- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Cause of chest pain: neuralgia or heart?
For the time being, the prospect of heart disease seems distant and hazy to most of us. But sooner or later, almost everyone is faced with an extremely unpleasant sensation - sudden chest pain. It is unlikely that one will be able to console himself with the thought that the hour has not yet come for a heart attack: if a person is impressionable, he, as a rule, will experience a feeling of panic, fear of imminent death. And yet it is easy to confuse pains of a neuralgic nature with heart pains.
Today we will talk about how to distinguish one type of pain from another, why neuralgia and chest pain occur, and how to maintain your health.

Source: depositphotos.com
Chest pain symptoms: similarities and differences
People who do not like to go to doctors (especially for men) often prefer to endure an attack, stopping it with an anesthetic drug. But the cost of an error in chest pain is prohibitively high: if you do not seek help in time for a heart attack, you can die.
On the other hand, many first of all sin on the heart - after all, it is in the chest that is located, and intercostal neuralgia, in theory, should be felt on the side, between the ribs? In fact, the localization of pain can be different, in addition, pain is sometimes given to both the arm and the back.
The main difference between a heart attack and neuralgia is duration. Attacks of intercostal neuralgia are quite long, up to several days. Heart pains are short - for example, an attack of angina pectoris lasts 5-10 minutes.
Neuralgic pains are acute, and angina pectoris is dull, burning, with lack of air. In the old days, angina pectoris was called "angina pectoris" precisely because of the feeling that a heavy and cold toad was sitting on the chest. Pain with angina pectoris extends to the entire chest area, a person finds it difficult to indicate exactly where he hurts. With neuralgia, however, it is usually possible to accurately localize the main site of pain.
Another very characteristic sign of neuralgia is a decrease or increase in the intensity of pain, depending on the position of the body, inhalation-exhalation. Heart pain does not depend on the position of the body, with one exception - with myocardial infarction during movement, it increases.
A nitroglycerin tablet can stop an attack of heart pain, but will not stop the development of a heart attack. Therefore, if the pain continues after taking nitroglycerin, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Why do chest pains occur?
A logical question: if everything was in relative order with health, why do seizures with high intensity immediately occur? In fact, rarely is anyone regularly examined by a cardiologist. Most cases of angina pectoris are so-called exertional angina, which occurs after physical or emotional stress. If the attack occurred after sleep, this is resting angina.
Actually, angina pectoris is a violation of the blood supply in the human heart muscle. Such constant oxygen starvation leads to the development of coronary heart disease and heart attack. The main risk factors here are:
- arterial hypertension;
- violation of fat metabolism and atherosclerosis;
- violation of carbohydrate metabolism and increased blood sugar levels;
- congenital or acquired heart disease.
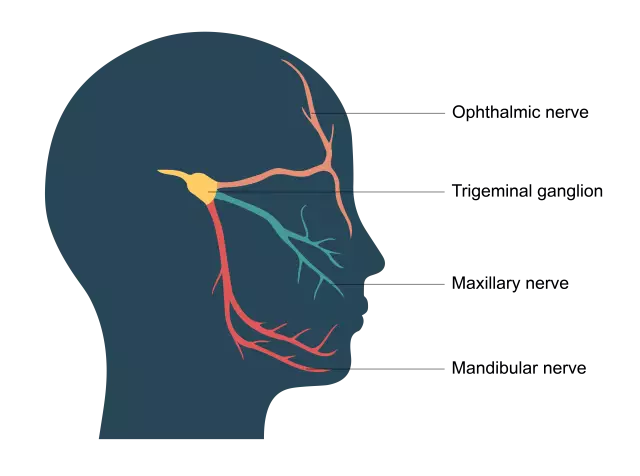
Intercostal neuralgia is pain that passes along the trunk and branches of any of the intercostal nerves (there are 11 pairs of them, and the 12th pair are subcostal nerves). It occurs due to compression, irritation or inflammation of the nerve. There are a lot of reasons for the appearance of neuralgia - and problems with the spine (osteochondrosis, displacement and herniated intervertebral discs), and infections (including flu), and sciatica, neuritis, and trauma, hypothermia, and excessive muscle tone …
Which doctors should I go to for help?
If you are seeking emergency care, doctors will help you navigate this issue, excluding or confirming heart problems. If you have had an attack of angina pectoris, then you cannot do without examination by a cardiologist. However, even if the attack turned out to be neuralgia, the cardiologist is worth a visit.
With neuralgia, the situation is somewhat more complicated - first of all, you need to visit a neurologist, make an X-ray or undergo a tomography. After the cause is clarified, the doctor will be able to give further recommendations for treatment or refer for consultation to another specialist, such as an osteopath.

Source: depositphotos.com
Chest pain: what to do
First, minimize any physical activity and sit or lie down. Often it is impossible to lie flat - in this case, you should take a reclining position, placing pillows under your back. It is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room, to open the collar of the clothes. If the cause of the pain is not clear, you should immediately take 1-2 tablets of nitroglycerin. (Remember that nitroglycerin can drastically lower blood pressure.) If it was not there, at least validol, valocordin or analogues. To calm down, you should additionally drink valerian or corvalol.
If the pain persists within 10-15 minutes, don't wait and call an ambulance. If the pain is acute, not changing with a change in body position, an ambulance should be called immediately.
With an attack of neuralgia, you can take painkillers, wrap your chest with a warm scarf, use ointments that have a warming and analgesic effect.
In the future, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapy sessions, novocaine nerve blocks, acupuncture. If the cause of repeated attacks of neuralgia is osteochondrosis, then it is advisable to seek help from a chiropractor, attend massage therapy and gymnastics. During an exacerbation of neuralgia, you cannot sleep on a soft surface, the mattress must be hard.
Try to remain calm during an attack of chest pain, but in no case neglect a doctor's examination afterwards, even if it seems to you that the attack has passed without a trace.
YouTube video related to the article:

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.