does not affect the lentigo and nevi of the iris; pigment deposition was not observed in the anterior chamber of the eye or trabecular meshwork.
The level of decrease in IOP does not depend on the degree of increase in the concentration of brown pigment in the iris. As a result, therapy can be continued with increased iris pigmentation, but in this case, patients require regular monitoring. The use of Xalacom may be discontinued depending on the clinical picture.
Increased pigmentation is noted mainly during the first year of therapy, much less often - the second or third. After 4 years of treatment, this reaction was not recorded. The rate of progression of color change decreases over time and stabilizes after 5 years. After the completion of therapy, there was no increase in the brown pigmentation of the iris, but the change in eye color may be irreversible.
Patients who use an ophthalmic agent to treat only one eye have an increased risk of developing heterochromia.
Timolol maleate
With local use of β-blockers, the development of the same adverse reactions is possible as against the background of their systemic use.
Patients with a history of severe heart disease require constant monitoring of the condition for the timely detection of symptoms of heart failure.
Before a major surgical intervention, it is necessary to assess the feasibility of gradual discontinuation of the use of β-blockers. Cases of prolonged severe arterial hypotension during anesthesia and difficulties in restoring and maintaining cardiac activity have been described. During surgery, such undesirable reactions can be eliminated by using adequate doses of adrenergic receptor agonists.
Drugs that have a β-adrenergic blocking effect are able to suppress the systemic agonistic effect of epinephrine, therefore, prior to surgery, it is necessary to inform the anesthesiologist that the patient is receiving timolol.
During the period of therapy with β-adrenergic receptor blockers, an increase in the hypoglycemic effect of oral hypoglycemic agents and masking of the manifestations and symptoms of hypoglycemia may be observed. Therefore, Xalak must be used with extreme caution in patients with diabetes mellitus (especially labile course) or with spontaneous hypoglycemia, taking oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin.
Therapy with β-adrenergic receptor blockers can mask the signs of hyperthyroidism, as a result of which a sudden cessation of their use can lead to an exacerbation of this disease.
When using β-blockers in patients with a history of indications of atopy or severe anaphylactic reactions to various allergens, it is possible to increase the response with repeated contact with these allergens. It should be borne in mind that in this case, the effect of epinephrine (adrenaline), used in usual doses to stop anaphylactic reactions, may be insufficient.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
Instillations of Xalacom can cause short-term blurred vision. Until this violation is removed, patients should not get behind the wheel of a car or operate other complex equipment.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy, adequate and well-controlled studies of the safety of Xalacom therapy have not been conducted. In the process of epidemiological investigations against the background of taking oral β-blockers, no cases of fetal malformations were recorded, at the same time, there was an increased threat of intrauterine growth retardation. Also, in newborns whose mothers received β-blockers during pregnancy, symptoms and signs of β-adrenergic receptor blockade were revealed (including decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, impaired respiratory function, hypoglycemia). If a pregnant woman has used β-blockers, the newborn needs careful monitoring in the first days of life.
In view of the above, the use of Xalacom during pregnancy is allowed only if the expected benefit of therapy to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Latanoprost and its metabolites can pass into breast milk, timolol maleate is also found in breast milk when used in the form of eye drops. If the appointment of an ophthalmic drug is necessary during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Pediatric use
The use of Xalacom in patients under 18 years of age is contraindicated due to the lack of data confirming its effectiveness and safety in adolescents and children.
Use in the elderly
Elderly people do not need to adjust the dose of Xalacom.
Drug interactions
Special studies on the interaction of Xalacom with other drugs / agents have not been conducted.
Interaction reactions that can be observed when Xalacom or one of its active components is combined with other medicinal substances / preparations:
- analogs of prostaglandins: a paradoxical increase in IOP may occur with the combined instillation of 2 prostaglandin analogs into the eyes; the simultaneous use of 2 or more prostaglandins, their derivatives or analogues is not recommended;
- other β-blockers (oral administration): may worsen the systemic manifestations of these drugs or a more significant decrease in IOP; this combination should be avoided;
- epinephrine (adrenaline): there is a risk of mydriasis when combined with timolol maleate;
- agents leading to a decrease in the content of catecholamines; blockers of slow calcium channels, cardiac glycosides, antiarrhythmic substances, β-blockers, guanethidine: their additive effect with timolol maleate may be noted, causing systemic arterial hypotension and / or severe bradycardia;
- inhibitors of the isoenzyme CYP2D6 (paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine): when combined with timolol, systemic β-blockade may increase (depression, decreased heart rate);
- clonidine: with its sudden cancellation, hypertension increases, the combined use of clonidine with β-blockers can increase the severity of this reaction.
Analogs
Analogs of Ksalakom are: Duoprost, DuoTrav, Taptikom, Azarga, Kosopt, Ksalatan, Latanoprost-Teva, Combigan, Ganfort, Ksalatamax, etc.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store in a place protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature of 2-8 ° C.
Shelf life is 2 years.
After opening, the dropper bottle with eye drops should be stored at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C for no more than 4 weeks.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Xalakom
According to a few reviews, Xalakom effectively and quickly reduces IOP, preventing its indicators from rising to critical values and helping to improve the state of the organs of vision in glaucoma. At the same time, patients often indicate the development of a large number of side effects during treatment. The disadvantages of the drug also include a significant number of contraindications and its high cost. In all reviews, it is noted that it is necessary to use this ophthalmological agent only as directed by a doctor and under his supervision.
Price for Ksalakom in pharmacies
The price of Ksalakom is approximately 640-720 rubles. per bottle containing 2.5 ml.
Ksalakom: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Ksalakom eye drops 2.5 ml 1 pc. 689 r Buy |
|
Ksalakom eye drops 2.5ml 874 RUB Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!