- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Plantar wart
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
Plantar warts treatment
- Electrocoagulation
- Cryodestruction
- Removal with a laser
- Surgical excision
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
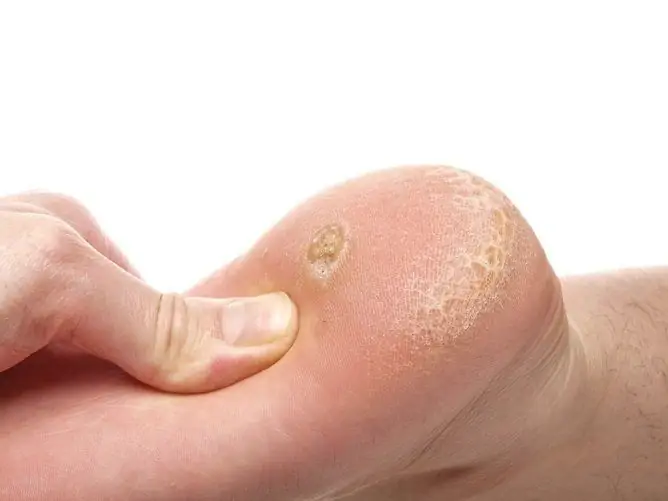
A plantar wart is a hard, flat, benign skin lesion that accounts for approximately 35% of the total number of warts. The location of the wart leads to its permanent injury and the occurrence of pain when walking. Plantar warts can appear at any age, but they are most often diagnosed at 20-30 years old, as well as in children and the elderly. A plantar wart in a child most often occurs after five years and practically does not occur in newborns.
Plantar warts can cause temporary loss of performance.

Large plantar warts require surgery
Causes and risk factors
The infectious agent for plantar warts is the human papillomavirus (HPV, papillomavirus), which can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or through common objects. Human papillomavirus is one of the most common viruses in the world; according to some data, carriage is observed in 90% of the adult population. When it enters the human body, the virus infects the basal layer of the epithelium, while the zone of transition of the multilayer flat epithelium is more susceptible to damage. In an infected cell, the virus can exist in an episomal form (outside the cell's chromosomes), which is considered benign, or in an introsomal form (incorporated into the cell's genome), which is malignant. A person can be simultaneously infected with several types of papillomavirus.
Infection is facilitated by irritation of the skin, as well as microtrauma (cuts, scratches, abrasions, etc.). The risk of developing a plantar wart increases with immunodeficiency states, as well as with frequent stressful situations. The most favorable environment for the development of the virus is a warm and humid environment. For this reason, infection often occurs in a bath, sauna, pool, gym. Since the virus dies quickly in direct sunlight, infection on public beaches is unlikely. Infection is possible when walking barefoot in rooms where a patient with a plantar wart lives. In this case, the disease can manifest itself several months after infection.

Plantar wart occurs in people infected with human papillomavirus (HPV)
In addition, risk factors include:
- diseases that lead to a violation of the trophism of the tissues of the foot (atherosclerosis, varicose veins of the lower extremities, diabetes mellitus);
- frequent diseases of infectious etiology;
- the presence of chronic pathological processes in the body;
- foot deformities (with arthritis of small joints of the foot, deforming osteoarthritis, flat feet);
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis), or, on the contrary, dryness of the skin of the feet;
- insufficient night sleep;
- poor nutrition;
- wearing tight, uncomfortable, low-quality (breathable) shoes;
- abuse of certain cosmetic procedures (peeling, hair removal);
- non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Forms of the disease
There are several types of warts:
- about byknovennye (vulgar) warts - painless greyish-white dense dry bumps that tend to merge to form large plaques;
- flat warts - painless flat nodules that are round or irregular
- genital warts - small nodules that can merge into large groups;
- filamentous warts are long appendages of the skin that usually appear on the neck, eyelids, near the lips, under the nose, and in the armpits.
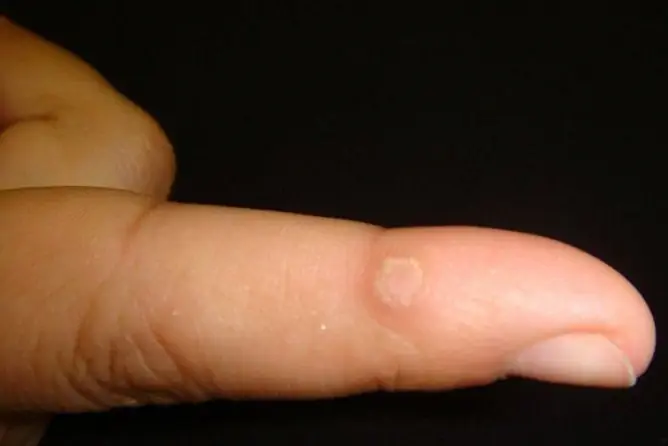
Plantar warts are a type of common warts that usually form on the skin of the toes or on the heels (where the shoe pressure is most).
Symptoms
A plantar wart is a 1-2 cm hard lump on the skin of the foot that is usually round or oval in shape. The neoplasm rises above the skin surface by about 1-3 mm. Its color at the beginning of the disease, as a rule, does not change, but it can be pink or light brown.

Brown-black dots occur when the capillaries of the plantar wart are thrombosed
In the initial stages of development, the surface of the plantar wart is smooth. As the pathological process develops, the wart becomes covered with layers of keratinized epithelium, becomes rough and becomes grayish-yellow in color. Sometimes a crater-like depression appears in the central part. Thrombosis of superficial capillaries in the affected area can lead to the appearance of brown-black dots on the surface. Usually, the neoplasm is single, the occurrence of several plantar warts may indicate high HPV activity. Multiple plantar warts form a mosaic pattern on the skin. As a rule, warts are not painful in themselves, but they can be injured when walking, bleed and cause severe discomfort and sometimes severe pain. Unlike calluses, plantar warts are more sensitive to friction.
Diagnostics
A plantar wart may have the appearance of a callus or cutaneous hyperkeratosis. To differentiate with these pathological processes, the dermatoscopy method is used. The identification of thrombosed capillaries in the affected area and the absence of a skin pattern on the surface of the neoplasm are evidence in favor of a plantar wart.

To diagnose a plantar wart, a scraping study is performed by PCR
In order to identify the infectious agent, a study of scraping from the affected area is carried out using the polymerase chain reaction method. To determine the depth to which the plantar wart has grown, they resort to ultrasound if necessary. If you suspect a malignant neoplasm, an oncologist should be consulted.
Differential diagnosis is required with keratoderma of the soles in Reiter's syndrome, palmar-plantar syphiloids, and similar conditions.
Plantar warts treatment
In about 27% of cases, there is a complete self-resolution of the plantar wart within 3-4 weeks. In this case, no traces remain on the skin of the foot. However, in most cases, due to permanent injury, the plantar warts do not self-heal. Compared to other types, plantar warts are more difficult to heal.
As a local therapy at the initial stage of the development of plantar warts, keratolysis is used, that is, exfoliation of dead epithelial cells using keratolytic agents. Such treatment of plantar warts is carried out with the help of preparations containing salicylic acid. To remove the neoplasm, daily warm foot baths are recommended for 5-10 minutes, then the feet are dried, the soles in the neoplasm are treated with pumice stone, followed by the application of an occlusive plaster or bandage to the wart. In this case, the upper layer of the affected area must be removed daily with a pumice stone, which facilitates the penetration of the drug into the interior. An important condition for the effectiveness of this method of treatment is the regularity of the procedure. Complete cure occurs within three months in 10-15% of patients.

Warm foot baths and pumice stone to help get rid of plantar wart
There are several techniques for removing plantar warts.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation - removal of a plantar wart by means of a surgical coagulator that generates a high frequency current. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. The wart is cut off with an electrode, which coagulates the tissue adjacent to the neoplasm. Electrocoagulation avoids bleeding and tissue infection at the site of intervention. The removed material is saved and sent to the laboratory for histological analysis. In case of deep germination of the wart, after its removal, a light, inconspicuous scar may remain on the skin of the foot. Electrocoagulation is not suitable for removing large or deep plantar warts.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction of the plantar wart with liquid nitrogen is carried out using a cold applicator. The freezing time depends on the size of the neoplasm and ranges from half to one minute. When removing plantar warts by cryodestruction, it is necessary to accurately calculate the depth of exposure (if too intense exposure may leave a noticeable scar, if insufficient exposure increases the risk of recurrence of the wart in the same place). The procedure is carried out several times with an interval of 3-5 days. After cryotherapy, an epidermal bladder appears at the site of exposure, which then gradually transforms into a dense crust, after the rejection of which an inconspicuous pink spot remains on the skin. This method is the most popular way to remove plantar warts.since it is characterized by painlessness, high cosmetic effect (does not leave behind a noticeable scar). For these reasons, it is cryodestruction that is recommended for the treatment of a plantar wart in a child.

The cryodestruction method is often used in the treatment of plantar wart in children.
Removal with a laser
Laser removal of plantar warts is carried out in layers under local anesthesia. A depression remains at the site of the removed plantar wart, which levels out within two weeks. The method is not painful, it allows you to accurately control the depth of exposure, while direct contact of the manipulator with the tissues is excluded, which eliminates the risk of infection. The advantages of the method include an extremely low risk of recurrence and a good cosmetic effect. The disadvantage of this method is the lack of the possibility of subsequent laboratory examination of the removed neoplasm. Laser removal can be applied to plantar warts that are difficult to remove with other methods.

Laser removal of warts is used in cases of ineffectiveness of other methods of treatment
Surgical excision
It is used for large plantar warts, as well as extensive lesions, when neoplasms merge into a conglomerate. The surgery is performed under local anesthesia. The plantar wart is excised with a scalpel to the papillary layer of the skin. The tissue of the neoplasm does not bleed; bleeding begins at the border of the plantar wart and healthy tissues. After excision, sutures are applied, for which thick threads and an atraumatic needle are used. Sutures are applied first over the entire length of the wound, then the edges of the wound are brought together, and the suture is tightened from the edges of the operating wound. Intradermal cosmetic stitches are removed about a week after surgery. After healing, a light thin scar remains on the skin. The removed neoplasm is sent for histological examination. In the case of multiple neoplasms,as well as with frequent relapses of the disease, surgical excision of plantar warts is supplemented with antiviral and immunomodulatory general therapy.
Immunotherapy can be used to treat plantar warts. Local immunomodulators are used to stimulate the production of cytokines. The drug is applied to the affected area once a week. Also, anticancer drugs from the group of antimetabolites can be applied to the affected area under the occlusive dressing.
In some cases, they resort to intralesional injections of antigens, which stimulate the response of the patient's immune system to the virus, which caused the development of the pathological process. This method is used when other methods of removing plantar warts are ineffective.
Possible complications and consequences
Plantar warts can cause difficulty in walking, with the friction and pressure of the shoe causing intense pain that causes the patient to choose looser shoes and / or to change gait. The latter can cause pain in muscles and joints. The addition of a secondary infection leads to the development of inflammation, which further increases the pain. Some HPV strains are carcinogenic, for this reason, malignant degeneration of the neoplasm is possible.
In some cases, aggressive therapy of plantar warts (especially their self-medication) causes bleeding, secondary infection, severe pain, edema, suppuration, and temporary inability to walk.
Forecast
Uncomplicated plantar warts are capable of self-healing. Resolution of the pathological process is determined by the restoration of the normal papillary pattern in the affected area.
With the right treatment, complete recovery occurs, in some cases, there is a recurrence of plantar warts.
Prevention
The primary prevention of plantar warts is to prevent infection with papillomavirus. For these purposes, it is recommended to use individual footwear in public places such as baths, saunas, swimming pools. Proper care of the skin of the feet is of great importance (regular pedicure, treatment of the skin of the feet with emollients, peeling of the soles). For persons with deformity of the feet, it is recommended to wear shoes with orthopedic insoles, the use of orthoses.
With increased sweating of the skin of the feet, it is important to select shoes from natural materials, as well as the use of drying agents. With dry skin of the legs and the occurrence of cracks, it is recommended to regularly use moisturizing cosmetics; therapeutic foot baths with the addition of essential oils and / or herbal infusions have a good effect.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!