- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Epidermal cyst

An epidermal cyst is a spherical formation that consists of the epithelium, hair follicle, and epidermis. This cyst is located on the face, scalp, neck, chest, and scrotum. An epidermal cyst can be both benign and malignant.
Causes and symptoms of an epidermal cyst
The main cause of an epidermal cyst is blockage of the hair follicle, increased sebum production and filling of the cavity with horny masses.
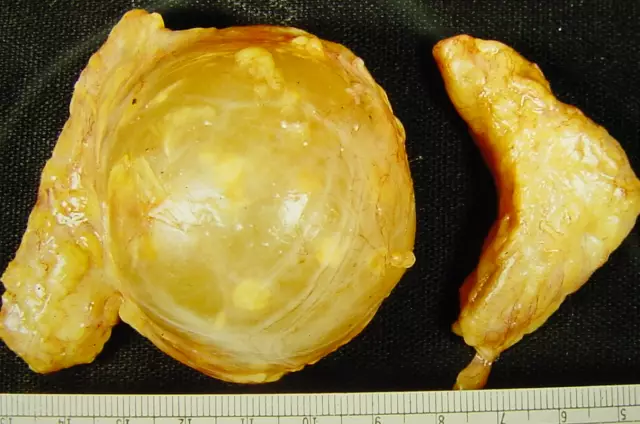
This cyst looks like a pinkish node with a diameter of 2 to 5 cm, covered with a network of dilated capillaries. Sometimes the pores of the epidermal cyst become dark in color and become enlarged. Inside the cyst is a thick, pasty mass of yellow tint.
If a bacterial infection enters the cyst, an inflammatory process begins, accompanied by a thickening of the cyst and severe pain.
An enlarged epidermal cyst can exert pressure on the structure of the brain, causing vision problems, headaches, weakness, irritability and imbalance. These symptoms are similar to the manifestations of various neoplasms and brain tumors. Some types of epidermal cysts can lead to meningitis.
Types of epidermal cysts
Epidermal cyst has several types, differing in structure, clinical manifestation and the presence of complications.
The most common occurrence in patients is atheroma, which is a skin cyst located on the face, arms, neck, and genitals. Atheroma can be both single and multiple. It is a formation of a round tumor-like type with a soft consistency. The skin around the atheroma has a yellowish or reddish tint, and the surrounding tissues are painless.
This cyst can remain the same size or gradually grow, rising above the surface of the skin. Often the epidermal cyst is prone to suppuration and inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue.
Diagnosis of the disease

Cystic tumors of the epidermal type are diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging or by scanning the brain with computed tomography.
If the epidermal cyst is located in the brain, then examinations of the pituitary gland and auditory canals are carried out in order to obtain detailed details of the state of the tumor and select the correct method of treatment.
Epidermal cyst treatment
In most cases, an epidermal cyst is treated with surgical removal. If the cyst is located close to important structures of the brain, then its complete removal is impossible. The neurosurgeon carries out an intermediate removal of the cyst, and for several years, they carry out regular magnetic resonance imaging studies to exclude the recurrence of the disease.
The main treatment for a malignant epidermal cyst is chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Atheroma of small size, asymptomatic, does not require surgical intervention. With an increase in the size of the cyst, an operation is prescribed under local anesthesia.
The epidermal cyst, which is located above the outer skin, is removed within 15-20 minutes. After the introduction of a solution of novocaine or other anesthetic, the doctor makes an incision in the center of the cyst and removes its contents with the capture of the capsule, and then scrapes the cavity and cleans the skin.
In case of recurrence of the epidermal cyst, a repeated surgical intervention is prescribed.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!