- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Teeth
Teeth are hard bony formations. In humans and most vertebrates, they are located in the oral cavity and perform the functions of grabbing food, holding it and chewing it.

In children, milk teeth begin to erupt from three months. Normally, in childhood, 20 deciduous teeth (eight incisors, four canines and eight molars) should erupt. In the period from six to twelve years old, milk teeth are replaced with permanent ones.
An adult normally has 28 to 32 permanent teeth - eight incisors, four canines, eight premolars (small molars) and 8 to 12 molars (large molars).
Tooth structure
A tooth consists of an apex (crown), a neck and a root (or roots). A crown is an area of a tooth that, after eruption, completely or partially protrudes above the gum. At the crown, doctors distinguish the occlusion (closure) surface, the vestibular (facial), lingual (lingual) and proximal (contact) surfaces. The roots of the teeth are placed in the alveolar holes - the recesses in the jaw. Incisors, canines, first premolars and second premolars have one root, while two roots extend from the first premolars of the upper jaw and from the molars of the lower jaw. The molars of the upper jaw have three roots. The dental root is retained in the alveolus due to the periodontium formed by the fusion of collagen fiber bundles.
From above, each tooth is covered with enamel - the hardest tissue in the human body. The enamel of a newly erupted tooth is protected by a cuticle - a thin but very strong film. Over time, the cuticle is replaced by a pellicle (a derivative of saliva).
Under the enamel layer is dentin - the base of the tooth. In the root zone, the dentin is permeated with collagen fibers and covered with cement. The periodontium is attached to the cement impregnated with mineral salts.
The space inside the tooth is filled with dental pulp - soft loose connective tissue. The internal space of the tooth is divided into a root canal and a crown cavity. The pulp is permeated with nerve fibers, blood and lymphatic vessels, which disintegrate in the roots into separate small branches. With caries, the tooth hurts precisely because of the presence of a huge number of nerve endings in the pulp.
Teeth functions
Each type of teeth has its own functions. So, the incisors grab and cut food, the canines break and hold the food, and the back teeth (large molars) grind the pieces of food mass.
In addition, teeth are involved in the formation of speech sounds.
Tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is an operation to extract it from the alveoli.
The reasons for removal are varied. Most often, teeth are removed that cannot be restored by other methods:
- Teeth with gum disease, especially when the tooth hurts and begins to loosen.
- Broken teeth that cannot be repaired.
- Incorrectly positioned teeth in the dentition.
Before deciding on removal, the dentist must collect a dental and general medical history, take the necessary X-rays. Using X-ray images, the doctor should assess the condition of the tooth and its roots, as well as the condition of the bone placed around the root. Anamnesis helps the doctor get all the necessary information about the patient's health.
Before the extraction procedure, the doctor will numb the tooth and the surrounding gums and bone. A high concentration of anesthetic gel is applied to the area where the needle is inserted, and the patient does not feel the penetration of the needle. This allows the pain relief process itself to be numbed.
To remove it, the doctor expands the socket by swinging the tooth with slight pressure back and forth. After this expansion, the tooth can be easily extracted.
Sometimes the tooth fits very tightly into the socket. In this case, the doctor cuts it into separate pieces and then extracts each piece.
A blood clot forms in the tooth socket at the site of the extracted tooth, which is later converted into fibrous tissue. The fibrous tissue degenerates into bone tissue after a few months.
Extraction of a tooth is contraindicated during menstruation, with various diseases in an acute form, in the early and last months of pregnancy, when taking drugs that reduce blood clotting.

Dental treatment
The following main types of dental treatment are used in dentistry:
- Reconstruction and restoration for various dental lesions;
- Root canal treatment (endodontics);
- Treatment of periodontal disease.
Dental treatment is most often painless (under anesthesia). Endodontics is the most difficult of all dental procedures. Late treatment of caries can lead to pulpitis - inflammation of the dental cavity and periodontitis - inflammation of the jaw bone. With pulpitis and periodontitis, the tooth hurts constantly, and any pressure on the tooth increases the pain.
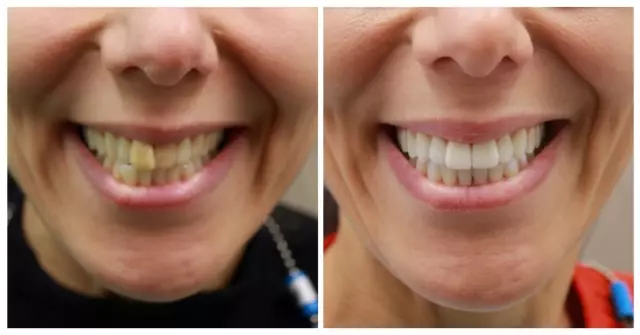
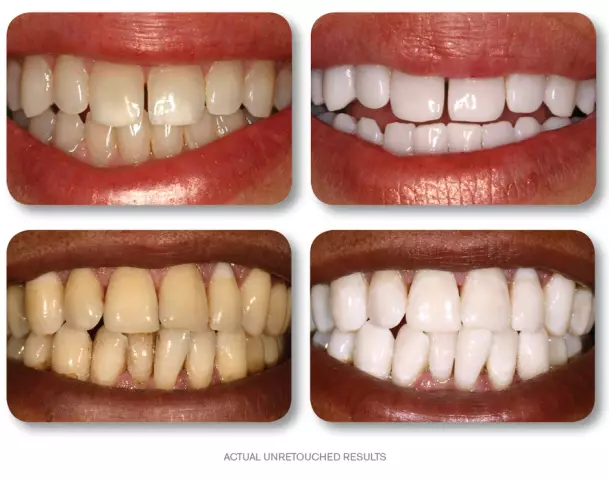
Teeth whitening
During the teeth whitening process, the doctor uses pads to isolate the teeth from the mouth and gums and apply a whitening gel to them. Whitening gel usually contains 25-30% hydrogen peroxide. The gel is activated by laser or lamp light. Then the dentist treats the teeth with fluoride to strengthen the tooth enamel. After one whitening procedure, teeth become eight shades lighter.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.