- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Amniocentesis

During pregnancy, for various reasons, a violation of the condition of the fetus can occur. The child is surrounded by amniotic fluid - amniotic fluid, which contains living cells of his skin, exfoliated, but in the process of growth, and other substances. Their research helps to find out valuable information about the health of the fetus, and this diagnostic method is called amniocentesis.
What is amniocentesis?
Amniocentesis is a method for examining amniotic fluid. It is a piercing of the abdominal wall of the uterus. In the process of its implementation, a small amount of amniotic fluid is taken and a number of studies are carried out: hormonal (amount, composition of hormones), immunological (detection of violations in individual links of immunity), biochemical (composition of amniotic fluid). The pooled analysis of these fluid studies helps to determine the general condition of the fetus and to identify the degree of risk of genetic abnormalities.
What pathologies can be detected by amniocentesis
There are several hundred types of genetic defects that can be detected by the amniocentesis method, including chromosomal diseases (Edwards, Patau and Down syndromes), neural tube defects (spinal hernia, etc.).
However, amniocentesis does not show such congenital defects as cleft palate and cleft lip.
Indications for the study
The decision to use the amniocentesis method can only be made by a pregnant woman, since this procedure is associated with certain risks. And opinions about the feasibility of this study differ. First of all, you need to be prepared for the fact that if an anomaly is detected, you may have to terminate the pregnancy. However, early detection of a defect in a child will give time to figure out what kind of help may be needed.
And since amniocentesis poses some threat to the health of the mother and her child, this test is offered only to women who have significant prerequisites for the development of genetic diseases in the fetus, including in cases where:
- An ultrasound scan reveals a serious problem, such as a heart defect, which may indicate a chromosomal abnormality;
- According to the results of screening tests, there is a risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities;
- One or more relatives of the woman and / or the child's father have some genetic disorder;
- A pregnant woman is more than 35 years old, since from this age the risk of having a sick child increases - 1 case in about 300 (for comparison, at the age of 20 years, this ratio is 1 in 2000).
- The woman has already had a pregnancy with genetic abnormalities in the fetus.
Amniocentesis - time and method
The amniocentesis method is used at a gestational age of 16 to 18 weeks (i.e., 14 weeks after the first day of the first menstrual period, which has not occurred). However, if the doctor has reason to suspect that the fetus has a heart defect or a serious genetic disorder, then amniocentesis is allowed for up to 14 weeks.

Also, in some individual cases, amniocentesis is also performed at a later date for the purpose of artificial termination of pregnancy, if there is a medical indication. In this case, a concentrated salt solution or other drug is injected into the bladder.
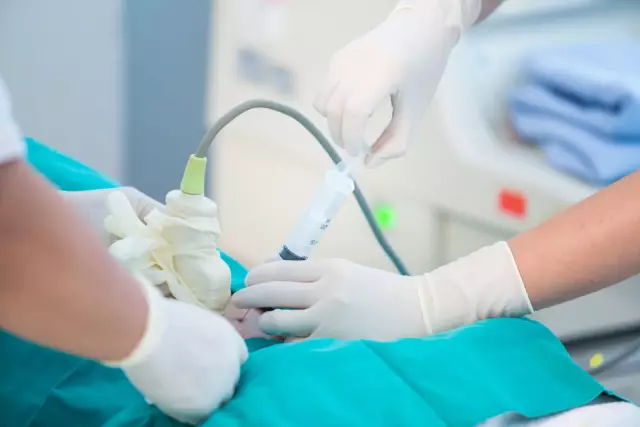
This diagnostic test is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist in the operating room. Before the procedure, the pregnant woman must undergo an ultrasound scan to determine the location of the placenta in order to avoid damaging it during a puncture.
The puncture itself is made through the anterior abdominal wall of the uterus, after pretreating a small area of the skin of the abdomen with a 5% alcohol solution of iodine. The puncture site is numbed with local anesthesia to relieve discomfort. Under the control of ultrasound, the doctor inserts a thin long hollow needle into the amniotic cavity and collects 15-20 ml of fluid, which is sent for laboratory analysis. In the laboratory, all chromosomes are counted and their structure determined, but the procedure lasts two to three weeks. The fact is that for diagnostic purposes, a certain number of baby cells are needed, which are grown in special conditions, which is why a woman does not receive results immediately.
Immediately after amniocentesis, patients may experience abdominal pain.
Some people have mild bleeding after amniocentesis. Therefore, as a rule, the doctor recommends bed rest for 24 hours.
Also, after amniocentesis, the doctor will check the baby's heartbeat for a while and monitor the woman to prevent possible uterine contractions.
Contraindications to amniocentesis
- the presence of a benign tumor in the uterus;
- malformations of the uterus;
- the location of the placenta on the anterior wall of the uterus;
- the threat of termination of pregnancy;
- infectious processes or feverish conditions.
Consequences of amniocentesis
There are some risks involved in conducting this study. The following consequences of amniocentesis are possible:
- Development of infection or other complications (in one in 200 women);
- Bleeding in a woman or fetus;
- Feeling of contractions within a few hours after the procedure is the most common consequence of amniocentesis;
- Miscarriage of a healthy child (1 in 500);
- Spontaneous abortion. Before the procedure, a mother with a negative Rh factor is given an injection of Rho-gamma globulin in order to protect the baby from her antibodies. In 2 cases out of 100, it is this injection that provokes a miscarriage;
- Injury to the fetus (the likelihood of such a consequence of amniocentesis is practically zero, but, nevertheless, it is possible if the doctor touches the vital area of the child with a needle);
- Damage to the fetal bladder, which leads to bleeding and leakage of amniotic fluid (the patient will have to lie down for preservation, the treatment can take up to several months);
- Premature birth.
Considering all of the above, every woman, before agreeing to a test, should consider the possible consequences of amniocentesis and weigh the pros and cons. In addition, the test result still cannot guarantee the birth of an absolutely healthy child, it only excludes some pathologies. Its accuracy is approximately 99.4%. Therefore, every pregnant woman should consult with a geneticist and only then make a final decision.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.