- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Anophthalmia
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Anophthalmia - underdevelopment or complete absence of the eyeball, visual pathways, optic nerve and junction. The frequency of birth of children with a similar pathology of the visual system is from 3 to 6 cases per 100,000 newborns. The disease occurs with the same frequency in all countries of the world, in children of both sexes.
Anophthalmia is also spoken of when the eyeball is surgically removed.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Causes and risk factors
Congenital anophthalmia is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means that in order for the disease to develop, the child must receive two copies of the altered gene, one each from the father and mother. If only one changed gene is inherited, then the child's eyeballs will develop, but they will be small (microphthalmia).
The cause of secondary anophthalmia is the surgical removal of the eyeball.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the onset of the disease, congenital and acquired anophthalmia are isolated. In turn, the congenital form of the disease is divided into two types:
- True anophthalmia. The patient has a complete absence of eye tissue. The onset of pathology is associated with hypoplasia of the anterior part of the brain or with improper lacing of the optic nerve. In this form of the disease, the lesion is usually bilateral.
- Imaginary anophthalmia. It occurs as a result of a delay in the development of the optic cup or the secondary optic vesicle. Eye damage can be both bilateral and unilateral.
Symptoms
The main clinical symptom of anophthalmia is the absence of an eyeball. With the true form of the disease, the patient retains the appendages of the eye, but their size is much less than the norm. The conjunctival cavity is small, the eyelids are small.
With imaginary anophthalmia, a rudimentary eye is found deep in the orbital cavity.
With anophthalmia, the bones of the orbit, eyelids, and nearby adipose tissue lag behind in development. This phenomenon becomes the reason for the appearance of asymmetry in the structure of the child's face.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of anophthalmia is carried out on the basis of the clinical picture of the disease, as well as data from X-ray images of the skull. With imaginary anophthalmia, the visual opening can be seen on the X-ray of the skull, but with the true form of the disease, it is absent.
Treatment
In case of anophthalmia, prosthetics of the eye cavity must be performed, which allows to ensure the correct growth and development of the child's facial skull, prevents the appearance of pronounced defects in appearance, and provides a good cosmetic effect.
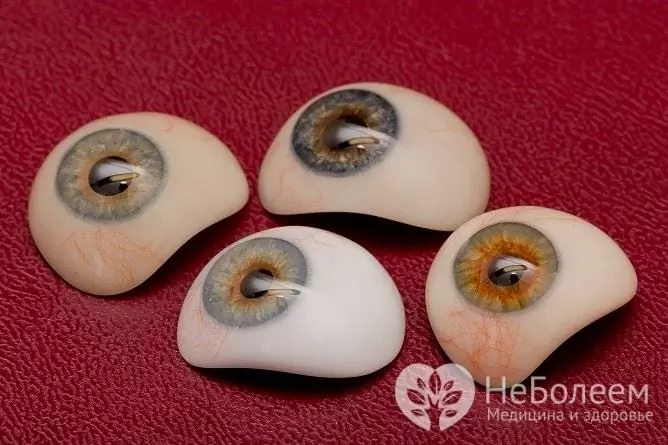
Prosthetics of the eye cavity prevents abnormal growth and development of the child's skull
As the child grows, the size of his skull also increases. This causes the need for repeated surgical interventions, which consist in removing the old eyeball prosthesis and replacing it with a new, larger one. That is why at present, most ophthalmologists in the treatment of anophthalmia in children prefer to adhere to a non-surgical technique: after local anesthesia, the child is injected into the depth of the orbit with a preparation of hyaluronic acid.
Injection treatment of anophthalmia can begin from the first days of a person's life. The therapy is performed on an outpatient basis and does not cause discomfort to patients. At the same time, the necessary conditions are provided for the correct growth and development of the tissues surrounding the eye socket, and the development of facial asymmetry is prevented. After the completion of the growth period, a traditional prosthesis is installed.
Possible complications and consequences
The main complication of anophthalmia is incorrect formation of the facial skeleton.
Forecast
It is impossible to restore visual function with anophthalmia. The prognosis for life is largely determined by the presence of concomitant malformations of the nervous system and internal organs.
Prevention
Congenital anophthalmia is a genetic disease that cannot be prevented. If in the family there were cases of the birth of children with anophthalmia or microphthalmia, then at the stage of pregnancy planning, a married couple is recommended medical and genetic counseling.
Prevention of acquired anophthalmia is to prevent injuries to the eyeball, timely detection and treatment of ophthalmic diseases.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






