- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Miscarriage

A miscarriage is a spontaneous interruption of gestation (gestation) during the first 20-22 weeks, which is determined by the viability of the fetus. A spontaneous termination of pregnancy after 22 weeks is called preterm labor. According to statistics, 15-20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage, of which 80% of pregnancies are terminated within the first 12 weeks. What does a miscarriage look like? How to determine the onset of miscarriage? Is it worth keeping a pregnancy when a miscarriage begins?
Miscarriage: An Overview of Spontaneous Abortion
Regardless of the reasons that provoked a miscarriage, spontaneous abortion occurs according to the same scheme: the action of a factor provoking a miscarriage, detachment of the fetus from the uterine wall, removal of the fetus from the uterine cavity. Most early miscarriages are not diagnosed as such, but are perceived by women as the natural onset of menstruation. The likelihood of a miscarriage decreases in direct proportion to the gestational age - the longer the gestational age, the less the likelihood of spontaneous abortion.
There are two main types of miscarriages:
- Accidental (sporadic) miscarriage is a manifestation of natural selection, when special mechanisms reject an obviously unviable fetus. Accidental miscarriages in most cases are caused by genetic disorders of the fetus;
- Habitual miscarriage is a condition of a woman who has a history of 2 or more miscarriages in a row. One of the signs is miscarriages at approximately the same period.
There are a number of factors that can trigger a miscarriage:
- Multiple pregnancy;
- Hypertension;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- STDs;
- Maternal genital herpes and its relapses in early pregnancy;
- Drinking alcohol, nicotine, caffeine;
- Uncontrolled use of drugs and self-medication;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Woman's age;
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (Stein-Leventhal syndrome).
It is important, if possible, to exclude risk factors when planning pregnancy. To prevent miscarriage in chronic diseases, pregnancy must be planned under the close supervision of doctors, as well as properly prepare for conception (complete examination of sexual partners and the necessary treatment). Also, special attention should be paid to planning pregnancy for women with 2 or more miscarriages in the anamnesis.
To reduce the risk of developing fetal genetic abnormalities, it is important to realize that the effect of many drugs can significantly affect the development of pregnancy. It is important to inform the doctor about all types of treatment, drugs that the woman took within six months before pregnancy.
What does a miscarriage look like?
Every woman who finds out about her pregnancy needs to know what a miscarriage looks like. In case of miscarriage, the symptoms are:
- Pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling, stitching, aching character;
- Back pain in the lumbar region;
- Bloody, bloody, brown discharge in any volume;
- Profuse bleeding;
- Isolation of blood clots.
In 50% of cases in women who seek medical help with bleeding in the early stages, pregnancy ends in miscarriage. Therefore, every woman, both planning a pregnancy and pregnant, needs to know what a miscarriage looks like. When planning a pregnancy, doctors recommend that you closely monitor changes in the body, diagnose pregnancy in a timely manner, so that, if necessary, take the necessary measures to preserve it.
If symptoms appear during miscarriage, a woman should immediately consult a doctor. Also, the reason for an immediate visit to the gynecologist before pregnancy is detected is:
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by minor spotting before the expected period of the onset of menstruation;
- Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle;
- Prolonged or very short menstrual bleeding, significantly different from normal, in each individual case.
These symptoms may indicate a miscarriage before pregnancy is diagnosed. In such cases, it is extremely rare to maintain a pregnancy, however, this situation is an alarming reason for an additional examination in case of pregnancy planning and a full examination in case of sporadic miscarriage during an unplanned pregnancy.
With sporadic miscarriages, symptoms may not appear for a long time if the fetus dies first. Fetal death is diagnosed by conducting a dynamic analysis for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), ultrasound monitoring. If the research data make it possible to establish that the pregnancy is intrauterine and alive, the fetal heartbeat is diagnosed, and its development corresponds to the term, then such a pregnancy in most cases is successfully maintained and ends with the birth of a child.
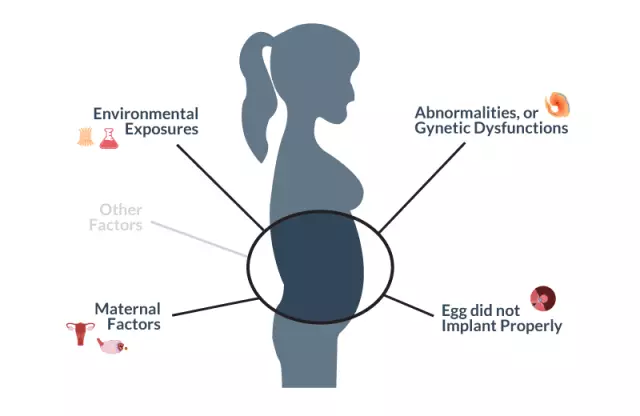
Miscarriage: causes of spontaneous abortion

In most cases, unfortunately, the causes of miscarriage remain unknown. The most common causes of spontaneous abortion are genetic disorders of fetal development. A biological individual is not capable of producing 100% quality cells (sperm and eggs). Healthy semen contains up to 2 million abnormal spermatozoa for every 1 ml. Female eggs are laid in the ovaries at 20 weeks of intrauterine development of the fetus, and unlike sperm, female reproductive cells are not renewed during life. Any negative factors, both external and internal, affecting a woman's health, in the same negative way affect her germ cells. The likelihood that a pathological germ cell will participate in the fertilization process is quite high. Therefore, there are natural mechanisms for the selection of viable individuals in the early stages of fetal development, which leads to miscarriages.
The reasons for the habitual termination of pregnancy (2 or more miscarriages) are disorders in the female body. Such causes of miscarriages are difficult to identify. These violations do not interfere with conception, but provoke an early interruption. The woman's body in this case is not able to create normal conditions for gestation.
With habitual miscarriages, the reasons may be as follows:
- Physiology of the uterus, violation of its structure - adhesions in the uterus, two-legged uterus, septum in the uterus;
- Immune disorders (autoimmune, alloimmune), when the female body rejects the fetus as a foreign body, producing antibodies to it;
- Miscarriages of unknown origin (for unknown reasons);
- Endocrine disorders;
- Lifestyle.
Is it worth keeping a pregnancy when a miscarriage begins? In the early stages, it is extremely difficult to diagnose fetal pathologies. It happens that after the pregnancy is maintained, the fetus reveals complex pathologies that are not compatible with normal life.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.