- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Strychnine poisoning
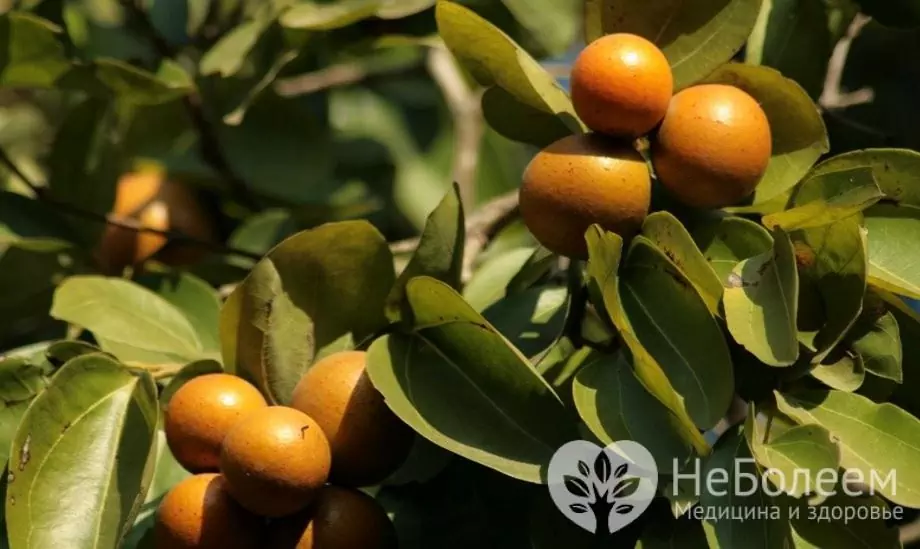
Strychnine is the main alkaloid in the seeds of chilibuha (vomit), which is common in Australia, tropical regions of Asia (Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos) and Africa. In addition to strychnine, the plant contains an equally powerful alkaloid - brucine, their total volume in seeds is approximately 2.5%.

Source: i.imgur.com
Strychnine, along with brucine, activates the activity of the central nervous system (which is associated with facilitating the conduction of excitation in the interneuronal synapses of the spinal cord), stimulates the sense organs (sharpens vision, hearing, makes more intense taste sensations, enhances tactile sensitivity), vasomotor and respiratory center, increases tone skeletal muscles, including the heart muscle, enhances metabolic processes.
In addition to affecting the transmission of nerve impulses, strychnine blocks inhibitory neurotransmitters (glycine and other amino acids), provoking and maintaining the excitatory effect.
The stimulating effects of the alkaloid have found application in medicine (in the form of nitrate, nitric acid salt, as well as in the tincture and extract of dry chilibuhi), allowing it to be used in a number of conditions:
- as a general tonic for asthenic syndrome, somatoform disorders, accompanied by hypotension, diseases characterized by a decrease in general muscle tone;
- with a critical drop in the activity of the respiratory and vasomotor center (asphyxia in infections, drug poisoning, etc.);
- in complex therapy in the composition of tonics for paresis and paralysis of smooth muscle organs (intestines, bladder), in the recovery period to relieve complications of motor disorders;
- with visual impairment (amblyopia, amaurosis, etc.).
Previously, strychnine was prescribed for some forms of urinary incontinence and, less commonly, as a bitterness to improve appetite. In the middle of the last century, it was used as a stimulant in professional sports. Its use was discontinued after several reported deaths.
Strychnine has a small breadth of therapeutic action, which leads to a high probability of poisoning if it is used incorrectly. It is a typical convulsive poison - in the picture of poisoning, the leading place is taken by convulsions.
It is completely and quickly absorbed into the systemic circulation both from the gastrointestinal tract and from the injection site (with any route of administration).
The lethal dose of strychnine is 50-100 mg.
How does strychnine poisoning occur?
Most often, strychnine poisoning occurs in the following cases:
- exceeding the dose and / or increasing the frequency of taking the medicinal product containing strychnine;
- self-administration of drugs with strychnine without a doctor's prescription;
- neglect of personal protective equipment (gloves, goggles, respirator) when using strychnine in the composition of means for fighting rodents and insects;
- taking a strychnine-containing drug by mistake (including children);
- taking drugs based on strychnine.
Poisoning symptoms
The first symptoms of acute intoxication with strychnine appear a few minutes later (according to various sources - from 15 to 60) after taking the substance, although cases of delayed action are described, up to 10 hours after the poison enters the body.
The initial symptoms are specific for this type of poisoning and develop gradually:
- difficulty breathing;
- pulling pain and stiffness, increased tone in the masticatory and back muscles;
- shallow trembling;
- hyperemia of the face;
- sharpening of hearing and vision;
- photopsies (bright flashes before the eyes);
- exophthalmos.
Suddenly, an intense painful generalized contraction of skeletal muscles (opisthotonus) occurs, the cause of which is the slightest external irritation. The body arches in an arched shape due to the fact that the muscles of the back have more strength than the muscles of the abdominal wall.
The face acquires a bluish color, on the face there is a "sardonic smile" (caused by a combination of contraction of the masticatory muscles with a spasm of the facial muscles).
In addition to specific symptoms, strychnine poisoning is manifested by general symptoms:
- changes in blood pressure (more often an increase, but hypotension is also possible);
- tachy or bradycardia;
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the chest and abdomen;
- nausea, vomiting.
Source: depositphotos.com
An attack of convulsions, lasting from 1 to 3 minutes, is replaced by extreme relaxation (10-15 minutes), then an attack follows again. Convulsive episodes can be repeated up to 3-6 times, then, some time after the next episode of tetanic seizures, death occurs from asphyxia due to paralysis of the respiratory center and spasm of the respiratory muscles. The victim's consciousness remains until the moment of death.
First aid for strychnine poisoning
- Give the victim's body a comfortable position, unbutton tight clothing.
- Provide absolute peace by eliminating even the most insignificant irritants (remove light sources, observe silence).
- Rinse the stomach (drink 1-1.5 liters of warm water, then induce a gag reflex by pressing on the root of the tongue), which is shown only in the absence of convulsions. If the victim has an increased convulsive readiness, manipulation is strictly prohibited, since it can lead to aspiration of vomit.
- Take a saline laxative (magnesium sulfate).
- Take enterosorbent (Enterosgel, Polysorb according to the scheme or activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of the victim's body weight).
When is medical attention required?
If you suspect strychnine poisoning, you must immediately call an ambulance or as soon as possible deliver the victim to the hospital yourself. The prognosis of the disease depends on the speed of medical care.
The victim is hospitalized in the toxicology department, where the following measures are taken:
- artificial lung ventilation;
- the introduction of tranquilizers, barbiturates or muscle relaxants that are antagonists of strychnine;
- antibiotic therapy for the development of aspiration pneumonia.
After 24 hours, the victim is usually transferred to spontaneous breathing, observation after the resolution of the poisoning is usually not required.
Possible consequences
The consequence of the postponed poisoning with strychnine can be:
- asthenoneurotic conditions;
- acute renal failure;
- multiple organ failure;
- reactive pancreatitis;
- aspiration pneumonia;
- acute hypoxia of brain tissue.
Prevention
To prevent strychnine poisoning, you must:
- strictly follow the doctor's recommendations when taking strychnine-containing drugs;
- do not take drugs containing strychnine without prior medical advice;
- if strychnine preparations are available at home, store them out of the reach of children;
- when working with pesticides containing alkaloid, use personal protective equipment.

Olesya Smolnyakova Therapy, clinical pharmacology and pharmacotherapy About the author
Education: higher, 2004 (GOU VPO "Kursk State Medical University"), specialty "General Medicine", qualification "Doctor". 2008-2012 - Postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty "Pharmacology, Clinical Pharmacology"). 2014-2015 - professional retraining, specialty "Management in education", FSBEI HPE "KSU".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






