- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Atypical autism
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Atypical autism is a neuropsychiatric disease caused by a violation of the structures of the brain. It belongs to a group of pathologies called autism spectrum disorders.
Atypical autism is characterized by impaired perception and understanding of the surrounding reality, stereotyped actions, poorly developed imagination, lack of interaction and social communication. Often, this pathology is combined with severe specific disorders of the development of receptive speech and deep mental retardation.
The incidence of atypical autism is 2 cases per 10,000 population. Boys get sick 2-5 times more often than girls.

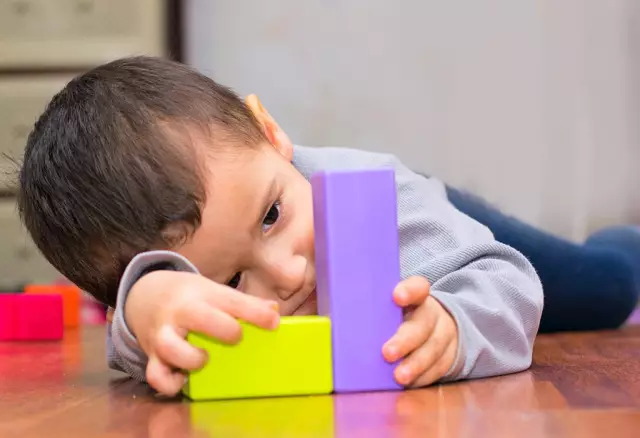
Social interaction disorders are one of the hallmarks of atypical autism
Causes and risk factors
Structural disorders of the brain are the cornerstone of atypical autism. Factors lead to their occurrence, the most frequent of which are:
- Hereditary predisposition. In patients with atypical autism, it is almost always possible to identify relatives with some of the disorders characteristic of this pathology. In the 90s of the XX century, a gene was discovered that is responsible for the predisposition to atypical autism. Its presence does not necessarily lead to disease, but increases the risk of its development when exposed to other factors.
- Complicated pregnancy and (or) childbirth. In women whose children suffer from atypical autism, in most cases, pregnancy and childbirth proceeded with various complications, such as toxemia, intrauterine infections, premature birth, uterine bleeding.
- Some diseases. Atypical autism is often observed against the background of the fragile X-chromosome syndrome, cytomegalovirus infection, phenylketonuria, and epilepsy.

A possible cause of atypical autism is intrauterine infection
Forms of the disease
In psychiatry, two forms of atypical autism are distinguished:
- with mental retardation (including mental retardation with autistic traits);
- without mental retardation (including childhood atypical psychoses).
Symptoms
Symptoms of atypical autism usually appear after three years of age. These include:
- Social networking frustration. The severity can be different - some patients are looking for loneliness, while others want to communicate with other people, but cannot build a communication process.
- Disorders of speech function. Patients do not clearly formulate thoughts, and the speech addressed to them is understood literally, that is, they cannot understand the words and phrases pronounced in a figurative sense.
- Emotional coldness. Patients find it difficult to express feelings, emotions, experiences, so they are perceived by others as indifferent, indifferent, cold. Many of them lack empathy. The development of violations of the emotional sphere is due to the difficulty of understanding non-verbal signals.
- Inflexible thinking. The patient experiences fear of any, even minor, changes in life or his environment. He strives to live surrounded by familiar things, to perform monotonous, familiar actions.
- Irritability. Due to disorders of the nervous system, patients become overly sensitive to irritants. In response, aggression and irritability often arise.
- Sensory disturbances. The brain processes and perceives the received sensory information (visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, gustatory) differently than in healthy people, which can manifest itself in different ways, including unusual abilities.

Behavior features of children with atypical autism
The severity of these symptoms can be different. Often, violations are so imperceptible that it is difficult to identify and correctly interpret them even for a specialist.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of atypical autism is difficult due to the variety of symptoms and their severity. Making a correct diagnosis requires a comprehensive medical and psychological examination and long-term observation of the child's behavior, an analysis of his communication abilities, skills and abilities.
Differential diagnostics with autism, Asperger's syndrome, schizophrenia is carried out.
Treatment
To date, no effective treatment for atypical autism has been developed. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and the social adaptation of patients. It is developed individually for each child and is spent most of the day for a long time.

It is important for children with atypical autism to provide conditions for social adaptation
Possible complications and consequences
Learning problems are common among children with atypical autism. In adulthood, it is difficult for them to start a family, difficulties arise with the choice and implementation of professional activities.
Forecast
With persistent therapy, in many cases, the symptoms of atypical autism do not progress without mental retardation, and sometimes it is possible to achieve that the patient's mental state practically returns to normal. In atypical autism with mental retardation, the prognosis is much worse.
Prevention
Preventive measures aimed at the occurrence of atypical autism do not currently exist.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!