- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
A cough without fever in a child: how to treat, why it occurs and how it manifests itself
The content of the article:
- What to do if a cough develops in children at a normal temperature
- Reasons for the appearance of cough in children without fever
- Concomitant signs of cough in various diseases
- Video
How to treat a cough without fever in a child, first of all, depends on what caused the development of this symptom in the patient.
The cough reflex is a defense mechanism that aims to clear the airways of foreign particles and accumulating mucus. By its nature, the cough is divided into dry and wet (wet). With a dry cough, the phlegm does not go away, therefore it is called unproductive, with a wet cough, the phlegm is released, it is called productive.
A cough at normal body temperature is not in all cases a sign of any disease, at the same time, the absence of temperature does not always mean the absence of a pathological process, therefore, with a persistent cough, it is necessary for the child to be examined by a doctor.

A persistent cough, even without a fever, can be a sign of a serious illness
What to do if a cough develops in children at a normal temperature
In some cases, to get rid of a child's cough, it is enough to remove the factor that provokes it, so it is necessary to determine the cause.
To diagnose the disease, complaints and anamnesis are collected, a physical examination, laboratory tests (general blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests). In difficult diagnostic cases, they resort to bronchoscopy, radiography, and sputum analysis. If you suspect an allergic origin of cough, allergy tests are performed.
Drug therapy for coughing in children includes the use of different drugs, depending on the cause of the development of the pathology. Any medicine should be given to a child only after consulting a qualified specialist and carefully following all his prescriptions.
To liquefy sputum and facilitate its removal from the body, expectorant, mucolytic drugs can be prescribed. Occasionally and with great restrictions with a dry cough (if there is no accumulation of mucus in the airways), antitussive drugs can be used. For bronchial obstruction, bronchodilators may be used. With helminthiasis, antihelminthic drugs are prescribed. In case of an allergic cough, the patient's contact with the allergen should be excluded or minimized; in some cases, the use of antihistamines is indicated. For diseases of viral or bacterial etiology, antiviral or antibacterial drugs can be used, respectively. In the case of the development of a psychosomatic cough, sedatives, that is, drugs with a sedative effect, can be prescribed.
Inhalation is a popular procedure that is prescribed for coughing in children without fever. Inhalation with a nebulizer with saline, alkaline mineral water, baking soda solution, as well as medications (expectorants, antimicrobials, etc.) prescribed by a doctor is recommended. Inhalation for children should be carried out strictly under the supervision of adults, at the first unfavorable signs (increased cough, difficulty breathing, etc.), the procedure is stopped.
With adenoids and acute respiratory diseases, you can flush the nasopharynx with antiseptic solutions.
In the absence of acute symptoms, drainage massage, breathing exercises, physiotherapy can be prescribed for the treatment of cough without fever in children.
In the room where the coughing child is, it is recommended to carry out regular ventilation, humidify the air - using a humidifier or by placing a container with water in the room. An abundant drinking regimen is required, it helps to moisturize the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, dilute sputum.
If a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, immediate hospitalization of the patient is required. First of all, the foreign object is removed, which may require surgical intervention, the method of which depends on the localization of the foreign body and the risk of complications.
If a cough develops against a background of stress, the child may need to consult a psychologist, psychotherapist and / or neurologist.
Traditional methods of treatment, despite their popularity, are not completely safe, especially when it comes to diseases of the respiratory system. For example, most medicinal herbs are strong allergens and are prohibited for use in children, just like steam inhalation. If you want to use this or that folk remedy to eliminate cough in a child, you must definitely consult a pediatrician.

Not all types of cough in children require treatment, but if you cough persistently, you need to see a doctor and find out the cause
Reasons for the appearance of cough in children without fever
The most common causes of cough in a child at normal body temperature include acute respiratory diseases, childhood infectious diseases and otorhinolaryngological pathologies in remission, that is, after the acute condition has resolved, as well as allergic reactions, helminthic infestations (helminthiasis). With weakened immunity, infectious diseases, even in the acute period, can proceed with a cough, but without an increase in body temperature.
Dry cough in a child in the absence of fever occurs at the initial stage of the inflammatory process in the pharynx, larynx, bronchi. Such a cough is most often observed during the day, with the progression of the pathological process it turns into a wet one.
One of the most common causes of dry cough at normal temperature in children 3-7 years of age is adenoids. At the same time, cough often develops at night.
In infants, coughing can occur during feeding (if fluid enters the baby's airways), as well as teething.
Another reason for coughing in a child without an increase in body temperature is reflux disease (GERD) due to the discharge of stomach contents into the esophagus and airways.
Cough in children can occur when inhaling vapors of chemicals, cigarette smoke, dust, foreign bodies, with too dry air in the room, hypothermia of the body.
Adolescents sometimes experience a psychosomatic dry cough that occurs during intense excitement and stops when the child calms down.
Concomitant signs of cough in various diseases
In acute respiratory diseases, cough is accompanied by nasal discharge, sore throat and / or sore throat, headache.
Barking paroxysmal cough, accompanied by choking, is observed with whooping cough, false and true croup.
In chronic diseases of the respiratory system (tracheitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, etc.), cough in children occurs periodically during periods of exacerbation. It is moist, the phlegm has a yellowish or greenish tint.
With otorhinolaryngological pathologies, a cough occurs when secreted mucus flows down the back of the pharynx. Most often, he worries the child at night when the patient is in a horizontal position.
With allergies, the cough begins suddenly, usually immediately after contact with the allergen. At the same time, the body temperature does not rise. Allergic cough is accompanied by a runny nose, itching, sneezing, lacrimation, conjunctival hyperemia, nasopharyngeal edema. Sputum (if any) is transparent, without impurities. In bronchial asthma, vitreous sputum is separated, a cough can turn into an attack of suffocation.
A tearful cough with whooping cough in a child can cause minor hemorrhages on the face. After suffering whooping cough, the child often has a residual cough that bothers him at night and is not accompanied by an increase in temperature.
With tuberculosis, periodic coughing occurs throughout the day. Cough is accompanied by weakness, poor appetite, weight loss. As the disease progresses, the cough becomes persistent, with abundant discharge, blood appears in the sputum.
With helminthiasis, the cough is usually dry, the body temperature is within the normal range. Coughing in a child is noted at regular intervals (for example, after 2-4 weeks) during periods of worm activity. Worm infestations are also accompanied by weight loss, dark circles under the eyes, pallor of the skin, rashes on the skin, and rapid fatigue.
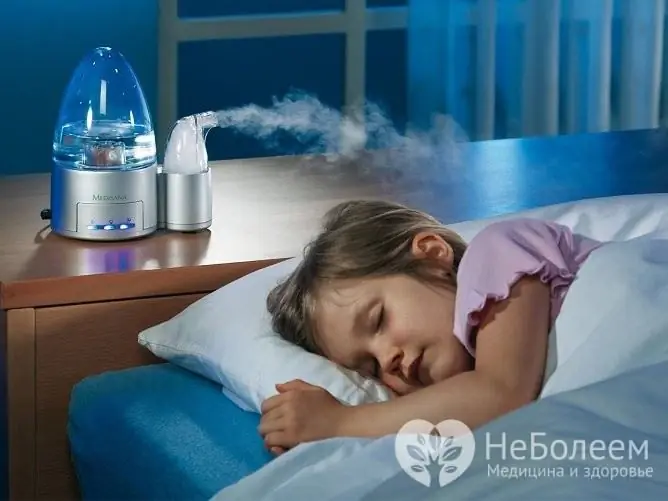

Dry indoor air can cause or worsen coughing, so we recommend using a humidifier
When irritants are inhaled, the child develops a cough without an increase in body temperature; if the concentration of irritants is high, a spasm of the larynx may develop.
When the humidity in the room is low, the child's mucous membranes of the respiratory tract dry out, resulting in reflex coughing without temperature. With a dry cough, the mucous membranes of the pharynx and larynx are constantly irritated, which makes them vulnerable to infection, can cause the development of edema and aggravate the patient's condition.
A severe cough in young children often ends in vomiting.
If a foreign body enters the child's respiratory tract (inhalation of sweets, small elements of toys), the symptoms depend on the time that has elapsed after inhalation of the object. During the passage of a foreign body through the child's larynx and trachea, a strong convulsive cough occurs, difficulty breathing, cyanosis of the skin and / or spots on the face may occur. If the object is large, there is a risk of suffocation and death. Small foreign bodies are often inhaled into the lower respiratory tract. In this case, the patient may experience coughing fits, noisy breathing, voice changes (hoarseness, hoarseness, loss of voice). If the object is sharp, there is pain behind the sternum, which is aggravated by movement and coughing, an admixture of blood may be found in the separated sputum. When coughing, a foreign object can get from the bronchi back into the larynx, causing the development of life-threatening conditions.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.