- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Swelling before menstruation: why do they occur and how to deal
The content of the article:
- Why does swelling occur before menstruation
- How does the edematous form of PMS manifest?
- Diagnostics
-
What to do, how to deal with edema
- Diet
- Diuretic herbal preparations
- Herbal preparations with progesterone activity
- Hormone therapy
- Video
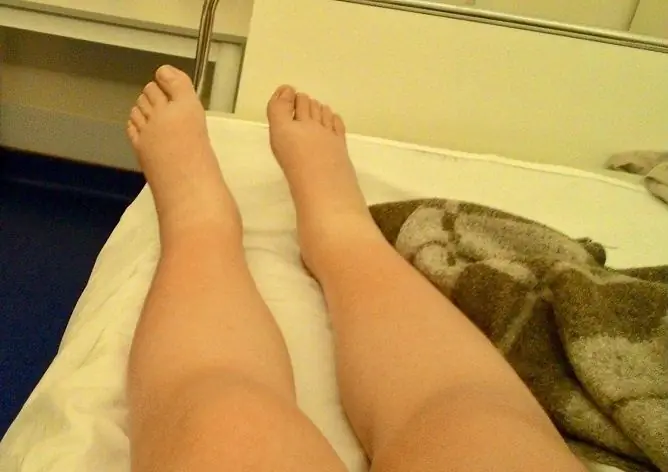
Swelling before menstruation is one of the signs of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). The incidence of PMS increases with the woman's age. By the age of 30, about one in five females have symptoms, after 30 - in one in two.

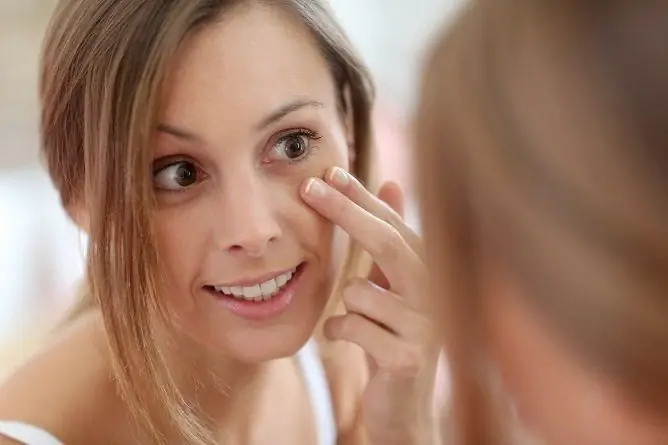
The appearance of edema before menstruation is one of the signs of premenstrual syndrome The appearance of edema before menstruation is one of the signs of premenstrual syndrome
Why does swelling occur before menstruation
The exact cause of the development of edema before menstruation has not yet been established. Medical science puts forward several theories: hormonal, allergic, psychosomatic, water intoxication.
Theory Explanation Hormonal Basic theory. It is associated with fluctuations in hormone levels during the menstrual cycle. The hormonal theory is based on an excess of estrogen and a lack of progesterone in the luteal phase, in connection with which PMS symptoms appear.
Lack of progesterone leads to excess fluid retention in the body. This is what causes the development of peripheral edema.
Water intoxication The theory of water intoxication explains what is happening by changes in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. An increase in aldosterone levels leads to sodium and fluid retention in the body. Allergic Associated with an increase in tissue sensitivity to progesterone. There are some risk factors that increase the likelihood of pre-period edema:
- emotional lability;
- hormonal imbalance;
- exposure to stress;
- brainwork;
- traumatic brain injury;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- inflammation of the reproductive system.
The genetic factor is also important, if the symptoms of PMS were present in the mother, the likelihood of developing pathology is several times higher. None of these factors cause PMS development with a 100% probability.
How does the edematous form of PMS manifest?
The most common form of edematous PMS occurs in women under 30. Symptoms begin 3 to 10 days before your period starts. Edema can be localized on the face or body:
- on the lower limbs (foot, shin);
- on the face - more often under the eyes;
- on the hands - fingers swell more often.
In addition to edema, other changes are observed:
- swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- bloating;
- increased sweating;
- sensitivity to strong odors;
- itchy skin;
- weight gain due to fluid retention in the body.
All phenomena take place shortly after the end of the critical days. The woman safely returns to her usual state.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic criterion is the cyclical nature of pathological symptoms. If a woman notices that pathological manifestations occur a few days before menstruation and disappear with its onset, most likely the case is in PMS. During the diagnosis, it is important to exclude organic pathology, which can manifest itself with similar symptoms.
For additional diagnostics, the following methods are used:
Method Description Determination of progesterone levels In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, there is a decrease in progesterone levels. Daily diuresis With the edematous form of PMS, there is a decrease in urine output by 500-700 ml per day. General urine analysis There may be a decrease in the specific gravity of urine, other indicators are within normal limits. Palpation of the mammary glands An increase in the mammary glands in the second phase of the cycle is determined, pathological formations are not palpable. Breast ultrasound The study is prescribed if there is pain in the area of the mammary glands. Ultrasound is performed in phase 1 of the cycle, it is prescribed to exclude other pathology. What to do, how to deal with edema
An integrated approach is used in the treatment of PMS, which includes relief of symptoms, normalization of hormonal and metabolic disorders.
Diet
With the edematous form of PMS, it is recommended to follow a diet that facilitates the course of the pathology. Basic nutritional principles:
- Limiting the intake of salt and foods that contain large amounts of it. Salt retains fluid in the body, which causes swelling.
- Increased consumption of foods that contain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These are fatty fish, avocados, olive oil, nuts and seeds.
- Adding foods that contain potassium and magnesium to the diet - these macronutrients reduce the manifestations of PMS. These include bananas, broccoli, pumpkin seeds, and potatoes.
- Limiting the consumption of dairy products, which can also retain fluid in the body.
- Restriction in the diet of fast carbohydrates - cakes, pastries, sweets, cookies.
The amount of fluid consumed during the day is not limited, it is recommended to drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water. But it is better to exclude heavy drinking just before bedtime. It is also recommended to stop smoking and alcoholic beverages, coffee.
Diuretic herbal preparations
Medicinal plants that have a diuretic effect can be used to reduce swelling before menstruation. Diuretic herbs increase the excretion of urine by the kidneys. Swelling disappears when excess fluid is removed from the body.
Diuretic recipes:
Plant Recipe Bearberry A decoction of bearberry leaves has a diuretic effect. Recipe:
1 teaspoon of bearberry leaves is poured with 100 ml of boiling water and boiled for 30 minutes, the resulting broth is diluted with 100 ml of water.
The broth is taken 5-6 times a day for 1 tablespoon 40 minutes after meals.
Horsetail An infusion can be prepared from the herb of horsetail. To do this, 1 tablespoon of chopped grass is poured with 200 ml of hot water, after which it is infused for 15 minutes.
You need to take an infusion of horsetail 4 times a day, 50 ml each 1 hour after eating.
Birch tree To prepare a diuretic broth, you need birch buds. 400 ml of boiling water is poured over 1 tablespoon of kidneys and simmered in a water bath for 20 minutes.
The broth is taken in 100 ml 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Herbal preparations with progesterone activity
If the second phase of the menstrual cycle is insufficient, plants can be used that contain progesterone-like substances:
- raspberry leaves and fruits;
- ordinary cuff leaves;
- stems and leaves of Potentilla goose.
Infusions, teas and decoctions for internal use are prepared from plants. It is recommended to take herbal infusions in the second phase of the cycle - 15-28 days from the onset of menstruation.

Raspberry leaves and fruits contain hormone-like substances that may be beneficial for PMS Raspberry leaves and fruits contain hormone-like substances that may be beneficial for PMS
Herbal remedies are an adjunct to mainstream treatment, not a substitute for it. Progesterone in plants is contained in small quantities, so only folk remedies are not enough for effective treatment.
Hormone therapy
Combined oral contraceptives suppress ovulation and, consequently, the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Oral contraceptives are selected individually, taking into account hormonal activity, the woman's age, the presence or absence of childbirth and abortion in the anamnesis. The following combinations are recommended:
- ethinylestradiol - drospirenone;
- ethinylestradiol - dienogest;
- ethinylestradiol - gestodene;
- ethinyl estradiol - desogestrel.
In most cases, taking these medications will help relieve PMS symptoms. It is highly discouraged to self-medicate and select combined oral contraceptives on your own.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.