- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Breast lipoma

A breast lipoma is a benign tumor arising from the cells of adipose tissue. A true lipoma is formed by mature adipose tissue and is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule outside. Among all nodal neoplasms of the mammary gland, lipoma occurs in about 10% of cases.
Symptoms
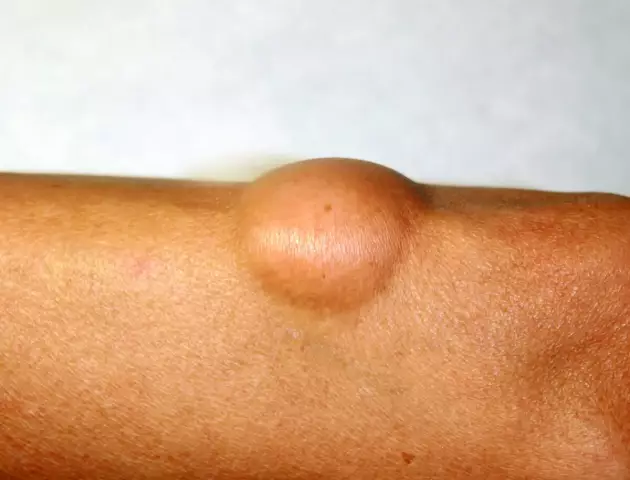
A breast lipoma is a mobile, painless, soft and elastic formation that has an oval or round shape. When a tumor is localized deep in the tissues of the gland, it usually does not manifest itself in anything and is detected by chance during an ultrasound or mammography.
As it grows, the lipoma leads to deformation of the mammary gland, and sometimes is the cause of the development of gigantomastia.
Lipoma almost never degenerates into a malignant tumor, i.e. not malignant. The literature describes isolated cases of liposarcoma development from lipoma.
Breast lipoma: symptoms
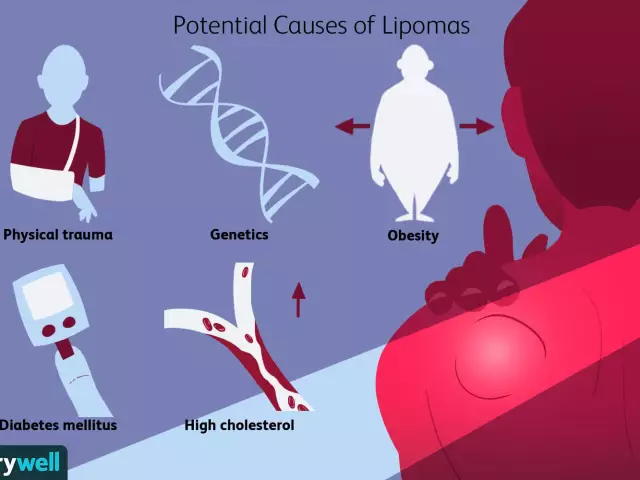
Currently, the exact cause of the formation of lipomas is not known. It is believed that their growth is associated with metabolic disorders in the body and, in particular, with the processes of lipolysis (destruction of adipose tissue).
Diagnosis of breast lipoma
The main methods for diagnosing breast lipoma are ultrasound and mammography.
On a mammogram with a lipoma, an area of enlightenment is found that has fairly clear, even contours. If necessary, sighting images of the palpable neoplasm are performed.
On ultrasound examination, the lipoma is detected as a compressible hypoechoic formation.
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe the patient to perform a puncture biopsy of the breast lipoma, followed by histological and cytological examination of the resulting tissue.
Classification of breast lipomas
Lipomas located in the mammary gland can have a fairly dense capsule. They are called knotty lipomas. Diffuse lipomas characterized by the proliferation of adipose tissue without the presence of a capsule are much less common.
A true lipoma, consisting only of adipose tissue cells, is very soft on palpation. If the tumor contains connective tissue fibers, then it becomes much denser and is called fibrolipoma. Also, angiolipoma (with a developed network of capillaries), mixolipoma (with the presence of mucous tissue) and myolipoma (containing muscle fibers) are isolated.
Breast lipoma: treatment

Lipoma is a formation that never resolves itself or under the influence of conservative therapy. Therefore, the main treatment for breast lipomas is their surgical removal. The indications for surgery are:
- Pronounced cosmetic defect and deformation of the mammary gland;
- A fast growing tumor;
- Painful lipoma;
- Gigantomastia (a significant increase in the size of the mammary gland);
- Breast tissue necrosis;
- The degeneration of a lipoma into a liposarcoma.
After the surgical treatment of breast lipoma, the surgical wound is sanitized, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. To prevent the re-formation of breast lipoma, a woman is prescribed medications that normalize metabolism - vitamins, immunomodulators and some homeopathic medicines.
Some women, especially with a small tumor, categorically refuse to undergo surgical treatment for breast lipoma. In this case, they should be under the regular supervision of a mammologist, because, although very rarely, lipoma can turn into liposarcoma. Breast ultrasound should be done every three months. Every six months, a woman should have a mammogram and / or thermomammography. If there is discharge from the nipple, a smear-imprint is made twice a year for cytological examination. With a high risk of malignancy of the breast lipoma, blood should be donated for tumor markers once a quarter.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!