- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Strongyloidosis
General information about the disease
Strongyloidosis is a chronic disease that manifests itself in various pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The causative agent of the infection - intestinal eel (Strongyloides stercoralis) - was first described by the French physician Normand, who isolated it from the feces of sick people in 1876. Over the next decades, strongyloidosis was studied quite well, however, in recent years, interest in this disease has increased significantly due to the fact that it is often found in people suffering from AIDS.
The source of strongyloidosis is always a person, or rather his feces, with which the eggs enter the external environment. In soil, the larvae hatch and then transfer to a new host through the skin or by eating contaminated food. In both cases, parasites migrate to the stomach and intestines, where females lay new eggs. As a rule, the analysis (strongyloidosis is quite accurately determined by stool samples) shows the presence of pathogens in the area of the Lyuberkun glands of the duodenum, but in the absence of treatment for strongyloidosis, the eel captures new territories and is often found throughout the small intestine and even in the pyloric section of the stomach.
Strongyloidosis symptoms
Since parasites are localized in a wide variety of organs and tissues, the clinical manifestations of strongyloidosis are very diverse. However, during the first 2-3 weeks, the disease is latent and almost asymptomatic. The first alarming symptoms of strongyloidosis appear only after the end of the incubation period and last for several years, and remissions can be replaced by sharp exacerbations.
Symptoms of strongyloidosis include:
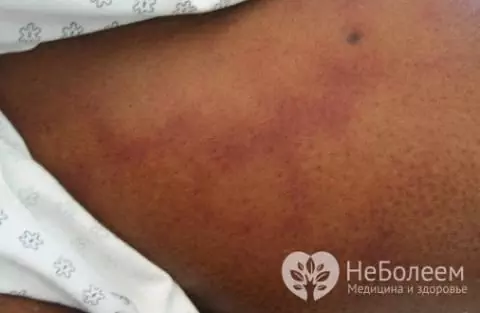
- allergic reactions in the form of skin rashes and blisters of pinkish-red color;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood;
- stomach ache;
- persistent diarrhea;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera (does not always appear).
Skin rashes with strongyloidosis last for 2-3 days, after which they disappear without leaving any traces. When diagnosed with strongyloidosis, skin symptoms appear several times a year, which is associated with the migration of parasites through the circulatory system. During periods of exacerbation, patients complain of dizziness, sleep disturbances, and weakness. Sometimes pulmonary pathologies caused by the release of larvae into the lumen of the bronchi are added to these symptoms of strongyloidosis.
When the disease becomes chronic, the clinical picture changes. Depending on the available manifestations, doctors distinguish several common forms of strongyloidosis:
- duadeno-bilious form of strongyloidosis - characterized by a slow course, dull aching pains in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite. Studies (x-ray, ultrasound) reveal deformities of the gallbladder;
- gastrointestinal form of strongyloidosis - manifested by clear signs of indigestion - prolonged constipation or, conversely, rampant diarrhea. The stool contains impurities of blood and mucus. The patient's tongue is coated;
- neuro-allergic form of strongyloidosis - severe itchy rashes appear on the skin. They quickly disappear, but the rash is replaced by headaches, sleep disturbances, irritability and weakness;
- pulmonary - the pathogen is localized in the respiratory system and provokes various pulmonary diseases.
Despite the abundance of forms, in medical practice the most common is mixed strongyloidosis, the symptoms of which combine the main lesions of all vital systems of the body. The most strongly destructive processes are manifested in people with weakened immunity.
Strongyloidosis - treatment of the disease
Mintezol (thiabendazole) and albendazole are used as the main drugs. The course of treatment for strongyloidosis lasts several days, after which the patient undergoes repeated tests for strongyloidosis for possible correction of the recovery process. Symptomatic remedies are used to relieve the strongest signs of the disease.
Prevention of strongyloidosis
Prevention of strongyloidiasis is aimed at early detection of patients and counteraction to environmental contamination with faeces. For disinfection of feces, bleach is used. The soil is cleaned with the pesticide carbation and various fertilizers (phosphate, nitrogen, potassium). Personal hygiene is also essential. It is advisable to give up walking on the ground barefoot, without the need not to contaminate the skin with earth, thoroughly wash vegetables, fruits and berries. For work in household plots, it is advisable to use special gloves and wash your hands before eating.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!