- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Lymphocytic leukemia
Brief description of the disease

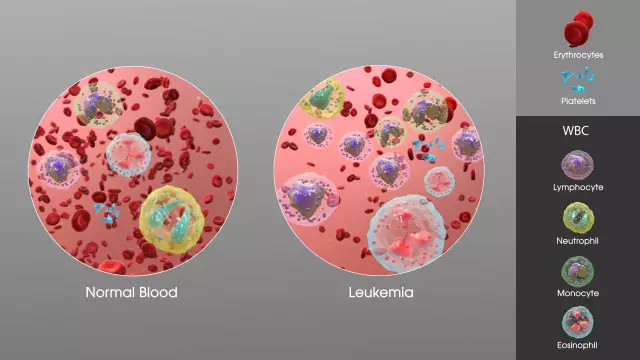
Lymphocytic leukemia is a malignant lesion of lymphoid cells.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia are distinguished.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia affects mainly children 2-4 years old, characterized by an increase in the growth of immature lymphatic cells in the thymus gland and bone marrow.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a disease in which lymphocytes affected by a tumor are found in the blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes and other organs. The chronic stage differs from the acute one in that the tumor develops slowly and disturbances in the process of hematopoiesis are noticeable only in the later stages of the disease.
The prognosis of lymphocytic leukemia in the chronic stage is much better than in its acute course. The chronic form is long and slow, most often treatment leads to recovery. The acute form without timely treatment leads to death in most cases.
The prognosis of lymphocytic leukemia in the acute stage without treatment - a person will live no more than 4 months, but if the patient has undergone therapy, the life span can be extended by several years, after which it is sometimes advisable to repeat the course of treatment.
Causes of the disease
Lymphocytic leukemia occurs due to poor heredity, exposure to ionizing radiation, carcinogenic substances. The disease can also occur as a complication after treatment of another type of cancer with cytostatics and other drugs that suppress hematopoiesis.
Lymphocytic leukemia symptoms

Symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia in the acute stage: pallor of the skin, spontaneous bleeding, fever, pain in joints and bones. If the central nervous system is affected, the patient is irritable, he suffers from headaches and vomiting.
In the chronic stage of the disease, the characteristic symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia are weakness, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, mainly in the right hypochondrium (due to an enlarged spleen), an increased tendency to infectious diseases, enlarged lymph nodes, increased sweating, and weight loss.
Diagnosis of the disease
To determine the acute stage of the disease, taking into account the external symptoms of lymphocytic leukemia, examine the peripheral blood. To verify the preliminary diagnosis, the blasts of the red bone marrow are examined. After carrying out a cytochemical, histological, cytogenetic study of the bone marrow, to plan the treatment of lymphocytic leukemia, additional examinations are carried out by a urologist, neuropathologist, otolaryngologist, MRI, CT, and ultrasound of the peritoneum are performed.
Diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia begins with a medical examination and a clinical blood test. After that, the bone marrow is also examined, a biopsy of the affected lymph nodes is made, a cytogenetic analysis of tumor cells is performed, the level of immunoglobulin is determined in order to calculate the risk of complications in the form of infections in the patient.
Lymphocytic leukemia treatment
Treatment of lymphocytic leukemia in the acute stage begins with the appointment of medications that suppress the growth of tumors in the bone marrow and blood. In cases where the tumor has struck the nervous system and the lining of the brain, the skull is additionally irradiated.
For the treatment of lymphocytic leukemia in the chronic stage, several methods have been developed: chemotherapy is carried out using purine analogs, for example, Fludar's drug, bioimmunotherapy - monoclonal antibodies are injected that destroy only cancer cells, without touching intact tissues.
If these methods are ineffective, the patient is prescribed high-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
If a large tumor mass is found, radiation therapy is prescribed as an additional treatment.
With lymphocytic leukemia, the spleen can be enlarged, therefore, with a significant change in this organ, its removal is indicated.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to limit the effects of factors that provoke lymphocytic leukemia: chemical and carcinogenic substances, ultraviolet radiation.
Prevention of its recurrence is of great importance for a good prognosis of lymphocytic leukemia.
It is recommended for those undergoing treatment for lymphocytic leukemia to eat protein-rich food, drink high-calorie drinks, regularly donate blood for research, strictly follow the therapeutic scheme, inform the observing doctor in time about an increase in lymph nodes in the groin, armpits, neck, and discomfort in the abdomen - this is how you can detect a relapse diseases, you can not take aspirin and other drugs containing it - bleeding may open. You should also avoid contact with people suspected of being infected with common infections. during radiation therapy, chemotherapy, the body is weakened.
In some cases, antiviral drugs and antibiotics are prescribed to patients to prevent infections after treatment of lymphocytic leukemia.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!