- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Ear diseases
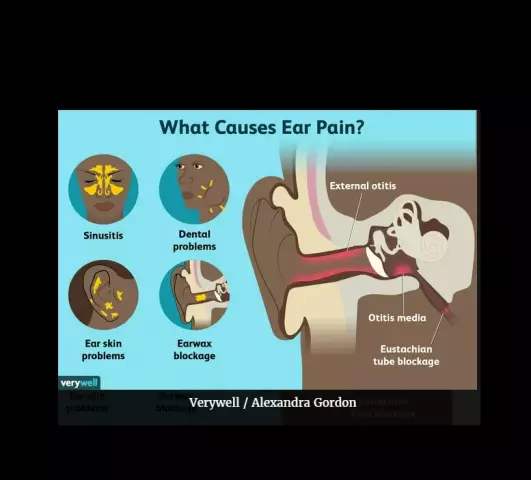
Many ear diseases are now known. However, most often you can meet two: an inflammatory process in the middle or outer ear and sensorineural hearing loss. Accordingly, the symptoms of ear diseases will also vary.
Otitis media or ear inflammation

Otitis media is an inflammatory process localized in the ear. The causative agents of infection in diseases of the ears can be hemolytic streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, as well as fungi and mycobacteria that cause such a serious pathology as ear tuberculosis.
Otitis media may be primary. However, it most often occurs as a complication of inflammation in other organs, when an infection with the blood flow, lymph enters the ear. This otitis media is called secondary. The most likely localization of the primary focus of inflammation is the organs of the nasopharynx. Often complicated: sore throats, scarlet fever, flu, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, etc. infections.
The risk group includes such patients who in the past had ear microtrauma, disorders of general or decreased local immunity, allergic predisposition, improper ear hygiene, congenital increase in the function of the glands of the ear canal, which leads to the occurrence of sulfur plug.
Patients who have previously received drugs of certain pharmacological groups are also at risk. Most often, when using them, complications of this kind are caused by aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Microtrauma is understood as a mechanical effect on the ears (blows, bruises, bites), and thermal, chemical, acoustic (long-term or short-term strong sound), vibration, as well as barotrauma arising from sudden changes in atmospheric pressure.
In children, various foreign bodies contribute to the onset of ear diseases: pebbles, buttons, peas, etc. Often such objects can remain in the ear for several days, and only when otitis media occurs, their presence is detected.
In adults, foreign bodies enter the ear more often when hygiene rules are violated. These are fragments of matches, cotton wool, less often insects.
Ear symptoms
The most common symptom of ear disease is pain. Its intensity is extremely variable: from a slight tingling sensation to an extreme degree of intensity that disrupts the patient's sleep. The pain can be given to the eyes, lower jaw, temple, and also cause a diffuse headache on the side of the affected ear. The pain syndrome can sharply increase when walking, swallowing, chewing.
Less common is a symptom such as redness. It is noticeable without examination with inflammation of the external ear.
With a pronounced inflammatory process in the ear, general infectious symptoms may appear: hyperthermia, weakness, chilling, decreased appetite, general weakness and sleep disturbance.
With otitis media, patients may feel a splash or transfusion of fluid in the ear cavity, especially when changing the position of the head.
In advanced cases with diseases of the ears, discharge of a different nature may appear: putrid, purulent, bloody, serous.
Ear symptoms can also include the following:
- hearing loss;
- feeling of noises in the ear;
- autophony (the perception of the sound of your own voice with a stuffy ear);
- hearing loss within any frequency;
- deafness;
- dizziness.
External examination reveals swelling, redness of the outer ear, crusts or small bubbles in the external auditory canal, traces of scratching.
Palpation with pressure on the tragus or mastoid is often painful.
Treatment of ear diseases
For the treatment of inflammatory ear diseases, local antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed. With a pronounced violation of the general condition, a far-reaching process, and also if otitis media is secondary, systemic antibiotics are prescribed. The selection of antibiotic therapy should be dealt with by a specialist.
Fungal diseases of the ears
The causative agents of mycoses of the ears are often yeast-like fungi. In many cases, the occurrence of fungal diseases of the ears is a beacon that there is a certain kind of immunodeficiency in the body.
The most common complaint with mycoses of the ear is a liquid discharge of white, yellowish, green colors. Patients are worried about tinnitus, itching, and ear congestion. Pain syndrome is usually absent. There may be hearing loss on the affected side, dizziness.
The reasons that predispose to the occurrence of mycosis are similar to the reasons that contribute to the development of otitis media.

For the treatment of fungal diseases of the ears, it is important to determine the species specificity of the fungi. After that, antimycotic drugs are prescribed: amphotericin B, natamycin, itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine. At the same time, antihistamines should be prescribed, because many fungi are highly allergens.
When treating fungal diseases of the ears, it is necessary to abolish antibiotics, as well as to carry out immunocorrective and restorative therapy.
Fungal infections are prone to recurrent course, therefore, after clinical cure, repeated mycological studies are recommended.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!