- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Atopic bronchial asthma
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Signs of the disease
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Video
Atopic bronchial asthma is diagnosed in 5-15% of cases of the total number of patients with this disease. According to statistics, it is registered in 4-8% of the population. Pathology develops as a result of exposure to the human body of non-infectious allergens. In recent years, the incidence of atopic asthma has increased, which is associated with an increase in the population's allergization.
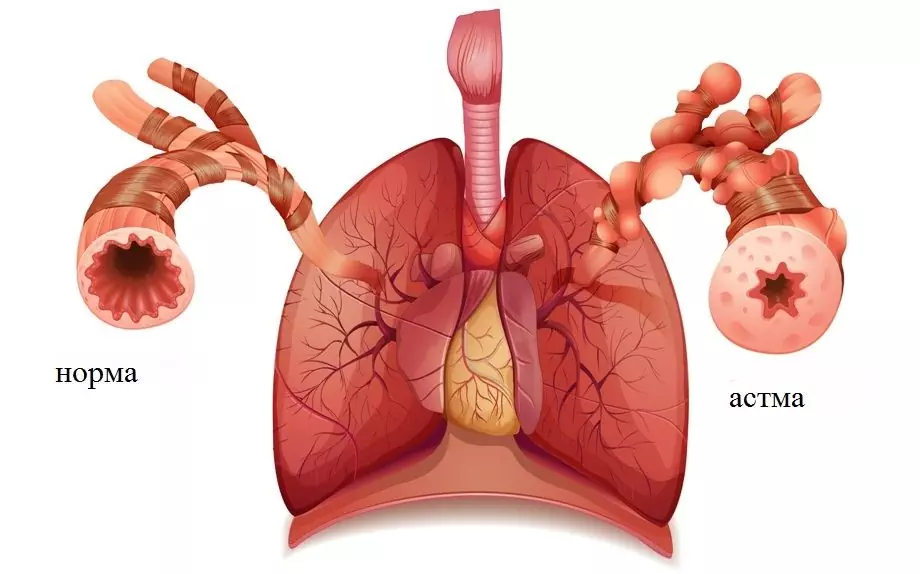
Atopic bronchial asthma is a broncho-obstructive pathological condition with a chronic course. The role of an allergen can be plant pollen, animal hair, fish food, bird feathers, ticks, fungal spores, dust (household, wood), as well as food allergens, of which strawberries, citrus fruits, and chocolate have the most pronounced sensitizing potential.

Atopic bronchial asthma develops in susceptible people under the influence of strong allergens, for example, pollen
Clinical signs of atopic asthma often first appear in children under 10 years of age. The disease occurs more often in boys than in girls.
Causes and risk factors
Among the main causes of the onset of the atopic form of the disease, a genetic predisposition is distinguished. So, according to statistics, in about 40% of cases, the disease is also detected in one or both parents and / or other close relatives of the patient. The tendency to asthma is 5 times more likely to be transmitted through the maternal line.
The disease develops due to the increased sensitivity of the bronchi to external non-infectious allergens that enter the human body along with the inhaled air and / or food. The risk of developing the disease increases when the body is exposed to unfavorable environmental factors, prolonged use of drugs, frequent infectious diseases, and reduced immunity.
Atopic asthma is classified according to the type of allergen. Dusty (household) asthma is the most common. The disease can manifest itself both year-round and at certain times of the year (for example, with the beginning of the heating season, with the beginning of flowering of certain plants, etc.). The seasonality of the fungal form of atopic asthma depends on the time of sporulation of the fungus that serves as an allergen. The pollen form of the disease develops during periods of the year when the amount of pollen in the air increases. This type of disease can also manifest itself all year round if the patient eats certain foods related to a certain type of pollen. The epidermal form of atopic asthma is caused by the hair and skin particles of animals. The most common pets that shed allergens are cats,perhaps for the simple reason that they are most popular as pets.
In about half of the cases, atopic asthma occurs against the background of respiratory diseases. The development of asthma in young children is facilitated by the presence of toxicosis in the mother during pregnancy, the early introduction of artificial mixtures into the diet.
Exacerbations of atopic asthma are promoted by smoking, acute respiratory viral infections, inhalation of smoke, vapors of household chemicals, industrial waste, and a sharp temperature drop. Intense physical activity and emotional upheaval can provoke the development of an attack.
Signs of the disease
At the initial stage of the disease, the patient often develops food sensitization, then skin and respiratory sensitization. In children, the first manifestations of the disease (seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis) usually occur at the age of 2-3 years. Symptoms typical for asthma in most cases manifest at 3-5 years of age.
Suffocating attacks often occur spontaneously against the background of the patient's well-being, often occurring at night. Asphyxiation either goes away on its own, or is stopped with the help of drugs. The attack may end with a cough, in which a small amount of clear phlegm is released. Choking may be preceded by sneezing, nasal congestion, nasal discharge, dry cough, discomfort in the throat, and hives. Children may have wheezing. Between attacks, the disease is usually asymptomatic. In the household form of atopic asthma, which occurs with the onset of the heating season, attacks usually appear in the living room and stop when leaving the house. In some cases, the reaction occurs 4-12 hours after exposure to the allergen. The attack can last up to two days even when the patient is using bronchodilator drugs.
In the first years of the disease, periods without seizures can be long, but with the progression of the pathological process, frequent contact with an allergen and / or in the absence of a properly selected treatment, the period of remission is shortened, seizures become more frequent, and the risk of complications increases.
Depending on the frequency of attacks and their intensity, 4 stages (severity) of the disease are distinguished:
- Mild intermittent stage - attacks develop 1 time in 1-2 weeks, nighttime suffocation - 1-2 times a month.
- Mild persistent stage - choking occurs no more than 1 time per day, night attacks are noted more often 2 times a month.
- Middle stage - seizures can be observed daily, they are accompanied by sleep disturbances, decreased physical activity.
- Severe stage - attacks occur 3 times a day or more.
Atopic asthma in women during pregnancy can occur in different ways. In some patients, the condition is aggravated, in some patients, on the contrary, their well-being improves, and some women do not observe any changes in the course of the disease. The greatest danger to the developing fetus is the development of hypoxia.
If the patient is in contact with an allergen for a long time, he may develop status asthmaticus, which can last for several days. It is characterized by severe attacks of suffocation, agitation, cyanosis of the skin. The person takes forced postures, shortness of breath increases with any of his movements. In severe attacks, there is a risk of death.
The chronic inflammatory process in the bronchial wall is maintained even during remission. The atopic form of bronchial asthma can be complicated by the occurrence of bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, emphysema, pneumothorax, cor pulmonale, respiratory and / or heart failure.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, data obtained during an objective examination, collection of complaints and anamnesis are used. Special attention is focused on the presence of a history of dermatitis, food and / or drug allergies, eczema, exudative diathesis. They resort to allergological tests, immunological tests, bronchoalveolar lavage. According to the results of the latter, changes in the cellular composition of sputum (the presence of Kurshman's spirals, Charcot-Leiden crystals, as well as eosinophilia) can be detected in patients. Skin tests are done to identify potential allergens. In order to diagnose food sensitization, the patient is recommended to keep a food diary, differential diagnostic fasting, provocative tests with food.
Differential diagnosis of atopic asthma is carried out with other forms of the disease, obstructive bronchitis.
Treatment
The main thing that is required for effective treatment of atopic bronchial asthma is the elimination or minimization of contact with the allergen. If necessary, the patient is advised to change the place of work, remove pets from the living quarters that can spread allergens, antimycotic treatment at home, remove down blankets and feather pillows, and daily wet cleaning of the premises. Shown is a hypoallergenic diet.

To relieve asthmatic attacks, inhalations with short-acting brocholytics are used
Pulmonologists, allergists, immunologists are engaged in the treatment of atopic asthma. Prescribed drug therapy, which is selected depending on the stage of the disease, which includes anti-inflammatory, bronchodilator, desensitizing drugs, immunomodulators. The selection of antibiotics, if necessary, their use is carried out exclusively under the supervision of a physician, since these drugs can also serve as allergens. To improve the patency of the bronchi, expectorant drugs are prescribed.
With a mild form of the disease, symptomatic therapy is sufficient - the use of short-acting bronchodilators orally or by inhalation.
With the development of status asthmaticus, rehydration therapy, oxygen therapy, and artificial ventilation are performed. Plasmapheresis, hemosorption may be needed.
Physiotherapy, spa treatment, physiotherapy exercises, and visits to salt mines have a good therapeutic effect.
The prognosis of the disease largely depends on the timeliness of the initiation of therapy, and is generally favorable. Atopic asthma caused by multiple allergens is less treatable.
To prevent complications for a pregnant woman with this disease, it is important to follow all the doctor's instructions. Patients with atopic bronchial asthma are advised to consult a qualified specialist at the stage of conception planning, which will reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.