- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
The consequences of hemorrhoids: what will happen if the disease is not treated
The content of the article:
-
The consequences of hemorrhoids in the early stages
- Bleeding
- Inflammation
- Defecation disorders
-
Consequences of hemorrhoids of late stages
- Hemorrhoidal vein thrombosis
- Infringement of the hemorrhoid
- Polyps
- Paraproctitis
- Anal fistulas
- Ulcerative colitis
- Colorectal cancer
- Cosmetic defect
- The consequences of hemorrhoids in women
- Treatment of advanced hemorrhoids
- Prevention of complications of hemorrhoids
- Video
The consequences of hemorrhoids can be very serious, in some cases life-threatening for the patient. Hemorrhoids significantly lower the patient's standard of living, causing him pain and discomfort even in the early stages. In the absence of treatment, the disease progresses rapidly, leading to even greater organic damage.

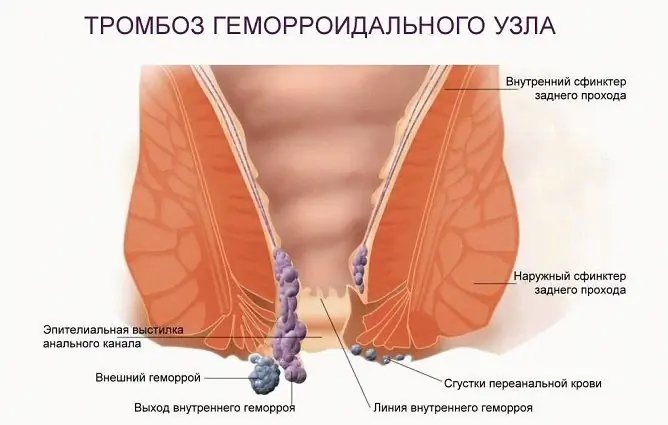
Hemorrhoid thrombosis is one of the dangerous consequences of advanced hemorrhoids
The consequences of hemorrhoids in the early stages
In the early stages, patients are worried about pain in the anal area, which can spread throughout the pelvis, especially during bowel movements, burning, itching. They also feel discomfort, a foreign body due to a seal in the rectum - this swelling mucous membrane narrows the intestinal lumen. When the surrounding tissue is compressed, small vessels rupture and bleed. At this stage, the main dangerous consequences are bleeding, inflammation and stool disorders.
Bleeding
Often the patient does not pay sufficient attention to minor bleeding. It can appear as small scarlet marks on toilet paper, or as streaks of scarlet blood in the stool. Do not underestimate the amount of such blood loss. Visceral bleeding leads to inflammation of the surrounding tissues, and prolonged blood loss inevitably leads to anemia.
Inflammation
Even if hemorrhoids are not visible from the outside of the anal sphincter, they are susceptible to bacterial invasion. The human rectum is inhabited by conditionally pathogenic microflora, which, when favorable conditions appear for itself, begins to actively multiply, which leads to purulent inflammation in the anus, paraproctitis, and requires massive antibacterial therapy.
Defecation disorders
The alternation of constipation with diarrhea and flatulence, the almost complete absence of normal feces with an acceptable color and consistency, regardless of nutrition - are frequent consequences of hemorrhoids, if not treated. Often, patients are simply afraid to go to the toilet because of the pain during the act of defecation. Stool stagnation injures the mucous membrane, and toxins, instead of being eliminated from the body, are absorbed into the systemic circulation.
Consequences of hemorrhoids of late stages
In the absence of treatment, the disease progresses, venous congestion becomes more and more pronounced, hemorrhoids fall out and cease to adjust on their own. This poses a certain danger due to a number of possible complications of hemorrhoids in men and women.
Hemorrhoidal vein thrombosis
In places where blood flow is slow, a blood clot is likely to form, and hemorrhoids are just such a place. After blockage of the lumen, the nutrition of the affected area deteriorates sharply, cutting pain joins. Blood accumulates in front of the thrombus, so the vessel wall expands. This leads to tissue necrosis that does not receive nutrition.
Infringement of the hemorrhoid
A formidable complication in which a hemorrhoid that has fallen out of the anus is compressed by a sphincter. A sharp cessation of blood circulation leads to the development of necrosis. This condition requires immediate surgical intervention.
Polyps
In the photo, polyps are finger-like growths. They occur in places of frequent bleeding due to the fact that the mucous membrane, compensating for damage, provokes an immoderate growth of connective tissue. The situation is complicated by bacterial agents of the rectum, feces, blood.

Stool disorders are a complication of the early stages of hemorrhoids, in turn, they contribute to the progression of the disease - a vicious circle is formed
Paraproctitis
Paraproctitis is a purulent inflammation of the tissues around the rectum. Inflammation can be superficial or develop in the thickness of loose connective tissue. The pus spreads quickly, burning through thin tissue, leading to rectal fistulas. It is accompanied by severe intoxication and fever, it is treated surgically.
Anal fistulas
They are manifested by functional insufficiency of the rectum - the function of removing waste products from the body is impaired. Feces can enter other cavities, causing microbial contamination. A serious condition is a fistula that opens from the outside past the anus.
Ulcerative colitis
The disease is caused by a bacterial infection that rapidly spreads up the colon, causing inflammation, malabsorption, and epithelial metaplasia.
Colorectal cancer
All of the above complications injure the epithelium, causing scarring. Chronic inflammation and permanent trauma to the rectal mucosa dramatically increase the risk of developing a tumor.
Cosmetic defect
An unpleasant consequence of hemorrhoids is also a cosmetic defect - bulging hemorrhoidal veins interfere with walking and sitting, anal fissures hurt and bleed, perianal dermatitis usually becomes chronic and can disturb long after the underlying disease is cured, causing dryness and itching. An unpleasant consequence of hemorrhoids in men and women is cryptitis - an inflammatory process of crypts (folds) of the rectum.
The consequences of hemorrhoids in women
Hemorrhoids in women can cause dangerous complications from the reproductive system - purulent fusion of the fascia with penetration into the uterine cavity, local inflammation, which, taking a long time, can lead to infertility.
Treatment of advanced hemorrhoids
Currently, medicine does not allow death from complications of hemorrhoids, although this possibility cannot be ruled out in the long term. Drug treatment of later stages ceases to be the main method - suppositories and ointment are not effective if there is a prolonged venous stasis with organic changes. Progressive hemorrhoids are treated promptly also due to disorders in other organs and systems - cardiovascular, urinary, etc.
Scarring, adhesions in the rectum, necrotic tissue do not allow the use of minimally invasive methods, the only way out in this case is to carry out a large-scale surgical intervention.
The following surgical techniques are used:
- Milligan-Morgan operation with modifications - total excision of hemorrhoids with subsequent hemostasis and suturing of blood vessels;
- operation by the Longo method, which includes the use of special braces to narrow the lumen of the veins and deprive the swollen nodes of trophism.
The operation can be combined with sclerotherapy and other methods. After the operation, patients do not return to their normal lifestyle immediately - a rehabilitation period of at least a week is required. A strict diet, taking supportive medications, and regular check-ups by the treating surgeon and proctologist is a recovery program.

An active lifestyle is the best prevention of hemorrhoids and its consequences
Prevention of complications of hemorrhoids
Even with a successful operation, the risk of hemorrhoid recurrence remains if the risk factors are not eliminated. The same factors reduce the effectiveness of therapy in the early stages of the disease, and increase the risk of adverse consequences. To exclude them, the following measures are necessary:
- rejection of bad habits, smoking and alcohol - the traumatic effect of nicotine on blood vessels has been proven, with regard to the effect on hemorrhoids, it is just as unfavorable as alcohol, which reduces blood viscosity;
- decrease in physical activity - it is forbidden to carry weights, engage in active sports, especially those associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure (power sports) and sitting (cycling, motorsport, rowing);
- exclusion of sedentary work - occupational hazards must be compensated, and this cannot always be done in the conditions of production and offices. In extreme cases, it is worth reducing the number of sedentary hours to 3-4, do a warm-up every 1-2 hours, install a special seat;
- a balanced diet with a high fiber content, a decrease in the diet of spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods, marinades;
- normalization of body weight, if necessary (by slightly reducing the calorie content of the diet and increasing physical activity);
- stool control. If the problem cannot be supplemented with nutrition, a doctor should be consulted, who may prescribe mild laxatives.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.