- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. Drug interactions
- 12. Analogs
- 13. Terms and conditions of storage
- 14. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 15. Reviews
- 16. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Ciprofloxacin-AKOS
ATX code: S01AX13
Active ingredient: ciprofloxacin (Ciprofloxacin)
Manufacturer: JSC Sintez (Russia)
Description and photo update: 2020-07-04
Prices in pharmacies: from 14 rubles.
Buy

Ciprofloxacin-AKOS is an antibacterial drug of the fluoroquinolone group for topical use in ophthalmology.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - eye drops: transparent slightly yellowish or yellowish-greenish solution (5 ml in vials for eye drops equipped with a dispenser nozzle, sealed with a screwed plastic cap; 5 ml each in polymer dropper bottles, sealed with a screw cap equipped with a stopper dropper; in a cardboard box 1 bottle and instructions for use of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS).
Composition of 1 ml eye drops:
- active substance: ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (in terms of ciprofloxacin) - 3 mg;
- auxiliary components: Trilon B (disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium EDTA), benzalkonium chloride, mannitol (mannitol), glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate trihydrate (sodium acetate 3-aqueous), water for injection.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug for topical use in ophthalmology.
The active ingredient - ciprofloxacin, belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones (a subgroup of monofluoroquinolones), inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase [namely, those responsible for supercoiling of chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) around nuclear ribonucleic acid (RNA) topoisomerase II and IV, necessary for reading the genetic code], thereby disrupting DNA synthesis, growth and division of bacterial cells. In addition, it causes pronounced morphological changes (including membranes and cell walls), which leads to the rapid death of bacteria.
On gram-negative microorganisms during the rest / division period, ciprofloxacin has a bactericidal effect, since it affects not only DNA gyrase, but also promotes cell wall lysis. It affects gram-positive microorganisms only during the period of mitosis. The drug increases the permeability of the bacterial cell wall. At the same time, Ciprofloxacin-AKOS exhibits low toxicity towards the cells of the macroorganism, since they lack DNA gyrase. Against the background of its use, resistance to other antibiotics that are not included in the group of gyrase inhibitors is not developed in parallel. This makes the drug highly effective in the treatment of bacterial infections resistant to cephalosporins, penicillins, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, and many other antimicrobial agents.
Ciprofloxacin is sensitive to:
- gram-negative aerobic microflora: enterobacteria (Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., Klebsiella spp., Proteus vulgaris, Proteus mirabilis, Serratia marcescens, Edwardsiella spp., Hafnia alpprive., Morganella morganii, Yersinia spp.); other gram-negative bacteria (Aeromonas spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus spp., Moraxella catarrhalis, Pasteurella multocida, Campylobacter jejuni, Plesiomonas shigelloides, Neisseria spp.); certain intracellular pathogens (Mycobacterium kansasii, Brucella spp., Legionella pneumophila, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Listeria monocytogenes, Corynebacterium diphtheriae);
- gram-positive aerobic microflora: Staphylococcus spp. (Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus hominis), Streptococcus spp. (Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes).
Most methicillin-resistant staphylococci also show resistance to ciprofloxacin. The susceptibility to it of intracellular bacteria (Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Mycobacterium avium) is moderate, therefore high doses are required to inhibit them.
Clostridium difficile, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Pseudomonas cepacia, Bacteroides fragilis, Nocardia asteroides, Ureaplasma urealyticum are resistant to Ciprofloxacin-AKOS.
Ciprofloxacin is ineffective against Treponema pallidum.
Resistance to the drug develops extremely slowly, which, on the one hand, is due to the almost complete absence of persistent microorganisms after its application, on the other hand, to the absence of enzymes in bacteria that inactivate ciprofloxacin.
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS has low toxicity.
Pharmacokinetics
After instillation, ciprofloxacin penetrates well into the eye tissue (cornea and anterior chamber of the eye), especially in the case of a violation of the corneal epithelial cover. The substance in the affected cornea is at a concentration effective against most bacterial infections of the cornea.
A single instillation of ciprofloxacin after 10 minutes provides its concentration in the anterior chamber of the eye at a level of 100 μg / ml. The substance reaches its maximum concentration (C max) at the level of 190 μg / ml within 1 hour after injection into the anterior chamber of the eye. After 2 hours, the content of ciprofloxacin begins to decrease, but its antimicrobial effect persists in the tissues of the cornea for up to 6 hours, and in the moisture of the anterior chamber - up to 4 hours.
After instillation, systemic absorption of the substance is also likely. As a result of topical application of eye drops in both eyes 4 times a day for 7 days in the blood plasma, the average level of ciprofloxacin is less than 2-2.5 ng / ml, C max is less than 5 ng / ml.
T 1/2 (half-life) from plasma when applied topically is 4-5 hours. Ciprofloxacin is subject to renal elimination, up to 50% is excreted unchanged in the urine, up to 10% in the form of metabolites. With feces, ~ 15% is excreted. A small part of the drug is excreted in breast milk during lactation.
Indications for use
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS is used to treat infectious and inflammatory ophthalmic diseases caused by microorganisms susceptible to ciprofloxacin:
- acute / subacute conjunctivitis;
- keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis;
- blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis;
- anterior uveitis;
- dacryocystitis;
- trachoma;
- bacterial corneal ulcer;
- meibomite (barley);
- infectious eye lesions as a result of injury or foreign bodies.
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS is also used for the prevention and treatment of infectious complications in case of injury to the eye and its appendages (including after removal of a foreign body from the cornea or conjunctiva, after exposure to chemical / physical means) and during operations on the eyeball (for perioperative prophylaxis bacterial contamination in eye surgery).
Contraindications
- children under 1 year old;
- pregnancy and the period of breastfeeding (lactation);
- individual hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, other drugs of the fluoroquinolone group and auxiliary components of drops.
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS, instructions for use: method and dosage
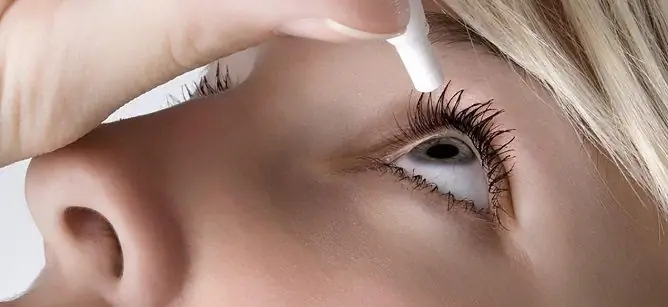
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS eye drops are intended for topical use by instillation into the conjunctival sac.
Recommended dosage: 1-2 drops in the affected eye; the frequency of use during the day depends on the severity of the inflammation.
In the treatment of mild and moderately severe infectious lesions, 1-2 drops are instilled into the affected eye (both eyes) once every 4 hours; for the treatment of severe bacterial lesions, 2 drops are instilled into the affected eye (both eyes) 1 time per hour. When the condition improves, the frequency and dose of instillations of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS are reduced.
Treatment and prevention of bacterial eye infections:
- acute bacterial conjunctivitis; simple, scaly and ulcerative blepharitis: 4-8 times a day, depending on the severity of the inflammatory process; the course of therapy is 5-14 days;
- keratitis: 1 drop at least 6 times a day; upon achieving a positive effect, therapy is continued until the cornea is completely healed; the course is usually 2 to 4 weeks;
- corneal damage caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 1 drop at least 8-12 times a day; the course usually depends on the course of the disease and ranges from 2 to 3 weeks;
- iridocyclitis (anterior uveitis): 1 drop of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS 8-12 times a day;
- dacryocystitis and canaliculitis: acute form - 1 drop 6-12 times a day, chronic disease - 4-8 times a day;
- bacterial corneal ulcer: the first day (during waking hours) - for 6 hours, 1 drop every 15 minutes, then 1 drop every 30 minutes; the second day - 1 drop every hour; from 3 to 14 days - 1 drop every 4 hours. If, after two weeks of treatment, epithelialization of the cornea does not occur, therapy can be continued;
- prevention of secondary infection in case of injury to the eye and its appendages: 1 drop 4-8 times a day; the course of therapy is 1-2 weeks;
- prevention of infection after surgery with violation of the integrity of the eyeball: 1 drop 4-6 times a day throughout the postoperative period, which can last from 5 days to 1 month.
Side effects
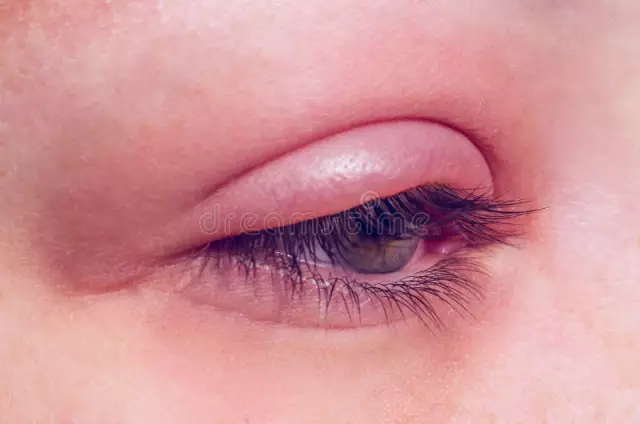
Topical application of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS eye drops can cause side effects such as mild pain, nausea, allergic reactions, burning sensation, itching, conjunctival hyperemia.
In rare cases, photophobia, swelling of the eyelids, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, lacrimation, immediately after instillation - an unpleasant taste in the mouth, decreased visual acuity, keratopathy, keratitis, the appearance of spots / corneal infiltration, the development of superinfection, in patients with corneal ulcers - formation white crystalline precipitate.
Overdose
To date, no cases of ciprofloxacin overdose have been reported.
special instructions
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS solution in the form of eye drops is not intended for intraocular injections.
The drug should not be injected directly into the anterior chamber of the eye or subconjunctivally.
If it is necessary to use other ophthalmic agents, it is required to observe the interval between their introduction of at least 5 minutes.
Patients who, as a result of the use of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS, develop and continue for a long time, or develop conjunctival hyperemia, should discontinue therapy and consult a specialist.
Wearing soft contact lenses is not recommended during treatment. If rigid lenses are used, they should be removed before instillation, and put on again 15-20 minutes after the procedure.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
With a temporary loss of clarity of visual perception after instillation of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS eye drops, one should refrain from driving a car or working with complex machinery, machine tools and production equipment until vision is completely restored.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
It is contraindicated to use Ciprofloxacin-AKOS eye drops for the treatment of pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Pediatric use
In pediatric practice, the use of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS for the treatment of children under the age of 1 year is contraindicated.
Drug interactions
Pharmaceutical interactions: Ciprofloxacin-AKOS eye drops are incompatible with physically or chemically unstable medicinal solutions with a pH of 3-4.
Other antimicrobial drugs (aminoglycosides, β-lactam antibiotics, metronidazole, clindamycin), when used simultaneously with ciprofloxacin, usually show synergy.
Analogs
Analogs of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS are Basigen, Betacyprol, Ifitsipro, Quintor, Ophtocypro, Procypro, Tseprova, Tsiprinol, Tsiprobay, Tsiprobid, Tsiprodoks, Tsiproxil, Tsiprolaker, Tsiprolet, Tsipromed, Tsipropanol, Ciprofloxa.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store at a temperature of 15-25 ° C in a place protected from light. Do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life is 2 years.
After opening the bottle, the eye drops should be used within 1 month.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS
Most patients leave positive reviews about Ciprofloxacin-AKOS. In their opinion, this is a fairly effective antibiotic, fast-acting, with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action. Excellent for irritation and eye contact. The result is often noticeable from the very first day of using the drops. The cost of the drug is most often called affordable or democratic.
Contraindications and possible side reactions are indicated as disadvantages. In one of the reviews, the patient complains that the solution is difficult to squeeze out of the bottle.
Price for Ciprofloxacin-AKOS in pharmacies
The approximate price of Ciprofloxacin-AKOS, 0.3% eye drops, for 1 dropper bottle containing 5 ml of solution, can be 14 rubles.
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Ciprofloxacin-AKOS 0.3% eye drops 5 ml 1 pc. RUB 14 Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!