- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor that originates from adipose tissue cells. Lipomas can be multiple

or single. They appear in any place where there is a fat layer - in the lumbar region, on the thighs, arms, abdomen, in the meninges, in the mammary glands, between muscle fibers, etc.
Lipomas most often occur in people over the age of 30. These tumors never shrink or disappear on their own. Although they belong to benign neoplasms, in some cases, for example, as a result of trauma, they can degenerate into a malignant tumor. Therefore, most doctors recommend that their patients carry out lipoma removal, even in cases where the tumor does not cause any discomfort.
Lipoma: causes
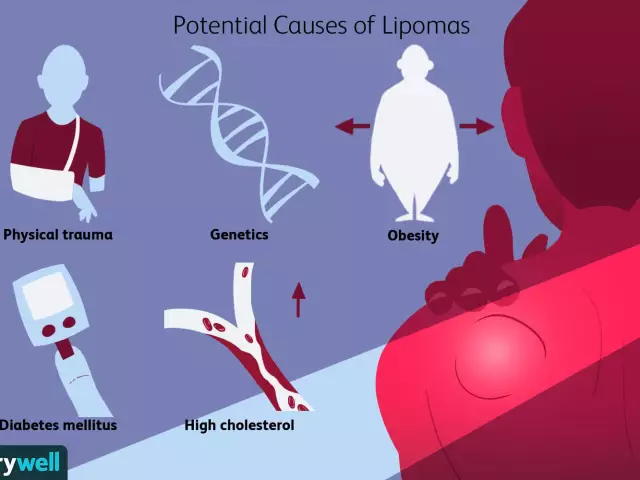
Lipomas occur as a result of lipolysis disorders (decomposition of adipose tissue) and some systemic metabolic processes. Lipomas are often observed in people suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland, pancreas, diabetes mellitus, and also with reduced pituitary function. Other causes of lipoma, experts believe, are malignant neoplasms of the respiratory tract, hereditary predisposition and alcoholism. But there are times when it is not possible to identify the cause of the lipoma.
Lipoma symptoms
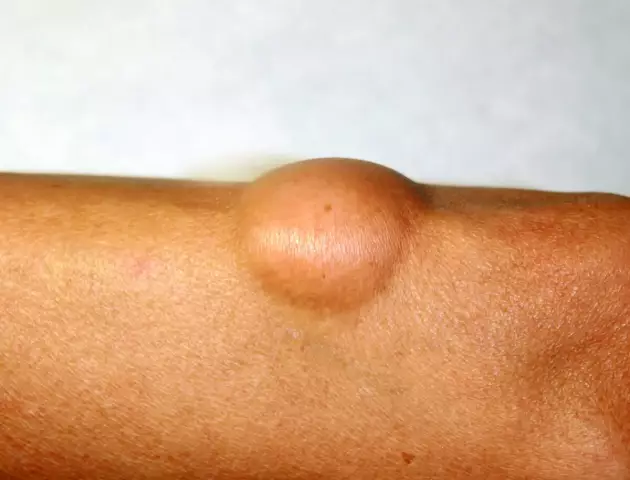
Lipoma has the appearance of a mobile, elastic, soft and painless formation and is most often located under the skin. But in cases where the tumor is located in the immediate vicinity of a large nerve trunk and, as it grows, begins to squeeze it, then due to nerve irritation it becomes painful.
Lipomas can vary in size. They often reach enormous sizes (about 20.0 cm in diameter).
There are several types of lipomas:
- Lipofibroma is a very soft to the touch tumor, in which adipose tissue cells predominate;
- Fibrous lipoma - in addition to fatty tissue, it also includes fibrous (connective) tissue. Such tumors are characterized by significant density and elasticity.
- Angiolipoma (cavernous lipoma) - it contains a large number of small blood vessels (capillaries).
- Myolipoma - this tumor includes adipose and muscle tissue, which gives it a bumpy appearance.
A characteristic symptom of a lipoma is that with the general weight loss of a person, the size of this tumor increases markedly.
Lipoma diagnostics
Lipoma is very similar in its characteristics to a tumor of the sebaceous glands - atheroma. Their distinctive feature is their location. Atheromas are usually located in places of accumulation of sebaceous glands, and lipomas - in places of accumulation of adipose tissue. In addition, the lipoma does not have traces of the excretory duct characteristic of atheroma.
In most

cases, with a superficial arrangement of a lipoma, the doctor makes the correct diagnosis already during the examination of the patient. For internal lipomas, instrumental diagnostic methods are used: X-ray with contrast, ultrasound, computed tomography.
Lipoma: treatment
Although a lipoma is a benign tumor, treatment should not be abandoned because there is a risk of malignancy (malignant transformation). In addition, superficial lipomas cause aesthetic discomfort as they grow. Internal lipomas can lead to the appearance of nervous disorders and disruption of the activity of the internal organs located next to them. Therefore, it is very important to consult a surgeon in a timely manner for the treatment of lipoma.
Conservative methods of treating lipoma are not used due to their ineffectiveness. Removal of the lipoma is performed surgically. During the operation, the doctor removes the contents of the lipoma and carefully scrapes out its capsule or completely removes it, which helps prevent recurrence of the disease. After that, the wound is sutured tightly.
Removal of a lipoma, subject to its superficial location, is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. Deep or very large lipomas are removed in a hospital under general anesthesia.
Removal of a lipoma can be performed using traditional open surgery or using endoscopic techniques. However, the use of endovideosurgical methods gives a greater percentage of relapses of the disease than conventional surgery.
The most modern method of treating lipomas today is their removal using a laser beam. Such operations are well tolerated by patients, and relapses almost never occur. In this case, the wound after removal of the lipoma heals very quickly, and the scar formed in its place is practically invisible.
After removing the lipoma in the clinic, the patient can immediately go home. But he will have to come to the doctor every day for stitches and wound dressings. The wound after removal of the lipoma usually heals within 7 to 8 days. Then the skin sutures are removed.
Lipoma: alternative treatment
There are various alternative treatments for lipoma. The most effective of them are honey-sour cream masks. To prepare them, you should take fresh fat sour cream, salt and honey in equal proportions. The ingredients are thoroughly mixed together and heated in a water bath. The hot mixture (but so as not to burn yourself!) Is applied to the surface of the skin over the lipoma and kept for about 20 minutes. The procedures are performed every other day. A course of lipoma treatment usually requires 15 to 20 masks.
Although alternative treatment of lipoma in many cases allows you to get rid of the tumor without surgery, you should not use it without consulting a doctor. Remember that sometimes a lipoma can degenerate into a liposarcoma, and in this case, delay in treatment, as well as warming up procedures, can lead to the spread of metastases and death!
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!