- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Oxybuprocaine
Oxybuprocaine: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. Drug interactions
- 12. Analogs
- 13. Terms and conditions of storage
- 14. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 15. Reviews
- 16. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Oxybuprocaine
ATX code: N01BA
Active ingredient: oxybuprocaine (Oxybuprocaine)
Manufacturer: Moscow Endocrine Plant, Federal State Unitary Enterprise (Russia)
Description and photo update: 03.10.2019

Oxybuprocaine is a local anesthetic drug.
Release form and composition
Dosage form - eye drops 0.4%: colorless, transparent (in a cardboard box 1 or 2 polymeric dropper bottles containing 5 ml of solution, and instructions for the use of Oxybuprocaine).
Composition of 1 ml drops:
- active substance: oxybuprocaine hydrochloride - 4 mg;
- auxiliary components: boric acid - 19 mg; sodium chloride - 8 mg; benzalkonium chloride (50% solution, equivalent to 0.1 mg of benzalkonium chloride) - 0.2 mg; disodium salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dihydrate (disodium edetate dihydrate) - 0.1 mg; water for injection - up to 1 ml.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Oxybuprocaine has a short-acting local anesthetic effect. The pharmacological actions of the drug include:
- reversible blockage of sensitive nerve endings;
- penetration through the membrane of nerve cells;
- violation of transmembrane transport of ions (especially sodium);
- decrease in the flow of impulses to the central nervous system.
The drug does not affect the pupil's ability to accommodate and its size.
In comparison with tetracaine and other local anesthetics, the irritating effect of Oxybuprocaine on the cornea and conjunctiva is less pronounced.
Pharmacokinetics
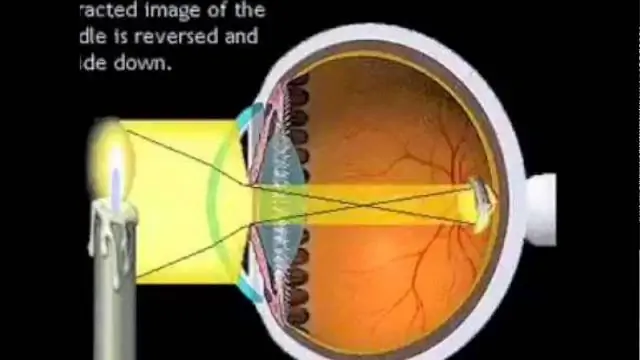
After a single instillation of drops into the conjunctival cavity, oxybuprocaine hydrochloride is easily absorbed into the corneal stroma through the mucous membranes. After 1-3 minutes, anesthesia occurs. Over the next 15 minutes, a quantitative decrease in the stromal concentration of the drug is noted, due to which, with a single instillation, an anesthesia period of 15 to 20 minutes is provided.
Indications for use
- tonometry;
- local anesthesia in ophthalmology, including superficial anesthesia of the conjunctiva and cornea;
- short-term operations on the conjunctiva and cornea;
- gonioscopy and other diagnostic examinations (before subconjunctival injections);
- extraction of sutures and foreign bodies from the conjunctiva and cornea.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- children under 2 years of age;
- individual intolerance to the components of the drug, including to other local anesthetics of the group of esters of para-aminobenzoic acid or amides.
Relative (Oxybuprocaine eye drops are used under medical supervision):
- pseudocholinesterase deficiency;
- malignant myasthenia gravis;
- epilepsy;
- selection of bacteriological smears (drops cannot be injected before the procedure, since they have bacteriostatic properties and prevent the development / reproduction of bacteria);
- pregnancy;
- period of breastfeeding.
Oxybuprocaine, instructions for use: method and dosage
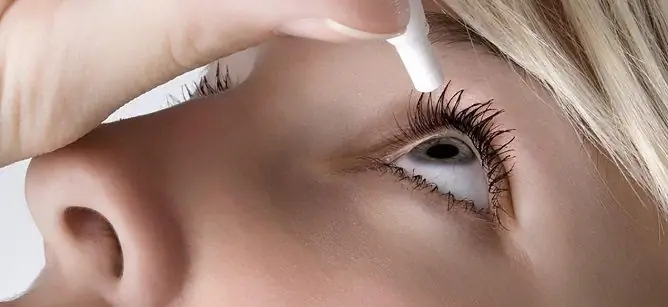
Oxybuprocaine eye drops are applied topically by instillation into the conjunctival sac.
Recommended dosage regimen:
- corneal and conjunctival anesthesia (to remove foreign bodies): 1 drop 3 times for 5 minutes;
- removal of deeply located foreign bodies: 1 drop from 5 to 10 times, observing an interval of 30 to 60 seconds between instillations;
- subconjunctival injections: before the procedure, 1 drop 3 times for 5 minutes;
- gonioscopy, tonometry and other examinations: 1-2 drops each.
Anesthesia for up to 60 minutes is provided by three times instillation of the drug, observing an interval of 4 to 5 minutes.
Before using drops for the first time, turn the cap (lid) of the dropper bottle clockwise until the neck is punctured. Next, the cap (lid) must be removed and by squeezing the body of the bottle with your fingers, drip the solution into the conjunctival sac. After each use, it is important to close the bottle with the cap (cap) until it stops.
Side effects
Possible adverse reactions (> 10% - very often;> 1% and 0.1% and 0.01% and <0.1% - rarely; <0.01% - very rare; frequency not established - determine the frequency of occurrence of unwanted reactions according to the available data is impossible):
- allergic reactions: the frequency has not been established - anaphylactic shock;
- local reactions: the frequency has not been established - a short-term tingling sensation, a feeling of hyperemia and burning of the conjunctiva;
- central nervous system: frequency not established - syncope, major epileptic seizure;
- sensory organs: frequency not established - excoriation and keratitis of the corneal surface, damage to the corneal layer of the epithelium;
- cardiovascular system: frequency not established - bradycardia.
Overdose
Data on oxybuprocaine overdose are not provided.
special instructions
Oxybuprocaine should be used only for instillation into the conjunctival sac. The drug should not be used for injection. It is not intended for self-help home therapy.
It should be borne in mind that long-term and repeated treatment with the drug, as well as with other local anesthetics, can cause stable corneal opacity. Oxybuprocaine is not intended for long-term therapy in complex eye pathology.
To avoid contamination when using the dropper bottle, it is important not to touch the tip to any surfaces.
When carrying out anesthesia, it is necessary to protect the eyes from friction, foreign bodies and irritating chemical influences.
Until the end of the anesthesia, it is forbidden to touch the eye.
Patients using contact lenses must remove them before instilling drops. You can resume wearing them only after the signs of anesthesia have completely disappeared.
During the treatment period, it is recommended to exclude alcohol intake.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and complex mechanisms
Patients during the period of use of Oxybuprocaine should refrain from driving and engaging in potentially hazardous activities, the implementation of which requires the speed of psychomotor reactions and increased concentration of attention.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
Oxybuprocaine during pregnancy and lactation can be used with caution only in cases where the predicted therapeutic effect for the mother outweighs the possible risks to the developing fetus and infant. This is due to the fact that clinical experience with the use of the drug in patients of these groups is limited.
Pediatric use
Oxybuprocaine is not prescribed for patients under 2 years of age.
Drug interactions
Possible interactions of oxybuprocaine with other substances / drugs:
- sympathomimetics, succinylcholine: enhancement of their effects;
- beta-blockers, sulfonamides: decreasing their action.
Oxybuprocaine is incompatible with alkaline substances, silver nitrate and fluorescein solution (due to the content of chlorhexidine diacetate in its composition, which forms a precipitate upon interaction).
It is recommended that you consult your doctor before using oxybuprocaine with any medications.
Analogs
Oxybuprocaine analogs are Inocaine, Benoxi.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store in a place protected from light and moisture at temperatures up to 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life is 2 years. After the first opening of the dropper bottle, the solution can be stored for 1 month (no more).
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews of Oxybuprocaine
Reviews of Oxybuprocaine, indicating its effectiveness, are few, since it is not available for sale.
Price for Oxybuprocaine in pharmacies
The price of Oxybuprocaine is unknown as it is not currently available from pharmacies. The approximate cost of an analogue of the drug - Inocaine (in the package 1 dropper bottle with 5 ml of eye drops) - from 109 to 123 rubles.

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!