- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Candidiasis in men
The content of the article:
- Causes of candidiasis in men and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms of candidiasis in men
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of candidiasis in men
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Candidiasis in men is common, it is one of the widespread infectious diseases, for the occurrence of which two conditions are necessary: the presence of a fungal infection and a decrease in immunity. As a rule, with candidiasis in men, damage to the mucous membranes and / or skin is observed, much less often internal organs are involved in the pathological process.
The disease occurs in men of all age groups.

Oral candidiasis symptoms
Causes of candidiasis in men and risk factors
Microscopic fungi of the genus Candida, the causative agent of candidiasis, are part of the normal microflora of the mucous membranes and skin of most people, without causing any pathological conditions. However, in favorable conditions, mushrooms begin to grow and multiply intensively, while releasing toxins, which leads to the development of an inflammatory process - candidiasis.
The activity of the pathogen is evidenced by the rapid formation of a filamentous form of a microscopic yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida. The cells of the fungus attach to the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, especially those that are rich in glycogen, and cause a gradual destruction of the cells with the formation of lesions.

The causative agent of candidiasis - microscopic yeast Candida
The disease occurs against the background of a decrease in general or local immunity. Candidiasis in men can be caused by taking, especially long-term, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs and steroids. The disease often develops with hormonal disorders. Glucosuria (glucose in the urine) can also be the cause of urogenital candidiasis. The pathogen can be transmitted sexually, but in most cases, the development of urogenital candidiasis in men is not associated with sexual contacts.
Risk factors for developing candidiasis in men include:
- the presence of chronic diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- parenteral nutrition or central venous catheters;
- renal replacement therapy;
- radiation therapy;
- long-term artificial ventilation of the lungs or intensive care;
- surgical interventions;
- iron deficiency in the body;
- occupational hazards (work in warm and humid rooms);
- non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Severe, generalized forms of candidiasis in men occur in the presence of malignant diseases, immunodeficiency states and during immunosuppressive therapy.
Forms of the disease
Candidiasis in men can be acute or chronic.
Depending on the location and etiology, there are:
- candidiasis of the mucous membranes (lips, mouth, larynx, trachea, tonsils);
- candidiasis of the skin and skin appendages (scalp, nails, smooth skin, skin folds);
- systemic candidiasis (cavity and visceral: eyes, bronchi, urinary system, gastrointestinal tract, generalized);
- allergic candidiasis.
Lesions of the urogenital system, in turn, are divided into:
- candidal urethritis (inflammation of the urethra);
- candidal postitis (inflammation of the foreskin);
- candidal balanitis (inflammation of the glans penis);
- candidal balanoposthitis (simultaneous inflammation of the foreskin and glans penis).

Candidal balanitis - one of the forms of candidiasis in men
The defeat of fungi of the genus Candida of the oral mucosa takes the following forms:
- pseudomembranous candidiasis;
- erythematous candidiasis (acute or chronic);
- chronic hyperplastic candidiasis;
- median rhomboid glossitis;
- seizures (angular candidal cheilitis).
Candidal infection can manifest itself as local lesions (much more often), and as a generalized process.
Symptoms of candidiasis in men
Signs of candidiasis in men depend on the localization of the pathological process.
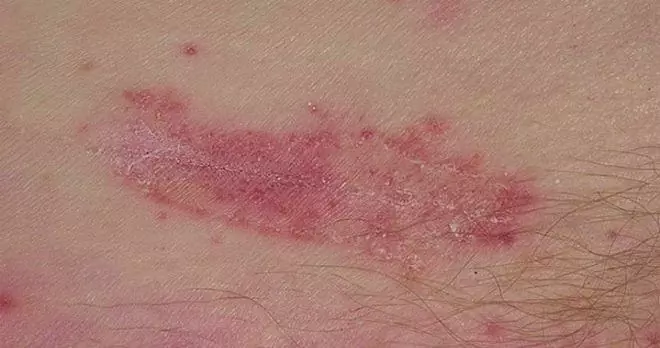
When the skin is affected by Candida fungi, hyperemic edematous areas with erosions, vesicles and papules appear on them. Erosions tend to merge with each other with the formation of extensive red lesions with a moist surface and a whitish coating, later these symptoms are joined by peeling and maceration of the skin. Most often, the pathological process is localized in the armpits and groin, as well as in the interdigital spaces.
The defeat of the nail plate is accompanied by compaction of the nail fold, its infiltration, edema and hyperemia. With candidiasis of the oral mucosa, the affected areas are usually covered with a white bloom, which resembles curd flakes.

With candidiasis of the nails, the nail fold is compacted, its edema and hyperemia are observed
With candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract, patients usually complain of flatulence and diarrhea. Traces of blood, mucus, whitish films can be found in feces.
With acute urogenital candidiasis in men, areas of hyperemia with a whitish bloom are formed, which can subsequently ulcerate. The process is accompanied by itching, burning, swelling. There is soreness during intercourse and during urination, pathological discharge with a sour odor. The inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged. Chronic urogenital candidiasis has similar, but less pronounced manifestations, or any one of the symptoms described (for example, pain when urinating).

Urogenital candidiasis is accompanied by itching, swelling, burning at the site of the lesion
Generalized candidiasis in men is accompanied by a worsening of the general condition: there is severe fever, weakness, lack of appetite, disorders of the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, and the central nervous system.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of anamnesis data, clinical manifestations of the disease and laboratory isolation of the pathogen. For this purpose, a microscopic and cultural study of biological material taken from the focus of the pathological process (smear, scraping or biopsy) is carried out, with the determination of the sensitivity of the isolated infectious agent to antimycotic drugs. Detection of microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida in the absence of symptoms of the disease does not confirm the diagnosis, since these fungi are normally present in the body of healthy people.
To identify primary pathology, an examination is carried out, which, in particular, includes a general and biochemical analysis of blood and urine, an immunological blood test, diagnosis of viral infections, etc.

To diagnose candidiasis in men, a biochemical and general blood test may be needed.
Differential diagnosis of urogenital candidiasis is required in men with sexually transmitted infections, skin candidiasis - with psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, favus, erythematous lupus.
Treatment of candidiasis in men
When treating candidiasis in men, first of all, it is required to eliminate or minimize the negative impact of the factors that gave rise to the development of fungal infection.
Treatment of candidiasis consists in the use of antimycotic drugs topically (in the form of a cream, ointment, suppositories, solutions, drying powders), and in some cases, orally.
The main effect of antimycotic drugs is to destroy the membranes of fungal cells, which causes their death. Some antifungal medications can cause side effects such as mild burning and irritation of the skin. Topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to relieve these symptoms.
Treatment of chronic candidiasis is usually long-term. In this case, general and local antimycotic drugs are usually used together. The main treatment is supplemented with immunomodulators, fortifying drugs.

Treatment of candidiasis in men consists in the use of local and systemic antimycotic drugs.
With candidiasis of the skin, laser therapy is sometimes prescribed as an adjunct to the main treatment.
With urogenital candidiasis in men, treatment is also indicated for all sexual partners of the patient.
An important condition for the success of the treatment of candidiasis is diet. The diet should be based on vegetables, fish, lean meat, dairy products. You should abandon high-carbohydrate foods (sugar and confectionery, baked goods), alcohol, fermentation products (kvass), industrial sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup), spicy, spicy, fatty, pickled, smoked dishes, canned food and semi-finished products.
Possible complications and consequences
In the absence of therapy or with improperly selected treatment, the disease can take on a chronic, and under unfavorable conditions, a generalized form. Urogenital candidiasis in men can be complicated by the development of painful erosions on the genital mucosa, phimosis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis. In addition, urogenital candidiasis increases the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases, due to damage to the mucous membranes of the genital organs, which facilitates the penetration of an infectious agent.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of candidiasis in men, it is recommended:
- timely detection and treatment of diseases that reduce the body's defenses;
- balanced diet;
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoiding casual sexual intercourse, using barrier methods of contraception during intimate contact;
- rejection of bad habits.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!