- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Collarbone
Collarbone. general information
The clavicle (from the Latin clavicula - "key") is a paired tubular bone of the shoulder girdle connecting the upper limb (arm) with the rest of the body. The bone resembles a slightly elongated S.
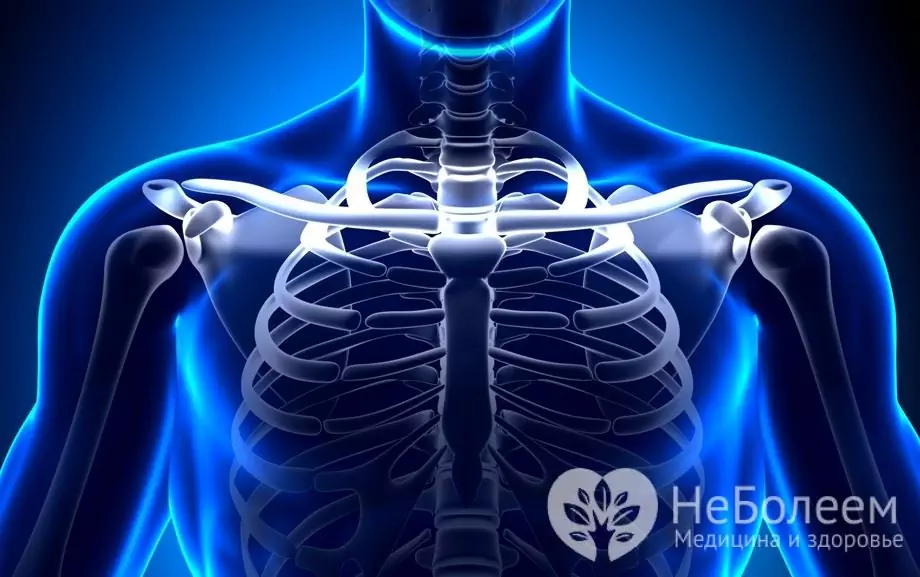
The clavicle is located above the first rib. Its outer end is attached to the processes of the scapula, forming the so-called acromioclavicular articulation, the inner (sternal) end is articulated with the sternum, forming the sternoclavicular articulation. Each of these joints is strengthened with ligaments.
A number of muscles are attached to the collarbone. So, the leg of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is attached to its sternal end, which is located on the neck. Attached to the outer end are the deltoid and trapezius muscles. The weak subclavian muscle is located on the underside of the clavicle.
There are large vessels under the collarbone, as well as the brachial plexus, which is responsible for the innervation of the hand.
Despite the fact that the clavicle is one of the first bones that begins the process of ossification in embryonic development (this occurs about 6 weeks from the moment of conception), this process is completed only by the age of 20-25.
The clavicle, contrary to the fact that it belongs to long bones, does not have a medullary cavity, that is, it lacks bone marrow. Its origin is based on cancellous bone with a compact shell.
Clavicle functions
The functions that the clavicle performs in the body:
- is part of a mechanism in which the clavicle is a solid support for attaching the scapula and free limb, which allows the hand to have maximum maneuverability of movements;
- protection of the cervical-muscular canal (located between the arm and the neck), as well as important structures passing through it;
- transmission of physical impulses to the axial skeleton from the upper limbs.
Collarbone injury
Typical collarbone injuries include:
1. Fracture of the clavicle is usually the result of a fall on the arm or shoulder. There are known cases of fracture of this bone in newborns when passing through the birth canal. With a fracture of the clavicle, a number of characteristic symptoms are noted: pain at the site of injury immediately after injury, the appearance of swelling and edema, limited movement, the inability to raise the injured arm. A fracture with a displaced clavicle is much easier to identify than in its absence. In this case, a change in the length of the broken limb is observed, the shoulder joint also changes its location, visually dropping lower. Often, with a fracture of the clavicle, sensitivity and mobility of the fingers and hands are lost, which indicates damage to the nerves and blood vessels. Treatment is specific, depending on the presence or absence of displacement of the clavicle in the fracture. So,in its absence, the imposition of a rigid fixation bandage is recommended, in extreme cases - surgical intervention. In case of a fracture with a displacement of the clavicle, two Cramer splints must be applied, tied into one. Complex fractures require surgical intervention, the installation of a special plate, a wire. As a rule, following the treatment, the patient is prescribed massage courses or therapeutic exercises to restore physical activity. In adults, a broken collarbone will heal within 8 weeks;after the treatment, the patient is prescribed courses of massage or therapeutic exercises to restore physical activity. In adults, a broken collarbone will heal within 8 weeks;after the treatment, the patient is prescribed courses of massage or therapeutic exercises to restore physical activity. In adults, a broken collarbone heals within 8 weeks;
2. dislocation of the clavicle is a fairly frequent phenomenon and accounts for approximately 5% of all dislocations. Just like a fracture, a dislocation of the clavicle is the result of a fall on the abducted arm or shoulder, in rare cases the cause may be a sharp compression of the shoulder girdle. Dislocation can be observed both from the acromial and sternal ends of the clavicle. In this case, the first is found ten times more often. The main complaints in case of damage are: the presence of pain in the clavicle, swelling in the damaged area, protrusion of one of the ends of the bone. The victim's movements are limited, and palpation causes pain. Acromial dislocation of the clavicle can be complete or incomplete (partial). Depending on this, the victim is prescribed treatment. So, in case of incomplete dislocation, immobilization of the joint is recommended, followed by the appointment of physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapy. Complete dislocation of the clavicle requires surgical intervention with fixation with silk thread or lavsan tape. With sternal dislocation, the presence of pain in the clavicle is also noted, deformation of the joint is noticeable in the form of protrusion (with anterior sternal dislocation) or sinking (with retrosternal), movements are constrained, palpation is painful. In order to clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is prescribed. Treatment is carried out with the use of a special eight-shaped plaster cast along with surgical methods and lavsanoplasty. In order to clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is prescribed. Treatment is carried out with the use of a special eight-shaped plaster cast along with surgical methods and lavsanoplasty. In order to clarify the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is prescribed. Treatment is carried out using a special eight-shaped plaster cast along with surgical methods and lavsanoplasty.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.




