- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Human heredity

All living things are capable of transmitting certain traits and properties to their descendants. It is this ability that determines the heredity of a person, which explains the similarity of the child and his parents. At the same time, the baby's signs characteristic of each of the parents are manifested differently. So, for example, outwardly the child can resemble the father, and the character will be passed on to him from the mother. This is due to the fact that there are two types of genes in the human body - dominant and recessive. The first of them necessarily manifest themselves in the development of the child, suppressing the action of the second.
The influence of heredity on humans
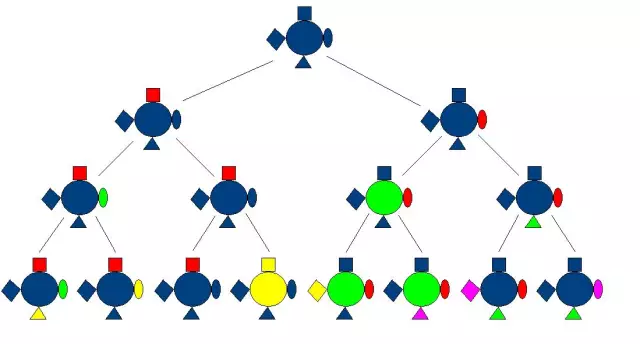
The genes responsible for human heredity transmit information to the child about all the traits of previous generations. The newborn receives a whole set of potential personal qualities, each of which was characteristic of either his parents, or grandparents, or more distant relatives. Among all the variety of possible paths for the development of a small person, only one is implemented, due to dominant genes.
Human heredity is reflected in his mental and physical development. At the same time, one cannot judge the potential of a child only by his parents. It is quite possible that the predominant qualities of the baby will be those that were distinguished by rather distant ancestors. In this regard, the study of human heredity is of great interest, first of all, by compiling a family tree. It allows you to trace the dominant traits in related persons over several generations.
From a practical point of view, such a study is very important for identifying various diseases transmitted as a result of the influence of heredity on a person. Studying the pedigree gives future parents the opportunity to learn about the likelihood of a serious illness before conceiving a child. Similar issues are dealt with by a geneticist - a specialist in the study of human heredity. He, if necessary, develops methods for the diagnosis and prevention of possible pathology.
Human heredity and environment
Every child, being born, has many different inclinations due to human heredity. Not all of them can manifest themselves in full. The individual developmental process depends not only on genetic factors, but also on the social conditions in which the baby develops. For the full realization of any potential quality, appropriate education and training is necessary. Thus, the heredity of a person and the environment of his existence should be in a state of harmony.
The factors of the world around the child play an essential role in providing the growing organism with all the necessary conditions for development. Correct, adequate upbringing, as well as training aimed at the full disclosure of innate inclinations, make it possible to form certain abilities on their basis. If human heredity is not supported by the necessary social conditions, natural capabilities do not receive further development. At the same time, as a result of systematic activities that encourage certain activities, a child can develop quite good abilities even in the absence of seemingly necessary inclinations.

The relationship between a person's heredity and the environment surrounding him is also seen in indicators such as, for example, body weight and height. These parameters, of course, largely depend on natural capabilities. However, the quality of nutrition and lifestyle of the child is of no small importance.
Genetic predisposition, or human heredity, is only a potential factor for the formation and development of any qualities, properties, diseases. Natural features can be identified using a pedigree that takes into account the presence of dominant and recessive genes. Depending on the conditions of the child's external environment, this predisposition may be further developed or remain in its infancy.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.